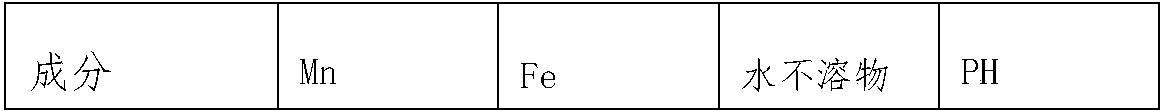Method for preparing microelement water-soluble fertilizer from manganese slag
A technology for trace elements and manganese slag, applied in the field of industrial waste slag resource utilization, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of nutrient elements, failure to maximize the utilization of manganese slag element resources, etc., and achieves low cost, ways to expand resource utilization, Simple production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
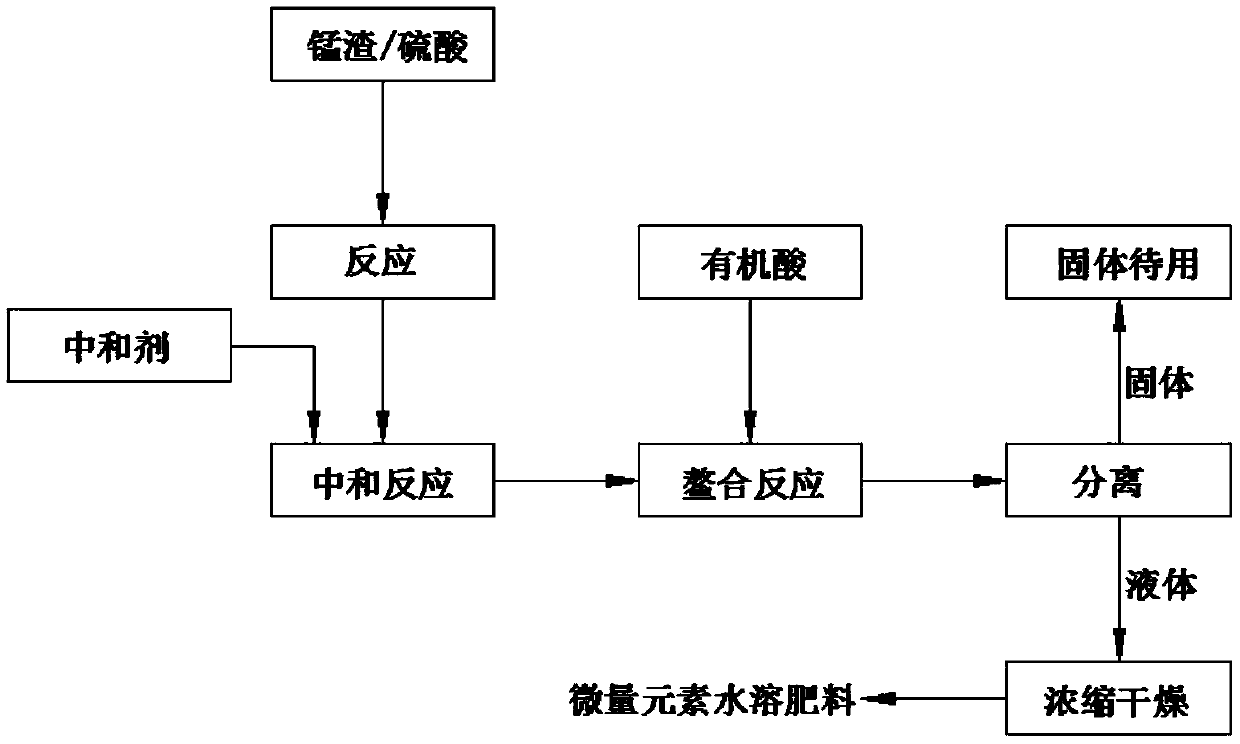
[0029] A method for producing trace element water-soluble fertilizer from manganese slag, comprising the following steps:
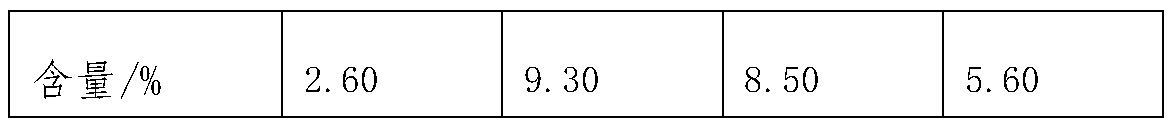
[0030] (1) Reaction: Grind the manganese slag to 90 mesh and mix it with sulfuric acid with a concentration of 30w% at a ratio of 1:4 (t:m 3 ) were mixed in proportion, placed in a reaction kettle to control the temperature of the material at 100°C, and reacted for 60 minutes to obtain solution a;
[0031] (2) Neutralization reaction: add sodium hydroxide to solution a for neutralization reaction, control the temperature of the material at 50°C, pH 2, and react for 60 minutes to obtain solution b; the ratio of solution a to sodium hydroxide is 1:0.03 (m 3 :t)
[0032] (3) Activation reaction: Add citric acid to solution a and trace elements in the system to carry out chelation reaction, control the temperature at 50°C, and perform solid-liquid separation after reacting for 50 minutes to obtain solid c and liquid c; among them, the solution The ratio of...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for producing trace element water-soluble fertilizer from manganese slag, comprising the following steps:
[0042] (1) Reaction: Manganese slag is pulverized to 80 mesh and then mixed with sulfuric acid with a concentration of 50w% at a ratio of 1:0.5(t:m 3 ) were mixed in proportion, placed in a reaction kettle to control the material temperature at 20°C, and reacted for 120 minutes to obtain solution a;
[0043] (2) Neutralization reaction: Add sodium hydroxide to solution a for neutralization reaction, control the material temperature at 25°C, pH 3, react for 90min, and obtain solution b; the ratio of solution a to sodium hydroxide is 1:6 (m 3 :t)
[0044] (3) Activation reaction: add ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid to solution a to carry out chelation reaction with trace elements in the system, control the temperature at 20°C, and perform solid-liquid separation after 150 minutes of reaction to obtain solid c and liquid c; Wherein, the ratio of solution ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A method for producing trace element water-soluble fertilizer from manganese slag, comprising the following steps:
[0053] (1) Reaction: Grind the manganese slag to 400 mesh and mix it with sulfuric acid with a concentration of 10w% at a ratio of 1:8 (t:m 3 ) were mixed in proportion, placed in a reaction kettle to control the material temperature at 120°C, and reacted for 5 minutes to obtain solution a;
[0054] (2) Neutralization reaction: add sodium hydroxide to solution a for neutralization reaction, control the material temperature at 100°C, pH 4, and react for 15 minutes to obtain solution b; the ratio of solution a to sodium hydroxide is 1:0.01 (m 3 :t)
[0055] (3) Activation reaction: Add organic acid to solution a and trace elements in the system to carry out chelation reaction, control the temperature at 90°C, and perform solid-liquid separation after reaction for 10 minutes to obtain solid c and liquid c; among them, the solution The ratio of b to organi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com