Lateral SCR device with high maintaining voltage
A high sustaining voltage and device technology, applied in the field of electronic science and technology, can solve problems such as inconsistent bias voltage of the emitter junction, circuit malfunction, burnout, etc., to reduce emission efficiency, improve latch-up resistance, and increase voltage drop Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
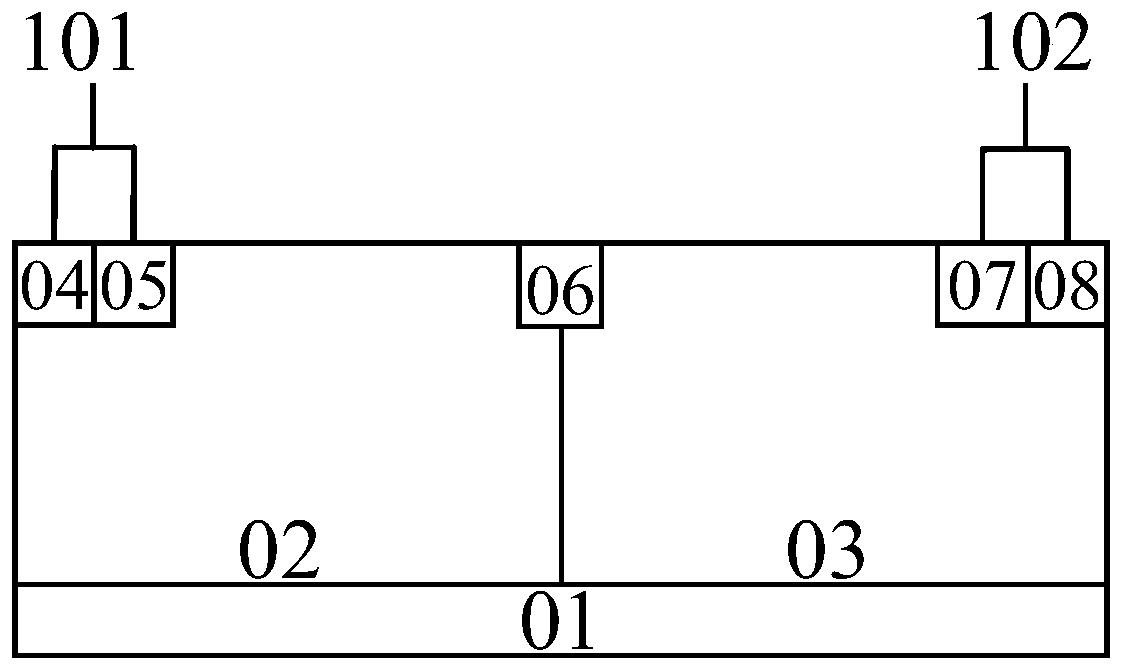
[0027] like figure 2As shown, the high sustain voltage lateral SCR device of this embodiment includes: a P-type substrate 01; an N-type well region 02 tangent to the left edge of the P-type substrate 01 above the inside of the P-type substrate 01; The P-type well region 03 on the upper right side of the bottom 01 is tangent to the N-type well region 02; the anode first N+ contact region 04 is located on the upper side of the N-type well region 02 and is tangent to the left side of the N-type well region 02; The first P+ contact region 05 on the right side of the first N+ contact region 04 and tangent to the first N+ contact region 04 of the anode; N+ low across the two wells is implanted at the junction of the P-type well region 03 and the N-type well region 02 The trigger region 06; the second P+ isolation region 22 of the cathode located above the interior of the P-type well region 03; the second N+ contact region 12 of the cathode located on the right side of the second P+...
Embodiment 2
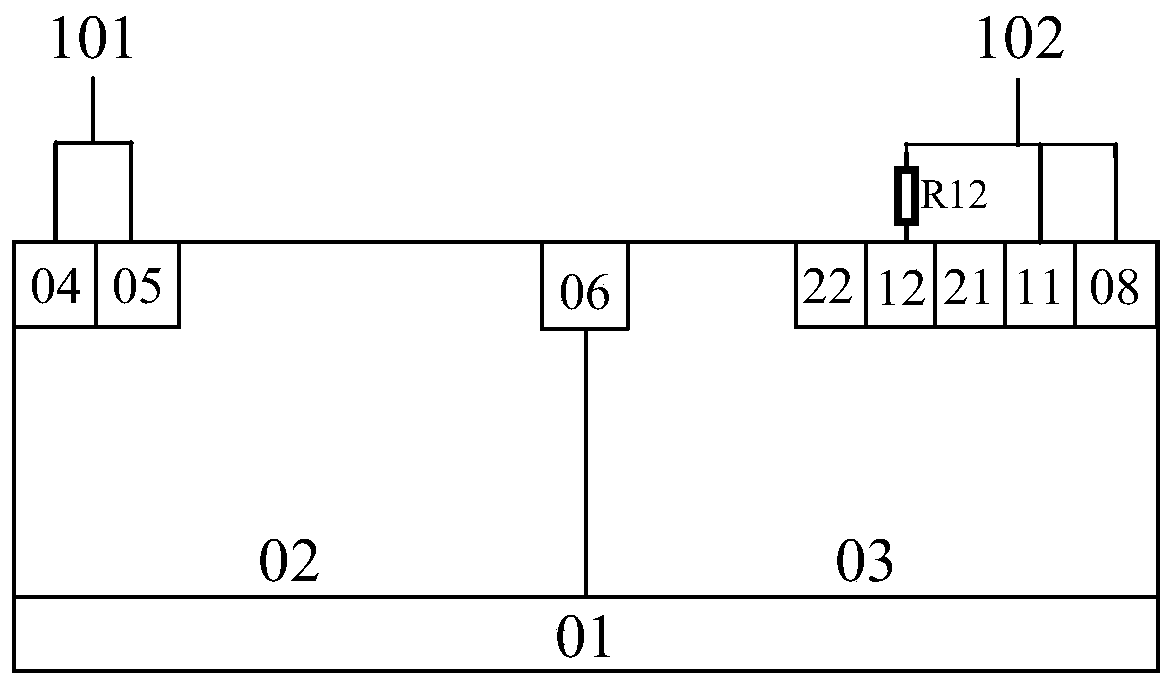
