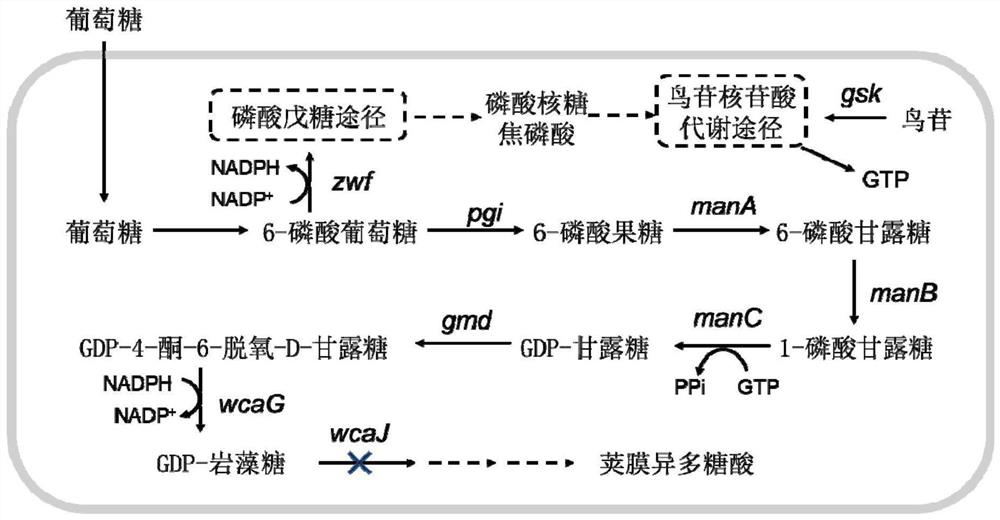
An Escherichia coli engineering strain that efficiently produces gdp-fucose
A technology of Escherichia coli and fucose, which is applied in the fields of microbial metabolic engineering and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of metabolic burden and flux imbalance, and can not achieve yield, so as to relieve metabolic pressure, have important industrial application value, and increase accumulation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
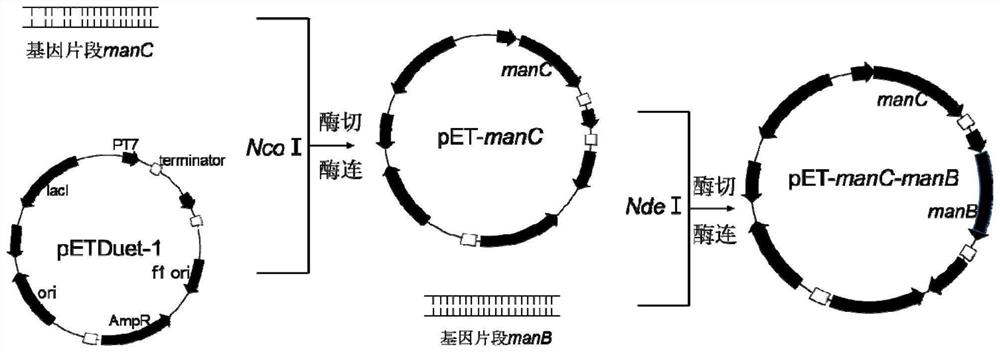
[0050] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant vector
[0051] The specific steps are as follows (the construction process can refer to figure 2 ):
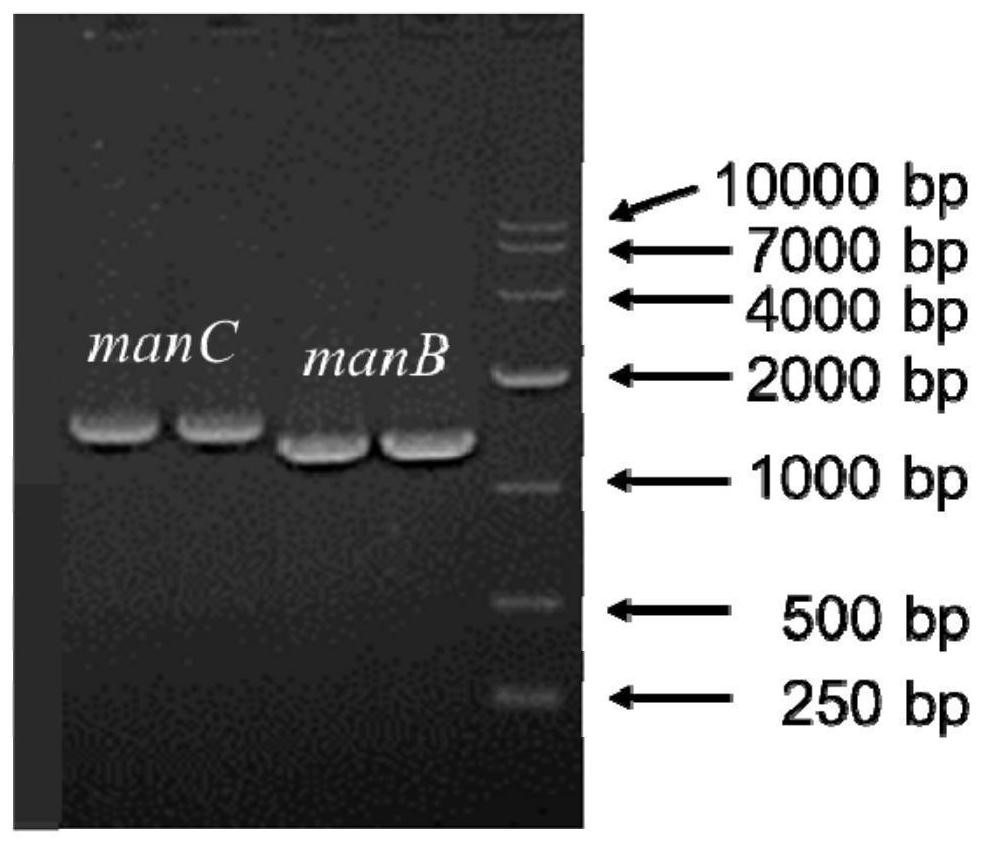
[0052] The genes manB, manC, gmd, wcaG, gsk and zwf encoding ManB, ManC, Gmd, WcaG, Gsk and Zwf in Escherichia coli MG1655 were passed through primers NdeI-manB-F / R, NcoI-manC-F / R, NcoI- gmd-F / R, NdeI-wcaG-F / R, NcoI-gsk-F / R and NdeI-zwf-F / R (see Table 1 for primer sequences) were amplified by PCR and recovered from DNA fragment gel to obtain relevant target gene fragments (PCR system see Table 2, PCR electrophoresis results see image 3 ). manB, gmd, and gsk were cloned into the first multiple cloning site of the corresponding Duet-1 plasmid after single-enzyme digestion (see Table 3 for the single-enzyme digestion system, and Table 4 for the enzyme-linked system), while manC, wcaG, and zwf were cloned by single-enzyme Excise cloned into the second cloning site of the corresponding Duet-1 plasmid, and finally obtained plas...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2: Replacement of the original ribosome binding site on the expression plasmid
