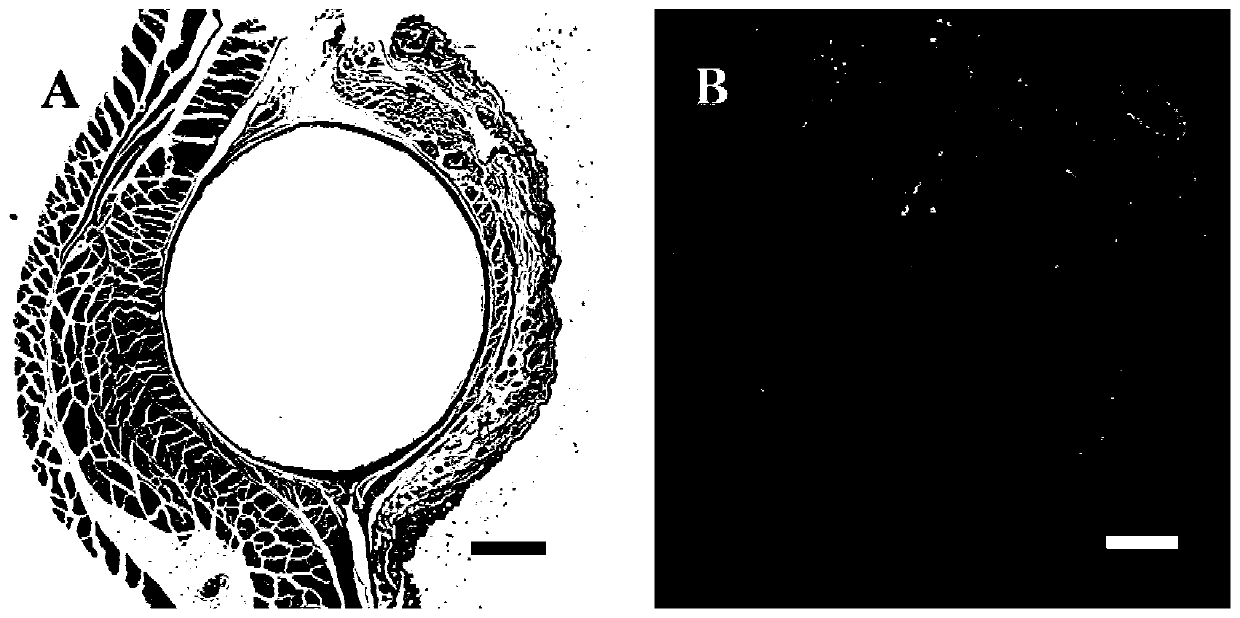
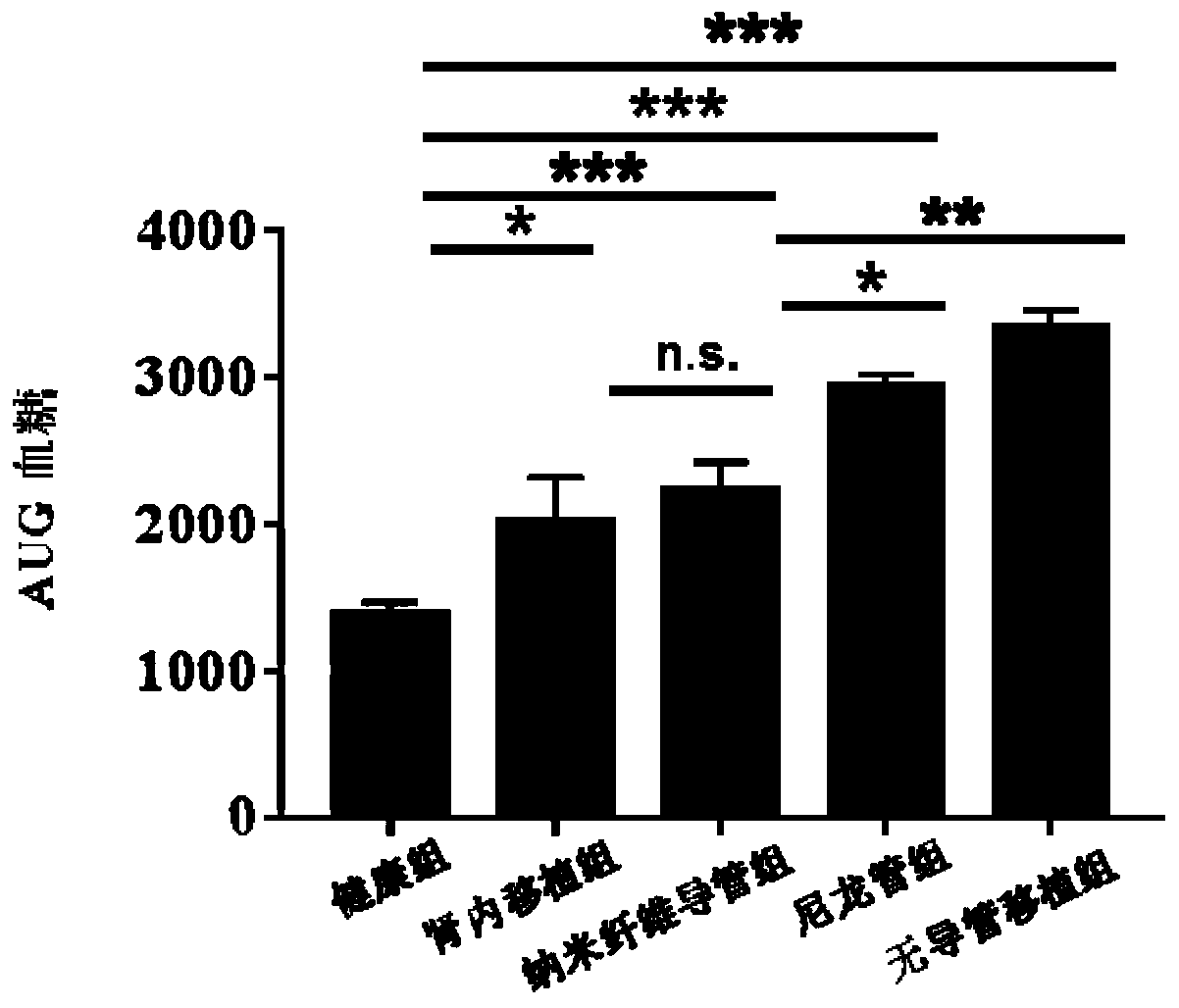
New blood vessel construct implanted into subcutaneous tissue of subject and preparation method thereof
A technology of subcutaneous tissue and new blood vessels, applied in catheters, pharmaceutical formulations, drug delivery, etc., can solve problems such as graft wear, inflammation, bleeding, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A method for preparing a neovascular construct for implanting into subcutaneous tissue of a subject, comprising:
[0046] Weigh 1.2g of polymer material (L-polylactic acid, PLLA, molecular weight 48000Da), put it in a 30ml glass beaker, add 10ml of organic solvent (hexafluoroisopropanol) into the beaker, and fully dissolve it to obtain an electrospinning solution.
[0047]Use a pipette to transfer the electrospinning solution from the beaker into a special electrospinning storage syringe, install the electrospinning nozzle (22G), adjust the electrospinning flow rate to 3.0mL / h, the voltage to 18kV, and the distance between the nozzle and the receiving device The receiving device is a cylindrical stainless steel tube with an outer diameter of 1.8 cm, the rotating speed of the receiving device is adjusted to 800 rpm, and the nanofiber catheter is obtained by electrospinning for 28 hours. Cut the nanofiber catheter into corresponding long sections as required, put it into ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This embodiment provides a preparation method for implanting a neovascular construct into the subcutaneous tissue of a subject, which is roughly the same as the preparation method provided in Example 1, except that the polymer material and the organic solvent are different, and the difference is as follows:
[0050] The polymer material is a polylactic acid glycolic acid copolymer obtained by copolymerization of lactic acid and glycolic acid with a molar ratio of 75:25;
[0051] The organic solvent is trifluoroethanol.
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment provides a preparation method for implanting a neovascular construct into the subcutaneous tissue of a subject, which is roughly the same as the preparation method provided in Example 1, except that the polymer material and the organic solvent are different, and the difference is as follows:
[0054] The polymer material is polyglycolic acid;
[0055] The organic solvent is tetrahydrofuran.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com