[0032] like Figure 7 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: a plurality of cathode N+ contact regions 11, 12, ..., 1n are provided on the left side of the second P+ contact region 08, and multiple cathode N+ contact regions are sequentially inserted between adjacent cathode N+ contact regions. A cathode P+ isolation area 21, 22, ..., 2n, metal contact is formed on the surface of the cathode N + contact area 11, 12, ..., 1n, and one end of the second cathode compensation resistor R13 is connected to the second N + contact area 12 of the cathode, and the other end is connected to the second N + contact area 12 of the cathode. The third N+ contact area 13 of the cathode is connected... One end of the n-1th cathode compensation resistor R1n is connected to the n-1th N+ contact area 1 (n-1) of the cathode, and the other end is connected to the nth N+ contact area 1n of the cathode, and the above n≥ 3.
Embodiment 3
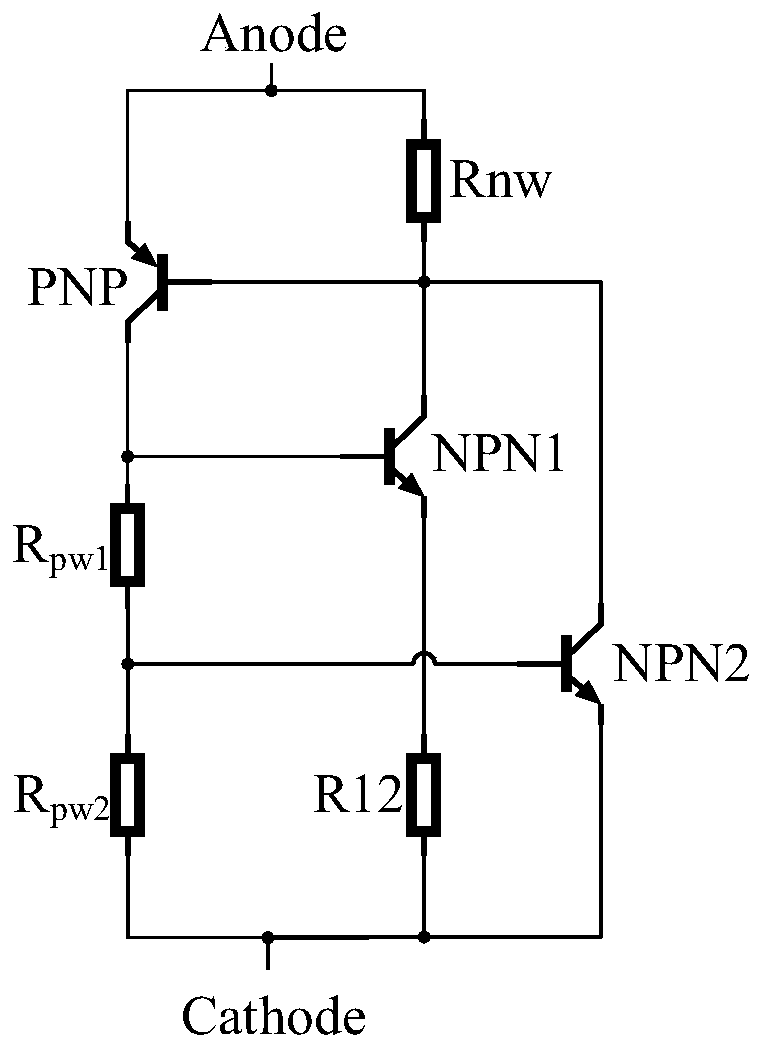
[0034] like Figure 8 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the first P+ contact region 05 of the anode of the device is split into two pieces, the first P+ contact region 31 of the anode and the second P+ contact region 32 of the anode, and between the two Insert the first N+ isolation region 41 of the anode, insert the second N+ isolation region 42 of the anode tangent to the second P+ contact region 32 on the right side of the second P+ contact region 32 of the anode; form a metal on the surface of the second P+ contact region 32 of the anode Contact and connect with one end of the first anode compensation resistor R22, the anode first P+ contact region 31 and the surface of the anode first N+ contact region 04 are short-circuited with metal and connected with the other end of the first anode compensation resistor R22 to form the device anode 101.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com