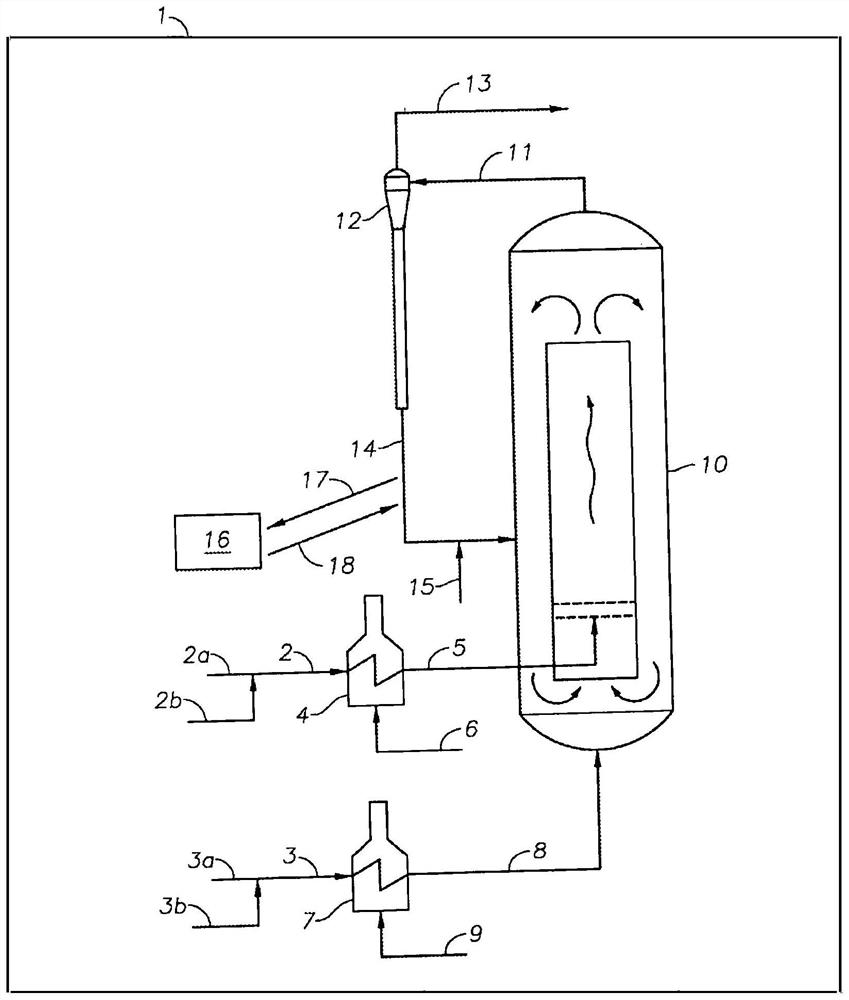
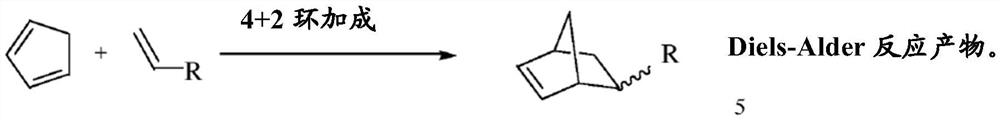
Methods and systems for converting acyclic hydrocarbons
A technology for acyclic hydrocarbons and cyclic hydrocarbons, applied in the field of conversion of acyclic hydrocarbons and systems, can solve the problems of carburizing, affecting product selectivity, catalyst life, catalyst activity loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0189] Example 1 - Modeling of Reactor Performance
[0190] Reactor modeling was performed using Invensys Systems Inc. PRO / II 9.3.4 to evaluate performance under various commercially relevant operating conditions. Depending on the details of the modeling, the results will vary, but the model will still demonstrate the relative benefits of the invention. Many modifications and variations are possible, and it should be understood that, within the scope of the claims, the invention may be practiced otherwise than as specifically described herein.
[0191] Example 1A - Methane diluent, 20psia outlet pressure, 10psia HC partial pressure
[0192] A fluidized bed reactor simulating 20 psia outlet pressure, 575 °C outlet temperature, where the feed contained n-pentane, which was preheated to 621 °C, was then fed into the fluidized bed, and the co-feed contained methane and hydrogen, which Separately preheated to a temperature that supplies 100% of the heat of reaction. Under these co...
Embodiment 1B
[0193] Example 1B - Methane diluent, 950°C co-feed preheat, 10psia outlet HC partial pressure
[0194] As a comparison to Example 1A, a fluidized bed reactor with an outlet temperature of 575°C was simulated, where the feed contained n-pentane, which was preheated to 621°C, and then fed into the fluidized bed, and the co-feed contained methane and hydrogen, which were separately preheated to 950°C. Under these conditions, the light selectivity of the catalyst (C 4- product) was -18%. The residence time within the catalyst bed is assumed to provide the CPD concentration to reach its thermodynamic concentration at the reactor outlet conditions. The hydrogen molar rate in the reactor co-feed was set so that the molar ratio of hydrogen:n-pentane in the feed was 1:1. The methane molar rate in the reactor co-feed was set to provide 100% of the heat of reaction. The total outlet pressure of all components except methane, including hydrogen, was set to 10 psia by adjusting the tot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com