A codon-optimized glucose oxidase gene and its application
A technology for glucose oxidase and codon optimization, which is applied in the fields of biological enzyme genetic engineering and biosensing, can solve problems such as failure to express successfully, and achieve the effect of avoiding inverted repeats.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1, glucose oxidase gene codon optimization and cloning
[0024] In this embodiment, the glucose oxidase g9669.t1 gene in the AspergillusnigerAn76 genome is used as the original gene, and the original gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. According to the differences in the frequency of use of different codons encoding the same amino acid in Pichia pastoris, the rare codons in the original gene of glucose oxidase g9669.t1 were removed to avoid the occurrence of inverted repeat sequences and ensure the stability of the RNA secondary structure. The splicing site of intronic attribute was removed, the glucose oxidase gene was optimized, and two sequences were optimized according to different strategies, as shown in SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.3 respectively.
[0025] The optimized glucose oxidase gene was synthesized, and Nanjing Nuoweizan was used according to the principle of homologous recombination The Ultra One Step Cloning Kit product homologously recombin...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2, glucose oxidase gene transformation Escherichia coli enrichment plasmid
[0027] The original glucose oxidase gene (SEQ ID No.1) and the codon-optimized glucose oxidase gene (SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.3) were mixed with the pPIC9K homologous recombination product and E.coli DH5α respectively, After heat shock for 90s, spread on 100ug / mL ampicillin-resistant LB agar culture plate and culture overnight at 37°C. Pick a single colony, then extract the plasmid for electrophoresis detection, and store the plasmid at -20°C. Then use EcoRI and NotI enzyme digestion to detect the target fragment, and then send the bacterial suspension to the company for sequencing, and transform the correctly sequenced plasmid into Escherichia coli in the same way to achieve plasmid enrichment.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment 3, glucose oxidase gene transformation Pichia host bacterium
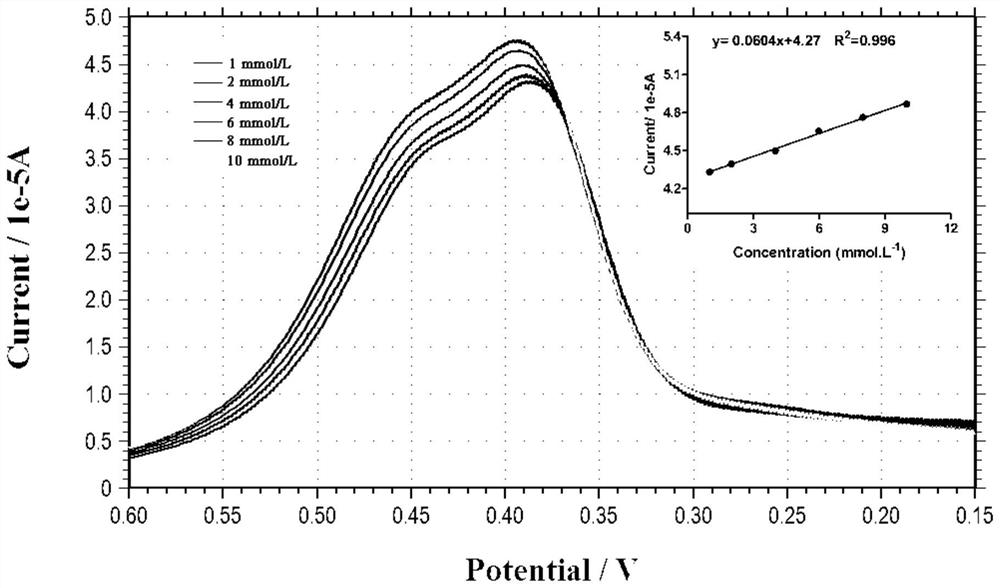
[0029] Inoculate a single colony of Pichia pastoris GS115 into a test tube containing 5mL of LYPD liquid medium, and culture overnight at 30°C. Transfer 1% of the inoculum to a Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of YPD liquid medium, culture overnight at 30°C until OD600=1.3-1.5; centrifuge the culture medium at 1500g at 4°C for 5min, discard the supernatant, and use a 50mL ice bath Resuspend the cells in double-distilled water; centrifuge the culture medium at 1500g at 4°C for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the cells in 25 mL ice-bathed double-distilled water; centrifuge the culture medium at 1500g at 4°C for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, Resuspend the cells with 2 mL of 1 M sorbitol solution in ice bath; centrifuge the culture medium at 1500 g for 5 min at 4 °C, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the cells with 1 mL of 1 M sorbitol solution in ice bath to make the bact...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com