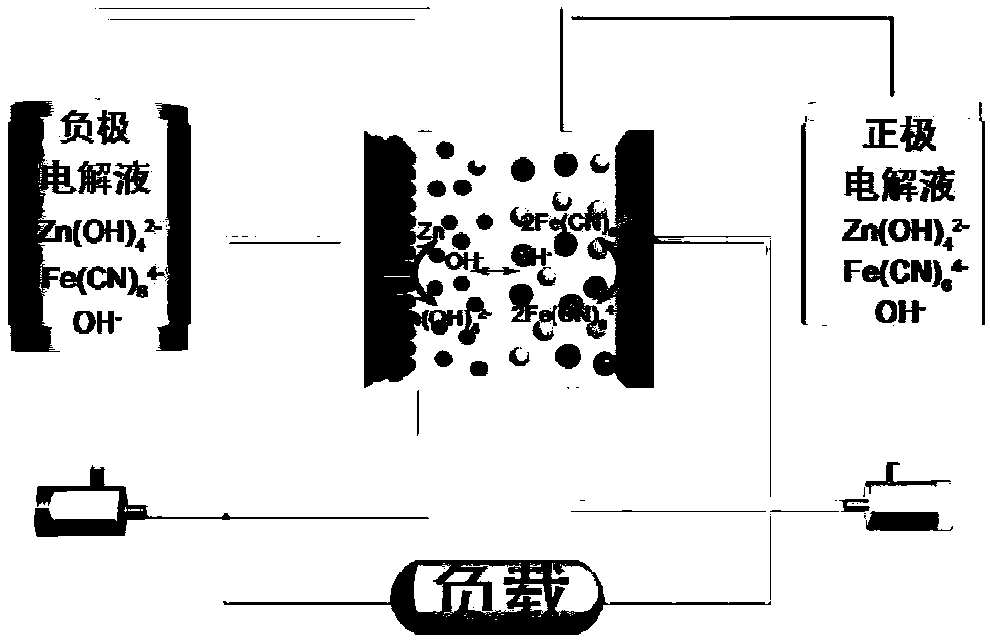
Negative electrode electrolyte for alkaline zinc-based flow battery as well as preparation and application of negative electrode electrolyte
An anode electrolyte, flow battery technology, applied in fuel cells, regenerative fuel cells, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of increasing battery maintenance costs, decreasing battery energy efficiency, and decreasing battery voltage efficiency, achieving easy purchase and high safety. performance, low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-5
[0040] The same test conditions for the alkaline zinc-iron flow battery in Examples 1-5: electrode effective area: 48cm 2 ; The battery adopts constant current charging and discharging mode, at 80mA cm -2 Charge for 18min under the condition of the current density, and then the voltage cut-off condition, 80mAcm -2 Discharge to 0.1V under the condition of current density; positive electrode electrolyte composition: 0.8mol L -1 Fe(CN) 6 4- +3mol L -1 KOH; the positive and negative electrolyte volumes are 100mL each; the positive and negative electrodes are porous carbon felt electrodes, and the graphite plate is used as a current collector; the ion-conducting membrane is a polybenzimidazole ion-conducting membrane. The difference is the composition of the negative electrode electrolyte, the specific situation is as follows:
[0041] Example Negative Electrolyte Composition Example 1 0.4mol L -1 Zn(OH) 4 2- +3mol L -1 KOH+0.3mol L -1 glucose
[0...
Embodiment 1
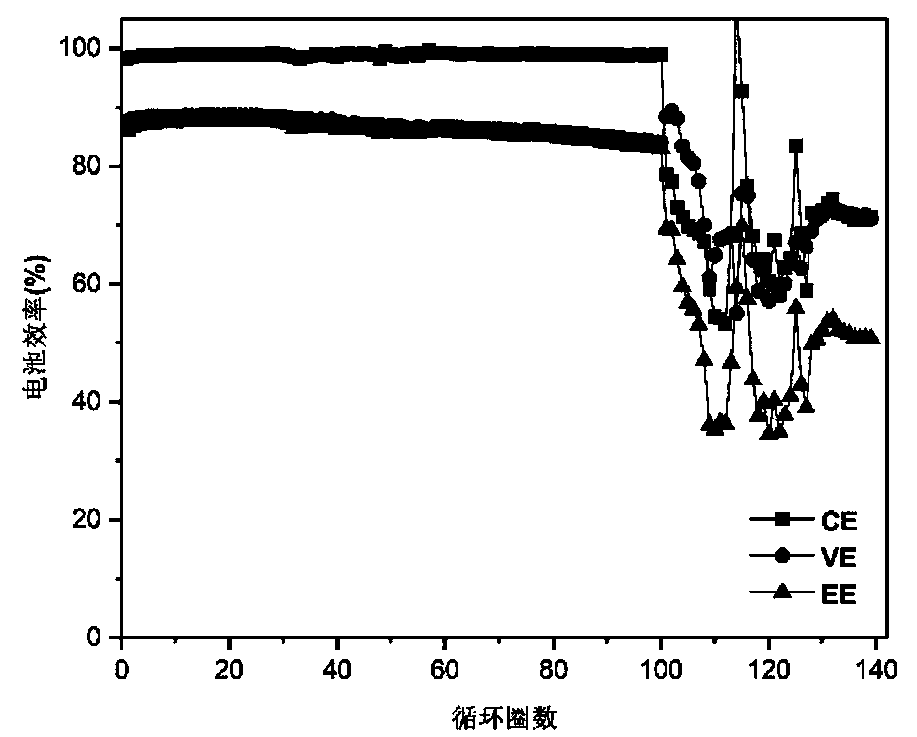
