Acesulfame optimized crystallization process
A kind of acesulfame potassium and crystallization technology, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, complicated process, poor quality, etc., and achieve the effect of improving production efficiency, simple process, and reducing shallow cooling load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
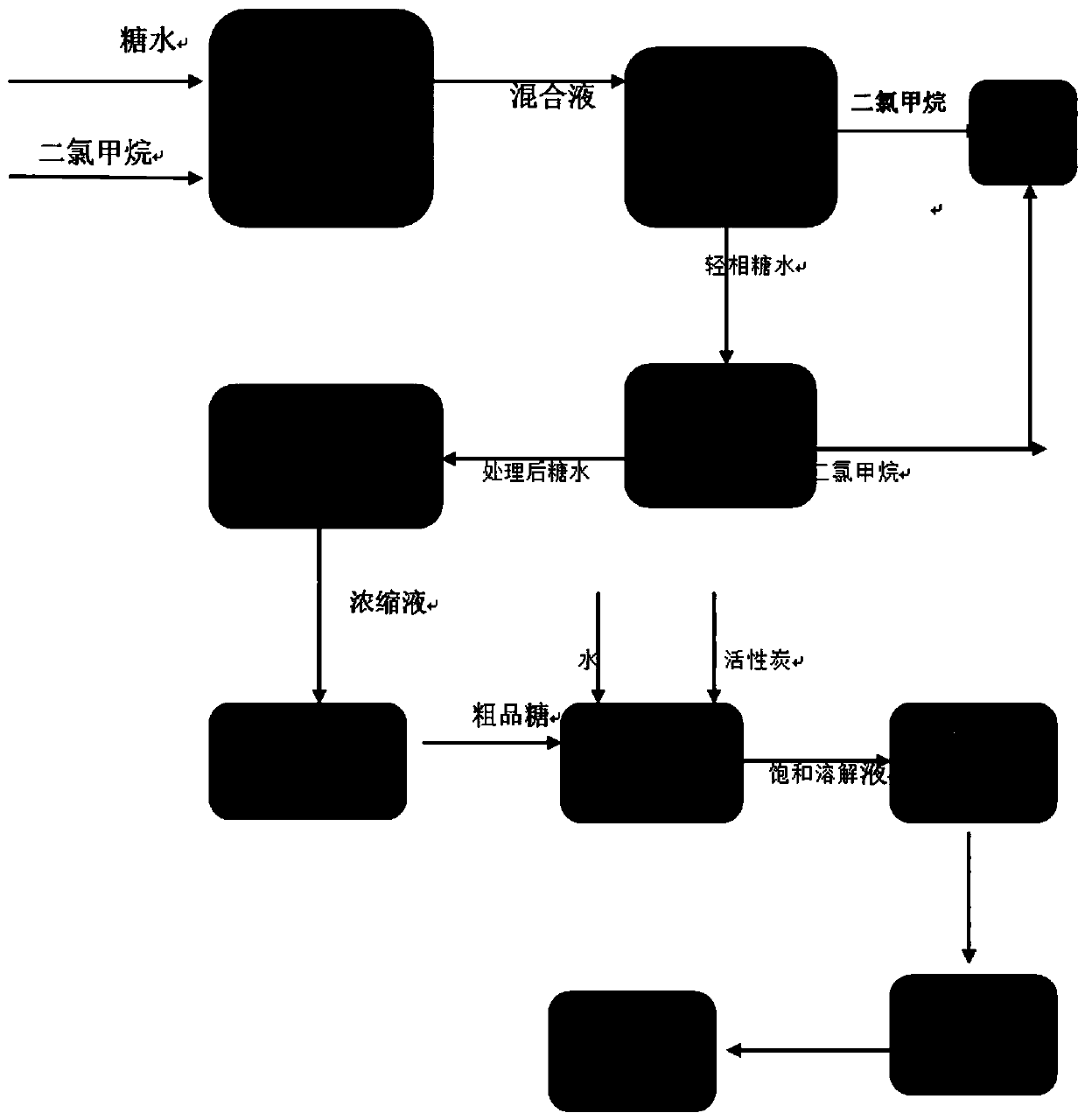
[0018] Embodiment one, such as figure 2 Shown:
[0019] 1. Put 70m³ of sugar water and 7 m³ of methylene chloride produced in the neutralization section of the acesulfame-K production process into the first mixer;
[0020] 2. After being mixed by the first mixer, it enters the separator, and 6.9 m³ of methylene chloride obtained from the layered heavy phase enters the rectification system, and 70.1 m³ of sugar water obtained from the layered light phase enters the second mixer, and the sugar water in the second mixer Add 10Kg of activated carbon, fully circulate through the circulation pump, and heat to 70°C through an external heat exchanger, and 550L of dichloromethane evaporates from the sugar water and enters the rectification system.
[0021] 3. After the preheating treatment, the sugar-water suspension is poured into the MVR in 4 batches, and concentrated at 85°C. When the concentrated liquid is 10m³, it is poured into the filter by a forced pump to remove 15Kg of acti...
