Preparation method of industrial-grade lithium chloride
A lithium chloride, industrial-grade technology, applied in the field of industrial-grade lithium chloride preparation, can solve the problems of great performance impact, high cost, process loss and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
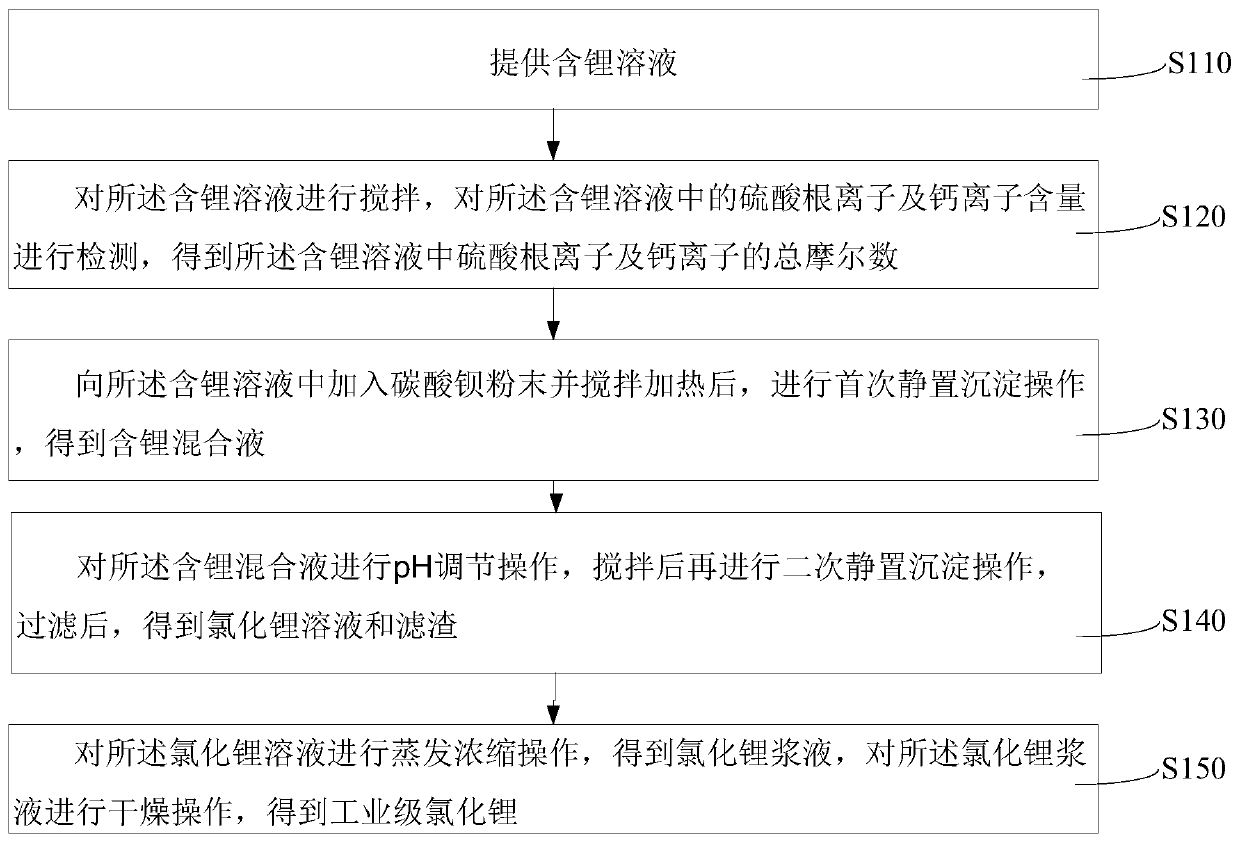
[0028] see figure 1 , in one embodiment, a kind of industrial grade lithium chloride preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0029] S110, providing a solution containing lithium.
