Lipid nano-scale ultrasound contrast agent for targeting tumor-associated macrophages as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for ultrasound contrast agents and macrophages, which is applied in echo/ultrasound imaging agents, antineoplastic drugs, and liposome delivery, and can solve problems such as nanoscale ultrasound contrast agents that have not yet been seen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
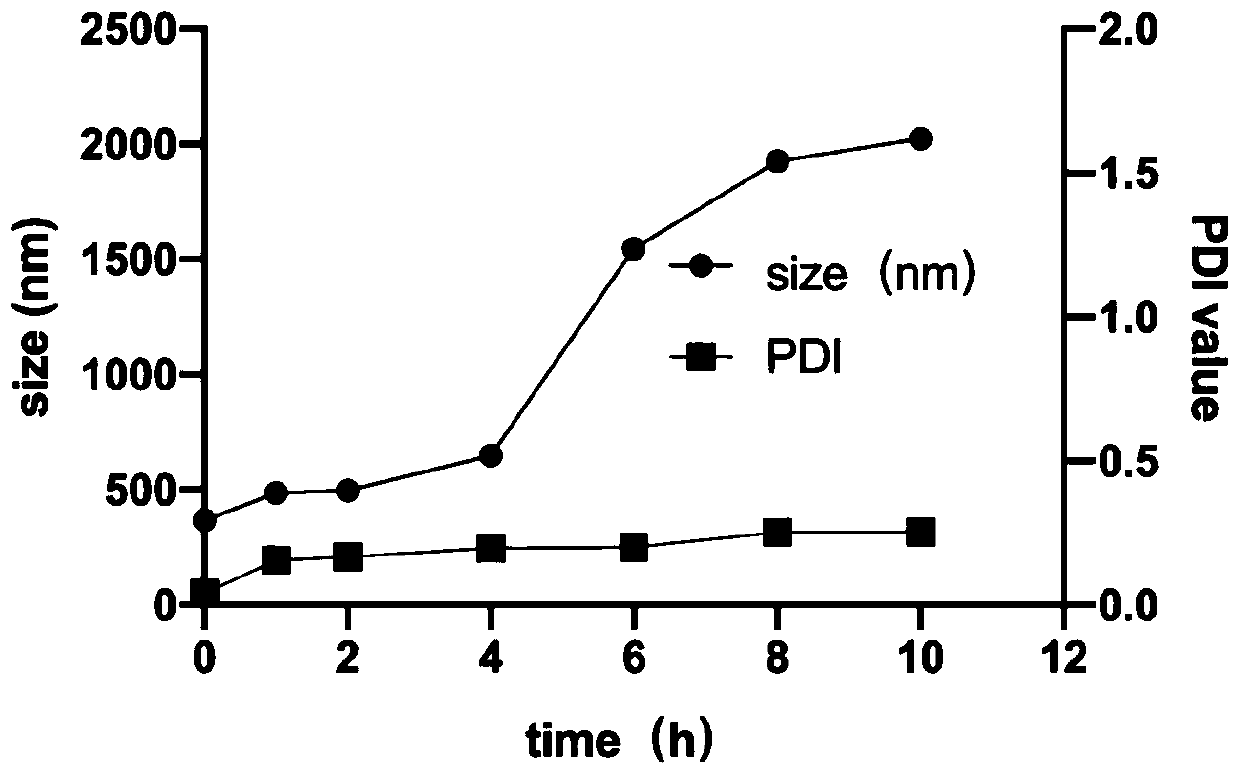
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1: Preparation of Lipid Nanoscale Ultrasonic Contrast Agent
[0060] A method for preparing a lipid nanoscale ultrasound contrast agent targeting tumor-associated macrophages, comprising the following steps:
[0061] (1) Mix glycerin and phosphate buffer at a volume ratio of 1:9 to make a hydration solution, take 0.4mL propylene glycol and 0.4mL hydration solution into a 1.5mL EP tube, add lipid, and the lipid is 0.7 mg dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), 0.2 mg distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DSPE), 0.4 mg distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol-folate (DSPE-PEG-FOL), additionally , in order to observe the structure of nano-scale ultrasound contrast agent under a fluorescence microscope, add 0.1mg of distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol-fluorescein isothiocyanate (DSPE-PEG-FITC) to obtain a suspension ;
[0062] (2) Pass perfluoropropane into the suspension in step (1) to replace the air, place the EP tube in a constant...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2: Establishing a tumor-associated macrophage model
[0069] The tumor-associated macrophage model was established by culturing RAW264.7 macrophages in conditioned medium. In order to verify the successful activation of RAW264.7 macrophages into tumor-associated macrophages, the morphological changes were observed using a light microscope, and real-time Fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction determined whether the expression of tumor-associated macrophage-associated genes mrc1, il10, nos2 and tnf was upregulated. The culture supernatant of the mouse Lewis lung cancer cells was collected and filtered with a 0.22 μm membrane filter to obtain the conditioned medium. In order to optimize the conditions for the activation of RAW264.7 macrophages into tumor-associated macrophages, different concentrations (0%, 50%, 100%) of conditioned medium were used to treat RAW264 at different time points (0, 24, 48, 72h). .7 macrophages and genetic testing.
[0070]...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3: Biosafety Evaluation of Nanoscale Ultrasound Contrast Agents
[0074] The tumor-associated macrophages obtained in Example 2 were mixed with 1×10 4 Inoculate each well in a 96-well plate, add culture medium, 37°C, 5% CO 2 After incubation for 24 hours, two sets of experiments were carried out. In the first set of experiments, the medium of tumor-associated macrophages was replaced with fresh medium containing lipids. The concentrations of lipids in the fresh medium were 25, 50, and 100 , 200, 300 μg / mL, the contained lipids are divided into two situations, one is that the lipids are dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DSPE) and two Stearoylphosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol-folic acid (DSPE-PEG-FOL), its mass ratio is 7:2:4, a kind of is that described lipid is dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) and Distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DSPE) with a mass ratio of 7:6; in the second set of experiments, the medi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com