Gas marker detection method based on radial basis function neural network and application
A neural network and detection method technology, applied in the field of model systems, can solve problems such as reduced reliability and versatility, complex types of human exhaled gas, and severe cross-sensitivity of sensor responses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
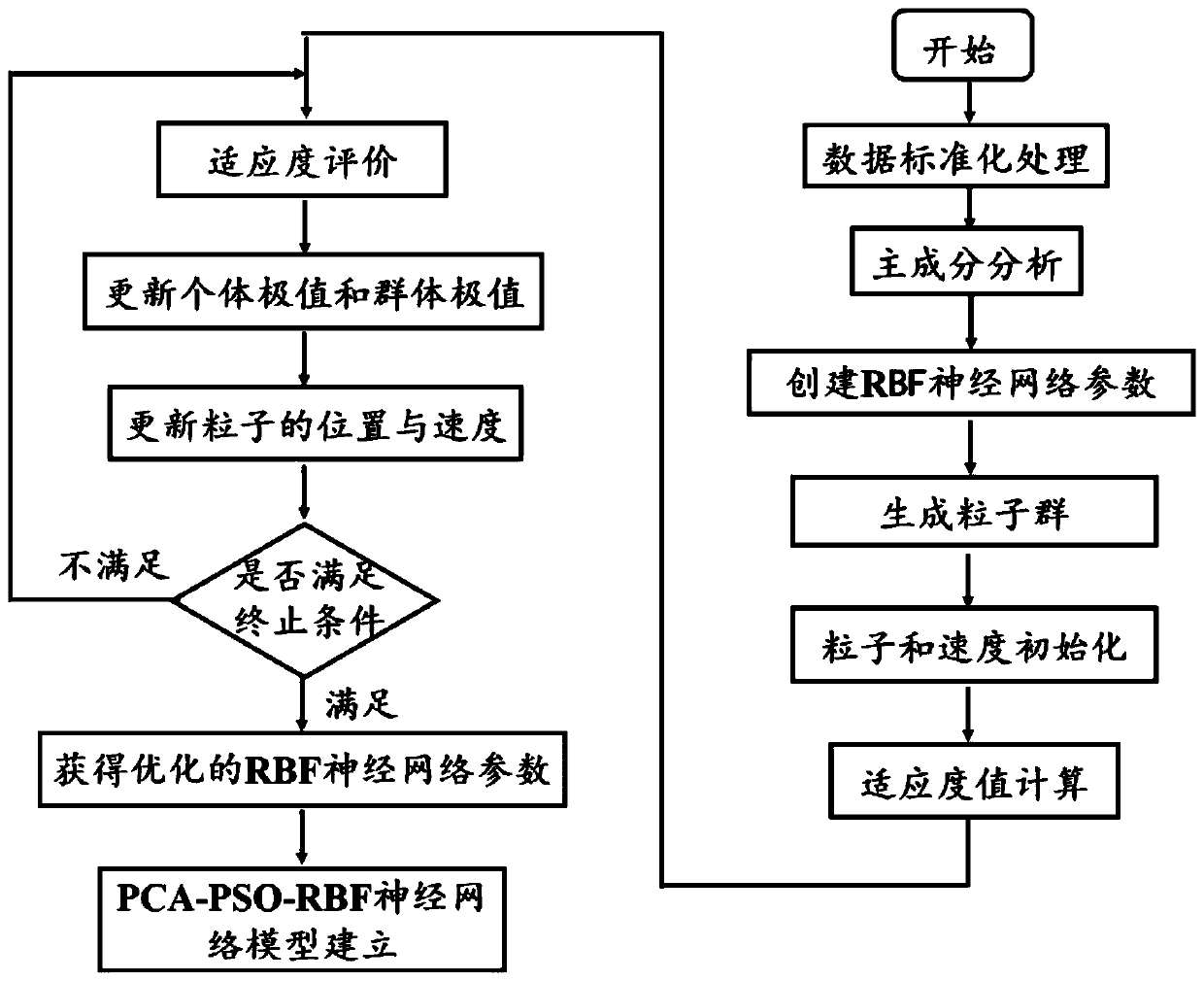
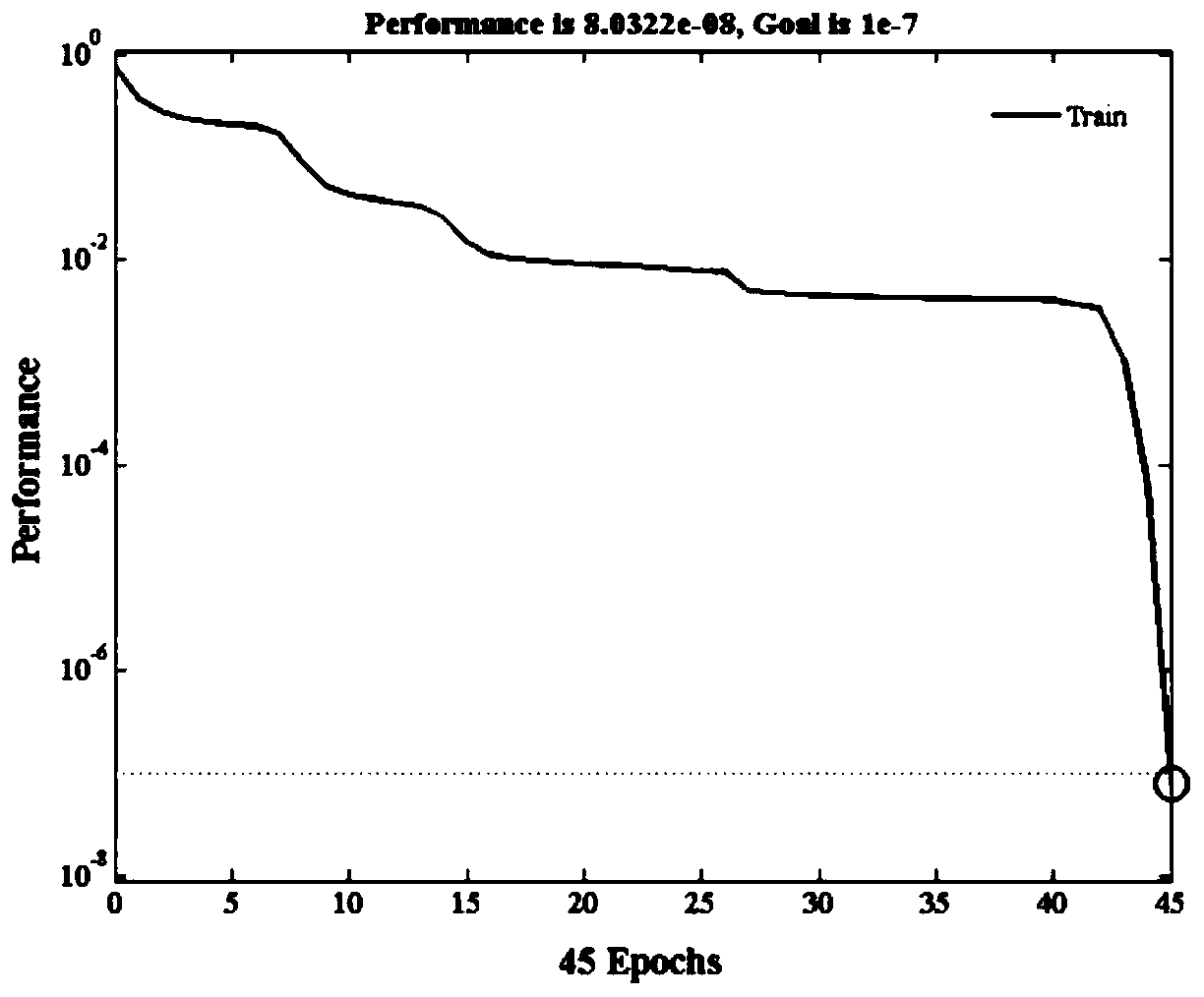
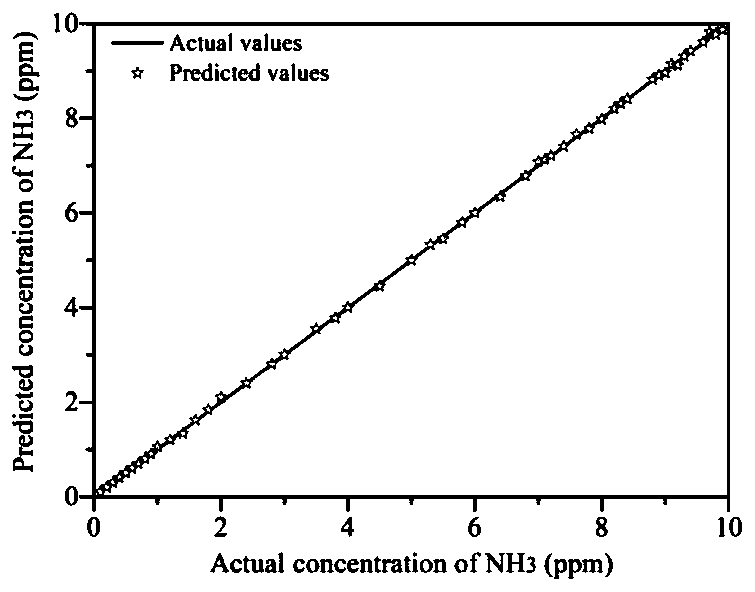
[0123] The detection method of exhaled gas markers based on radial basis function neural network, first, use the gas sensor to detect and calibrate the human exhaled gas markers, build a multi-dimensional sensor array to test the exhaled gas when simulating the sick state, and obtain several samples data; then, use the principal component analysis-particle swarm optimization-radial basis function (referred to as PCA-PSO-RBF) neural network algorithm model to preprocess the sample data, reduce the variable dimension, and reduce the cross-sensitivity of the gas sensor; finally, Prediction of human exhaled gas concentration.