[0030] It can be understood that lithium is the lightest alkali metal element. The metal has strong mobility and strong electrochemical activity. There are more than 150 kinds of lithium-containing minerals, mainly spodumene, lepidolite, lithium permeal, etc. Lithium is also contained in seawater, but the concentration is small, and it is difficult to extract. Lithium exists in the form of compounds in nature. Lithium metal and its compounds are widely used in various industries. They are known as "industrial monosodium glutamate", "aerospace alloy", "energy metal "And other good names, lithium chloride is a compound of lithium, lithium chloride is a white crystal, has deliquescence, tastes salty, and is easily soluble in organic solvents, such as ethanol, acetone, pyridine and other or...
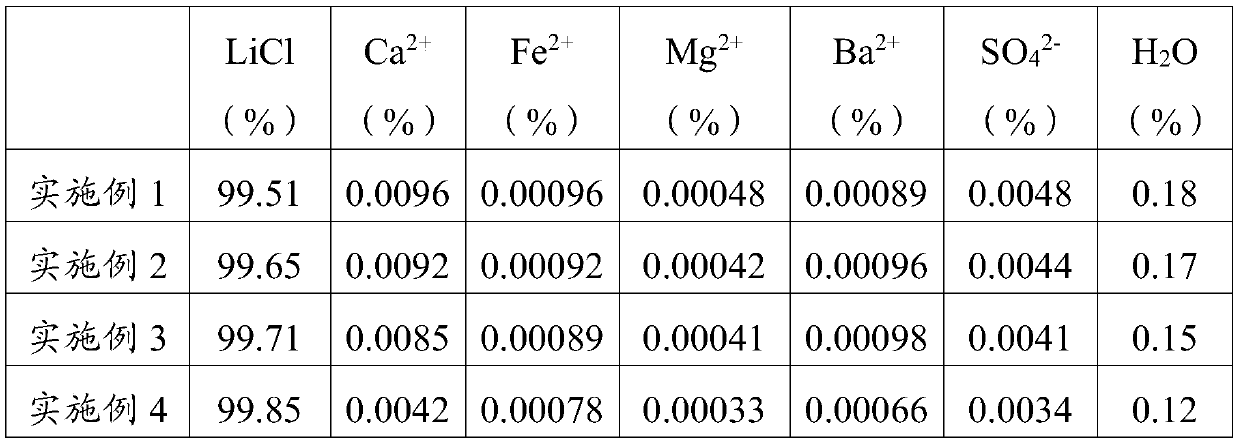
Embodiment 1
[0062] Provide 10kg of lithium-containing solution obtained by leaching spodumene;
[0063] The lithium-containing solution is added to the stirred reactor for stirring, and the molar number of sulfate ions in the lithium-containing solution is detected to be 0.11mol, and the molar number of calcium ions is 0.012mol. The total number of moles of ions is 0.122mol;
[0064] Add 24.03g of barium carbonate powder into the stirred reactor, heat the stirred reactor to 60°C, stir for 1 hour, then carry out the first static precipitation operation, and let it stand for 2 hours to obtain a lithium-containing mixed solution;
[0065] Using lithium hydroxide solution and hydrochloric acid solution mixed solution to adjust the pH value of the lithium-containing mixed solution to 11, stirring for 1 hour, then performing a second static precipitation operation, standing for 4 hours, and filtering to obtain lithium chloride solution and filter residue;
[0066] Add the lithium chloride solu...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Provide 10kg of lithium-containing solution obtained by leaching lepidolite;
[0069] The lithium-containing solution is added to the stirred reactor for stirring, and the molar number of sulfate ions in the lithium-containing solution is detected to be 0.09mol, and the molar number of calcium ions is 0.011mol. The total number of moles of ions is 0.101mol;
[0070] Add 39.8g of barium carbonate powder into the stirred reactor, heat the stirred reactor to 80°C, stir for 1.2h, then carry out the first static precipitation operation, and let it stand for 3h to obtain a lithium-containing mixed solution;
[0071] Using lithium hydroxide solution and hydrochloric acid solution mixed solution to adjust the pH value of the lithium-containing mixed solution to 11, stirring for 1.2 hours, then performing a second static precipitation operation, standing for 5 hours, and filtering to obtain lithium chloride solution and filter residue;
[0072] Add the lithium chloride solution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com