A low-altitude near-real-time building earthquake damage assessment method
A near-real-time, architectural technology, applied in neural learning methods, instruments, biological neural network models, etc., can solve the problems of inability to reliably grasp the damage of building facades, time-consuming manpower and material resources, low efficiency, etc., and achieve improved prediction. The effect of precision and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
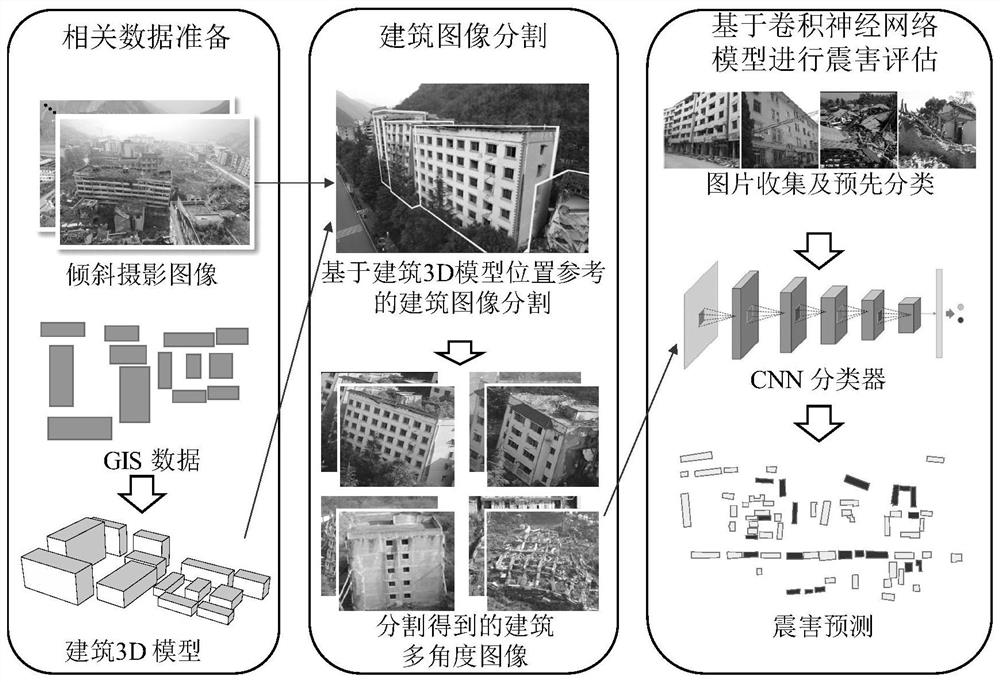
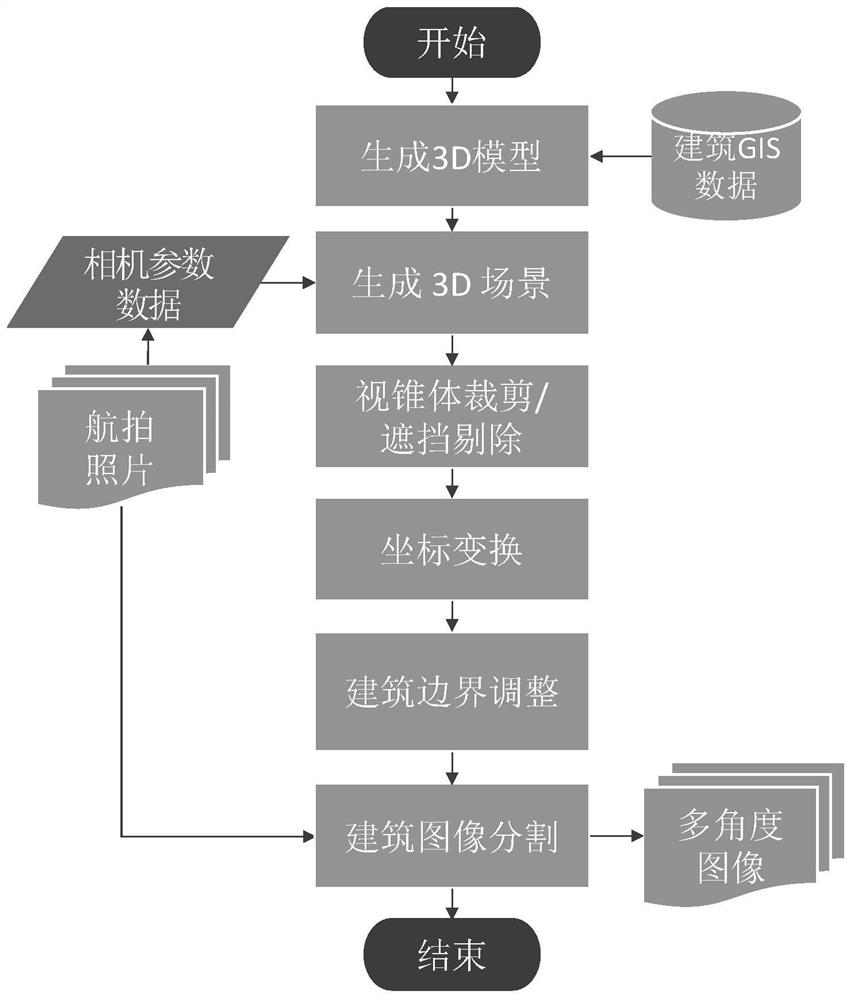
[0036] In this embodiment, combined with the means of deep learning, building earthquake damage assessment is performed based on a large number of oblique photographic images of buildings acquired by low-altitude drones. This embodiment discloses a low-altitude near-real-time building earthquake damage assessment method, including the following steps:
[0037] 1) Obtain building-related data in the area to be evaluated. Wherein, the building-related data includes pre-earthquake 3D models of buildings in the area to be evaluated, pre-earthquake 2D-GIS (Geographic Information System, geographic information system) data, post-earthquake original aerial photos, and camera parameter data of post-earthquake original aerial photos. The camera parameter data includes the shooting position of the aerial photo, the camera orientation and the camera viewing angle data.
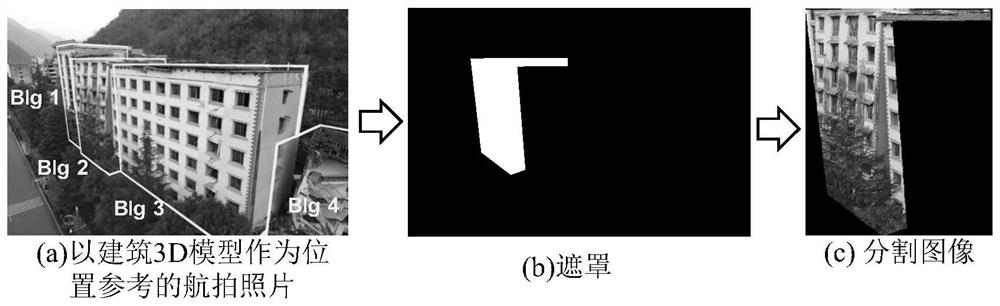
[0038] 2) Use the building 3D model as a location reference to segment the regional building image, and obtain aerial...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com