Smelting process for improving near-surface flaw detection defects of shaft rudder system steel
A near-surface, shaft-rudder system technology, applied in the field of steel, can solve problems such as restricting the development of shaft-rudder systems and ship parts, and achieve the effects of improving the qualified rate of flaw detection, reducing the scrap rate and improving economic benefits.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
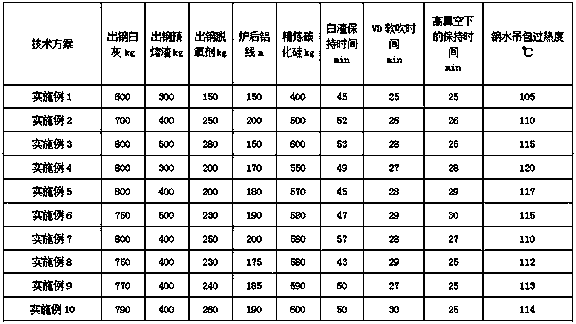
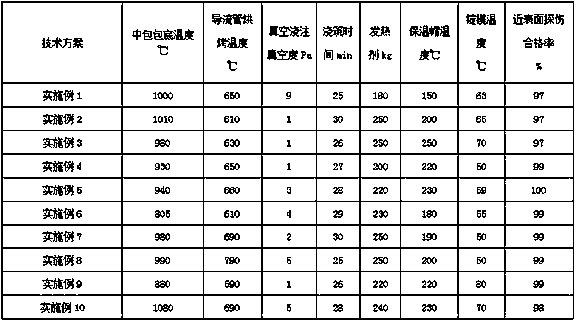
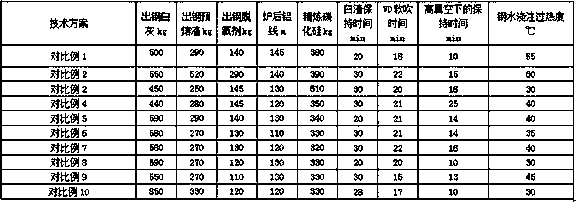
[0038] A smelting process for improving near-surface flaw detection defects of shaft and rudder steel, comprising the following steps:
[0039] 1) Converter tapping carbon ≥ 0.06%, tapping phosphorus ≤ 0.012%; converter tapping temperature 1610-1660°C.
[0040] Add steel core aluminum 150-280 kg during the tapping process; add lime 600-800 kg; add pre-melted slag 300-500 kg; feed aluminum wire 150-200 meters after tapping.
[0041] 2) SiC deoxidation for refining, 400-600 kg; refining white slag time: 43-60 minutes;
[0042] 3) Holding time under high vacuum: 25-30 minutes. During the vacuum holding period, it is necessary to observe that the molten steel surface is obviously exposed to ensure the vacuum degassing effect.
[0043] 4) After the VD is broken, feed 250-300 meters of manganese nitride wire; feed 40-80 meters of calcium wire. VD soft blowing time: 25-30 minutes;
[0044] 5) When pouring molten steel, the superheat of the hanging bag: 105-120°C; add 100-200 kg of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com