Embodiment 2
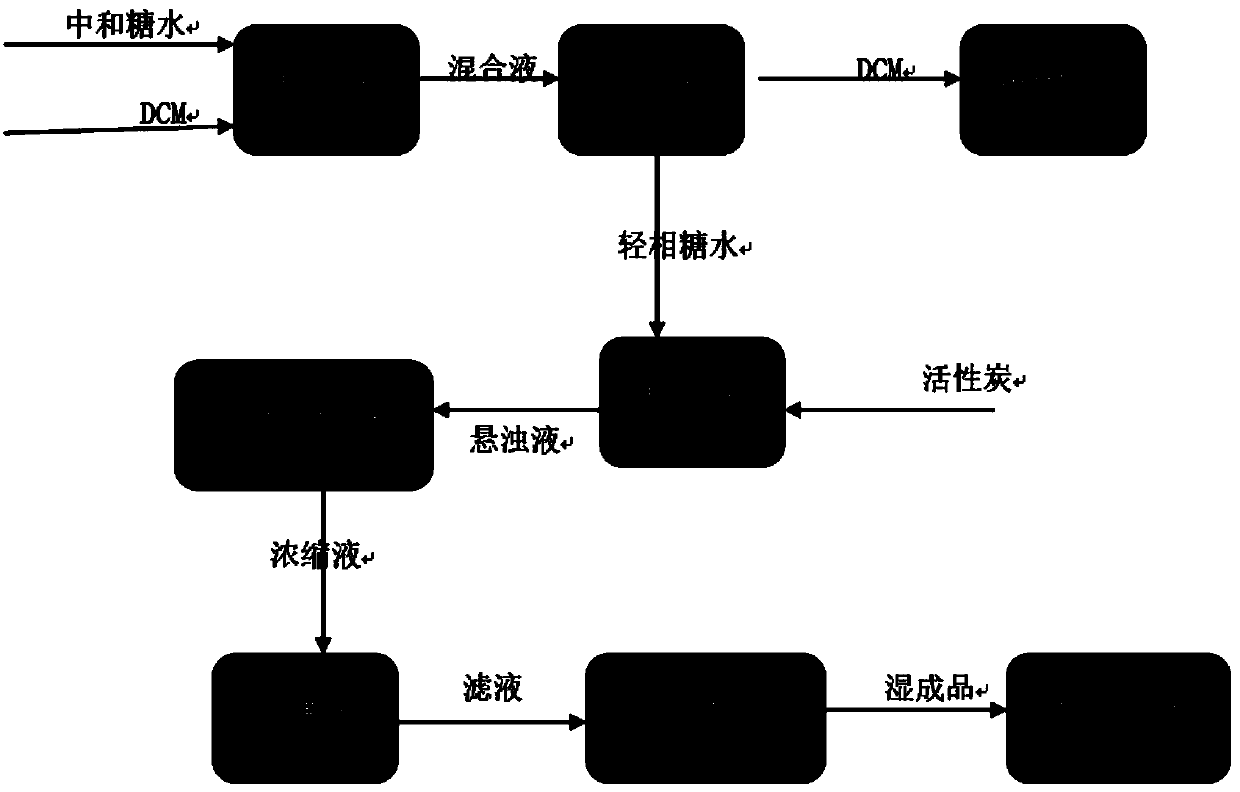
[0023] Embodiment two, such as figure 2 Shown:
[0024] 1. Put 70m³ of sugar water and 10m³ of dichloromethane produced in the previous section into the mixer;
[0025] 2. After being mixed by the mixer, it enters the separator and separates 70.1 m³ of sugar water and 9.9 m³ of dichloromethane. Add 20Kg of activated carbon to the separated sugar water, fully circulate through the circulation pump, and heat to 70°C through the external heat exchanger , Evaporate 550L dichloromethane in sugar water.
[0026] 3. After the preheating treatment, the sugar-water suspension is poured into the MVR in 4 batches, and concentrated at 85°C. When the concentrate is 10m³, it is poured into the filter by a forced pump to remove activated carbon (35Kg);
[0027] 4. Put the filtrate into the freezer to freeze for about 1 hour. When the temperature is 10°C, shake the material. The weight of the dried product is 10.2-10.5T, and the measured organic impurities are 8-11ppm.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment three, such as figure 2 Shown:
[0029] 1. Put 70m³ of sugar water and 5m³ of dichloromethane produced in the previous section into the mixer;
[0030] 2. After being mixed by the mixer, it enters the separator and separates 70.1 m³ of sugar water and 4.9 m³ of dichloromethane. Add 20Kg of activated carbon to the separated sugar water, fully circulate through the circulation pump, and heat to 70°C through the external heat exchanger , Evaporate 550L dichloromethane in sugar water.
[0031] 3. After the preheating treatment, the sugar-water suspension is poured into the MVR in 4 batches, and concentrated at 85°C. When the concentrate is 10m³, it is poured into the filter by a forced pump to remove activated carbon (35Kg);
[0032] 4. Put the filtrate into the freezer to freeze for about 1 hour. When the temperature is 2°C, shake the material. The weight of the dried product is 10-10.4T, and the measured organic impurities are 9-12ppm.
[0033] compared to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com