[0124] In this embodiment, commercially available gas sensors for ammonia, acetone, and hydrogen sulfide (Digi-Key Electronics Co., Ltd.) are used as multi-dimensional sensor array construction elements for raw sample data collection.
[0125]In the PCA-PSO-RBF algorithm model, the principal component analysis (PCA) model is used to conduct principal compon...
Embodiment 2
[0185] In this example, if Figure 14 , Figure 15As shown, the human disease diagnosis model system uses the cluster analysis module to analyze the preprocessed markers; specifically, the algorithm of the K-means cluster processing framework in the cluster analysis module is as follows:
[0186] (1) Suppose the sample data set X is X={x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x N}, the number of clusters is k; if I=1, the initial clustering center is {Z j :j=1,2,3,...,k};
[0187] (2) Calculate the distance from each data point in the sample data to the cluster center, D(X i ,Z j (I)), where i=1,2,...,N; j=1,2,...,k; when D(X i ,Z j (I))=min{D(X i ,Z j (I)):j=1,2,...,k}, then X i is classified into the t category, denoted as
[0188] (3) Calculate the new cluster center in the sample data:
[0189]
[0190] (4) If Z j (I+1)≠Z j (I), j=1, 2,...,k, then I=I+1, return to step (2) and restart the calculation, otherwise the algorithm ends.
[0191] Effect of disease diagnosis based on cl...
Embodiment 3
[0197] In this embodiment, the human disease diagnosis model system uses a Deep Belief Neural Network (DBN) module to analyze the preprocessed sample data; specifically, the restricted Boltzmann Machine (restricted Boltzmann Machine) in the module , RBM for short) energy function is:
[0198]
[0199] The formula for converting to energy is:
[0200]
[0201] The probability distribution is expressed as:
[0202]
[0203] Among them, n and m respectively represent the number of neurons in the visible layer and hidden layer of the DBN neural network;
[0204] v and h respectively represent the state vectors of the visible layer and hidden layer of the DBN neural network;
[0205] a and b represent the state vectors of the visible layer and the hidden layer of the DBN neural network, respectively;
[0206] w represents the weight matrix connecting the visible layer and the hidden layer of the DBN neural network, θ={w, a, b};
[0207] is the partition function; P(v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com