[0068] In addition to expressing the ribosome binding site (RBS-ori) of the plasmid itself, the present invention has selected two RBSs, one is the standard ribosome binding site (RBS-32) reported in the literature, and the other is manB, manC, gmd and wcaG have their own wild-type ribosome binding site (RBS-WT) on the genome, and replace the corresponding RBS into the original expression vector, thereby regulating the protein translation intensity of each target gene (for different RBS sequences, see table 5).
[0069] Table 5 RBS sequence
[0070]
[0071] Using the constructed plasmids pACYC-manC-manB and pET-gmd-wcaG as templates, primers manC-[RBS-32]-F / R, manC-[RBS-WT]-F / R, manB-[RBS- 32]-F / R, manB-[RBS-WT]-F / R, gmd-[RBS-32]-F / R, gmd-[RBS-WT]-F / R, wcaG-[RBS-32] -F / R, wcaG-[RBS-WT]-F / R obtained the corresponding fragments and vectors (see Table 6 for primer sequences), an...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3: the knockout of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) genome gene
[0082] The specific steps are as follows (the specific operation process can refer to Figure 4 ):
[0083] (1) Use primers ΔwcaJ-upflank-F / R and ΔwcaJ-downflank-F / R to amplify the upstream and downstream fragments of the wcaJ gene by PCR respectively (see Table 8 for PCR primer sequences);
[0084] (2) Use primers ΔwcaJ-upflank-F and ΔwcaJ-downflank-R to carry out fusion PCR amplification of the upstream and downstream fragments to obtain a complete template gene (for the results of nucleic acid gel electrophoresis of PCR amplification products, see Figure 5 );
[0085] (3) Use primer N20-F / R to perform PCR amplification on the existing pTargetF plasmid to obtain the pTargetF plasmid with targeting wcaJ;
[0086] (4) transfer the pCas plasmid into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) by means of electroporation, and add 10 mM arabinose to induce the expression of the λ-Red Escherichia coli gene recombin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com