[0044] For alkaline zinc-iron flow batteries with organic additives, the positive electrolyte composition is 0.8mol L -1 Fe(CN) 6 4- +3mol L -1 KOH; negative electrode electrolyte composition is 0.4mol L -1 Zn(OH) 4 2- +3mol L -1 KOH+0.3mol L -1 Glucose; the positive and negative electrolyte volumes are 80mL each; the positive and negative electrodes are porous carbon felt electrodes, and graphite plates are used as current collectors; the ion-conducting membrane is polybenzimidazole ion-conducting membrane; at 80mA cm -2 Charge for 18min under the current density condition, and then cut off the voltage as the condition, 80mA cm -2 Discharge to 0.1V under the condition of current density. Measure the volume of the positive and negative electrolytes at the end of discharge. After 402 cycles, the volume of the negative electrolyte is 90mL, the volume of the positive electrolyte is 70mL, and the electrolyte migration is small. At the same time, after more than 635 charge ...
Embodiment 2
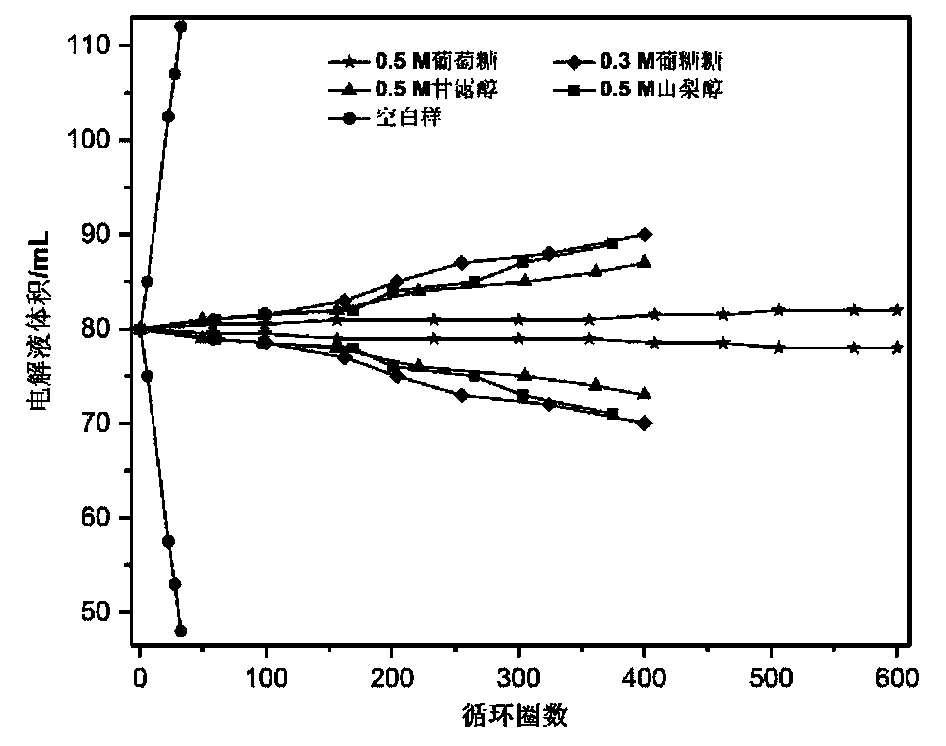
[0046] For alkaline zinc-iron flow batteries with organic additives, the positive electrolyte composition is 0.8mol L -1 Fe(CN) 6 4- +3mol L -1 KOH; negative electrode electrolyte composition is 0.4mol L -1 Zn(OH) 4 2- +3mol L -1 KOH+0.5mol L -1 Glucose; the positive and negative electrolyte volumes are 80mL each; the positive and negative electrodes are porous carbon felt electrodes, and graphite plates are used as current collectors; the ion-conducting membrane is polybenzimidazole ion-conducting membrane; at 80mA cm -2 Charge for 18min under the current density condition, and then cut off the voltage as the condition, 80mA cm -2 Discharge to 0.1V under the condition of current density. At the end of the discharge, measure the volume of the positive and negative electrolytes, such as figure 2 , the blank sample is a flow battery without additives, and the alkaline zinc-iron flow battery after adding additives to the negative electrolyte has no significant change in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com