Internet-of-vehicles backoff method and device based on sender packet loss distinguishing mechanism
A technology for packet loss differentiation and car networking, applied in the field of car networking, can solve problems such as increasing additional network overhead and poor channel stability, and achieve the effects of adapting to environmental changes, improving accuracy, and improving system performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
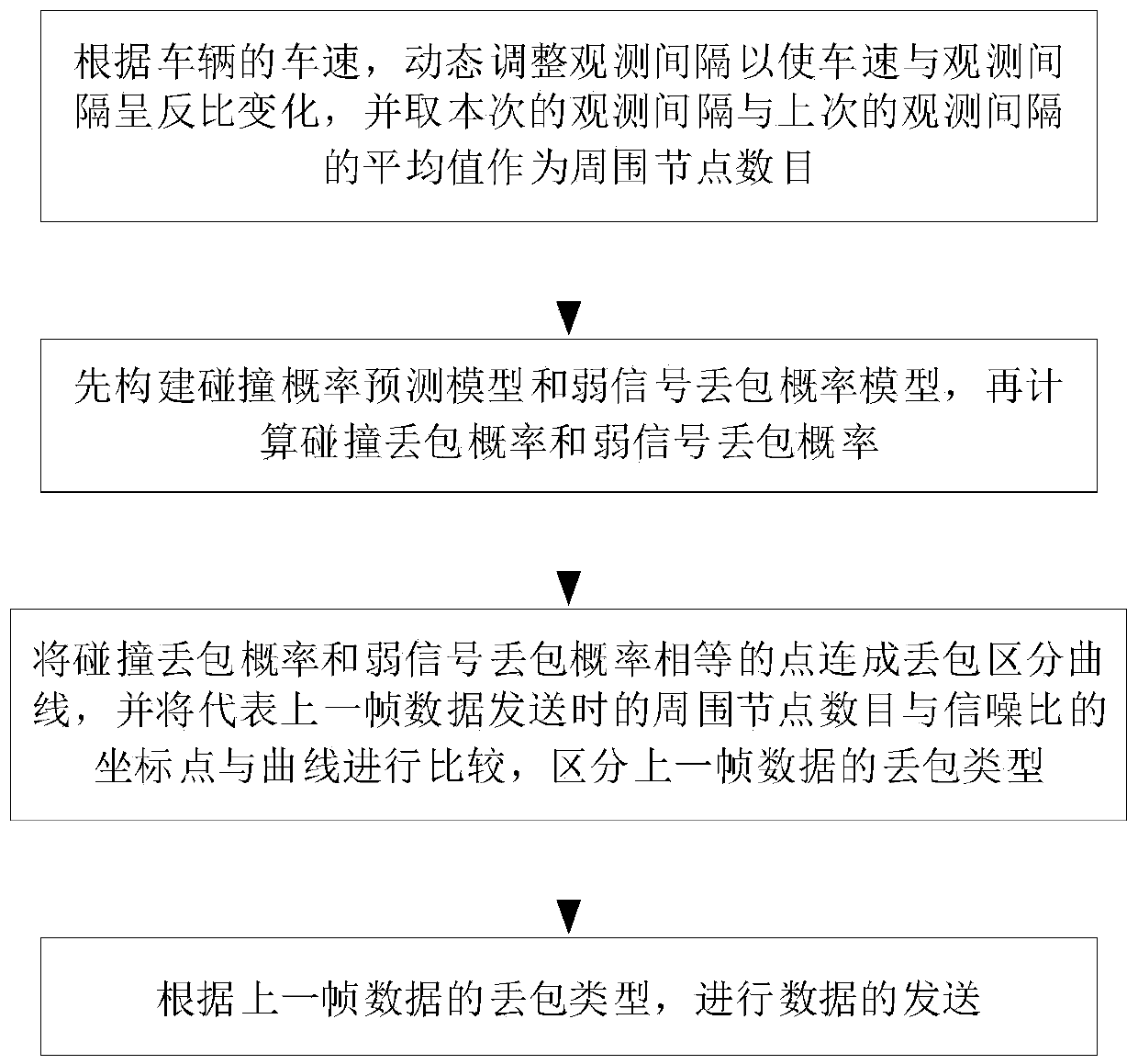
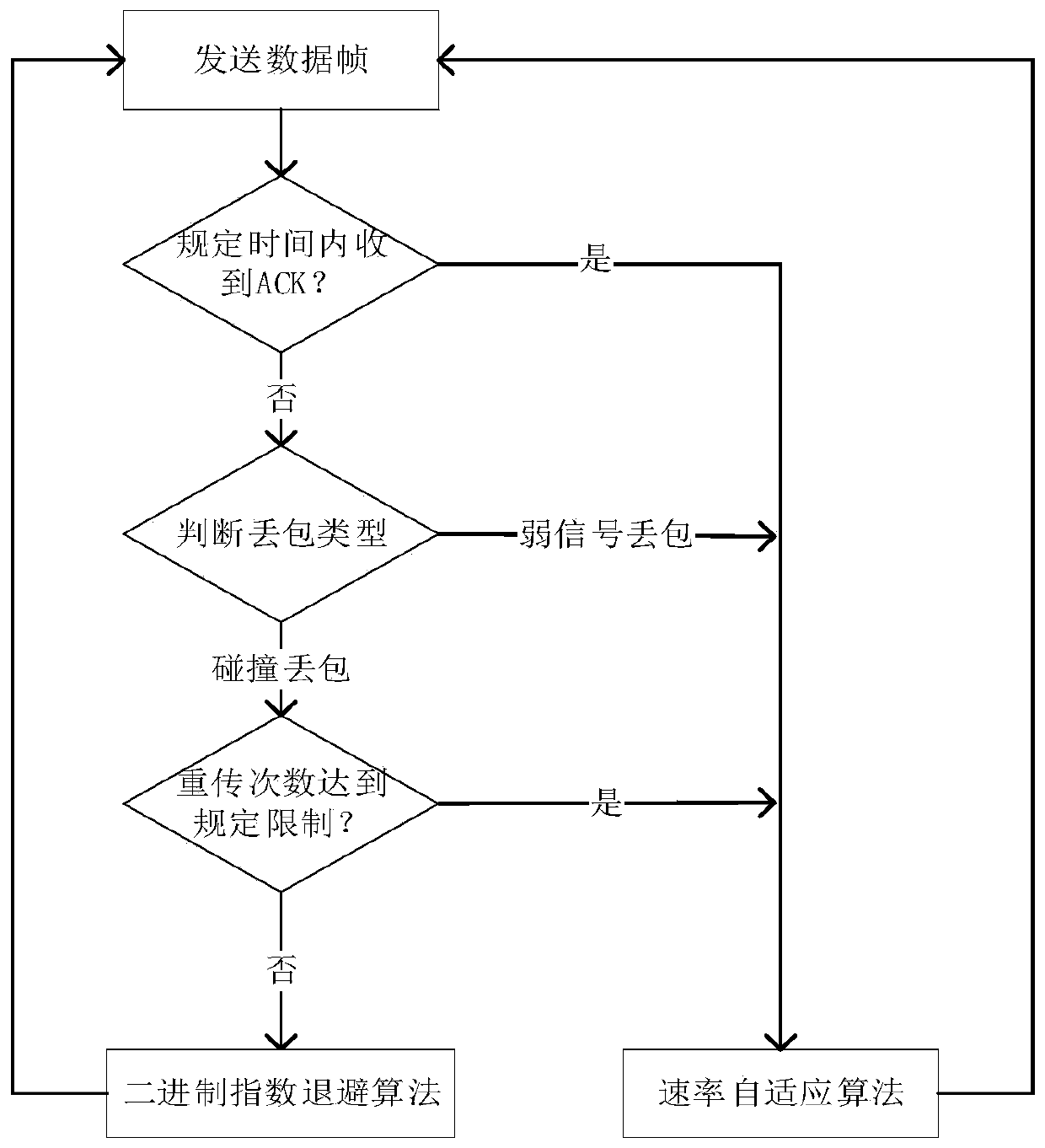
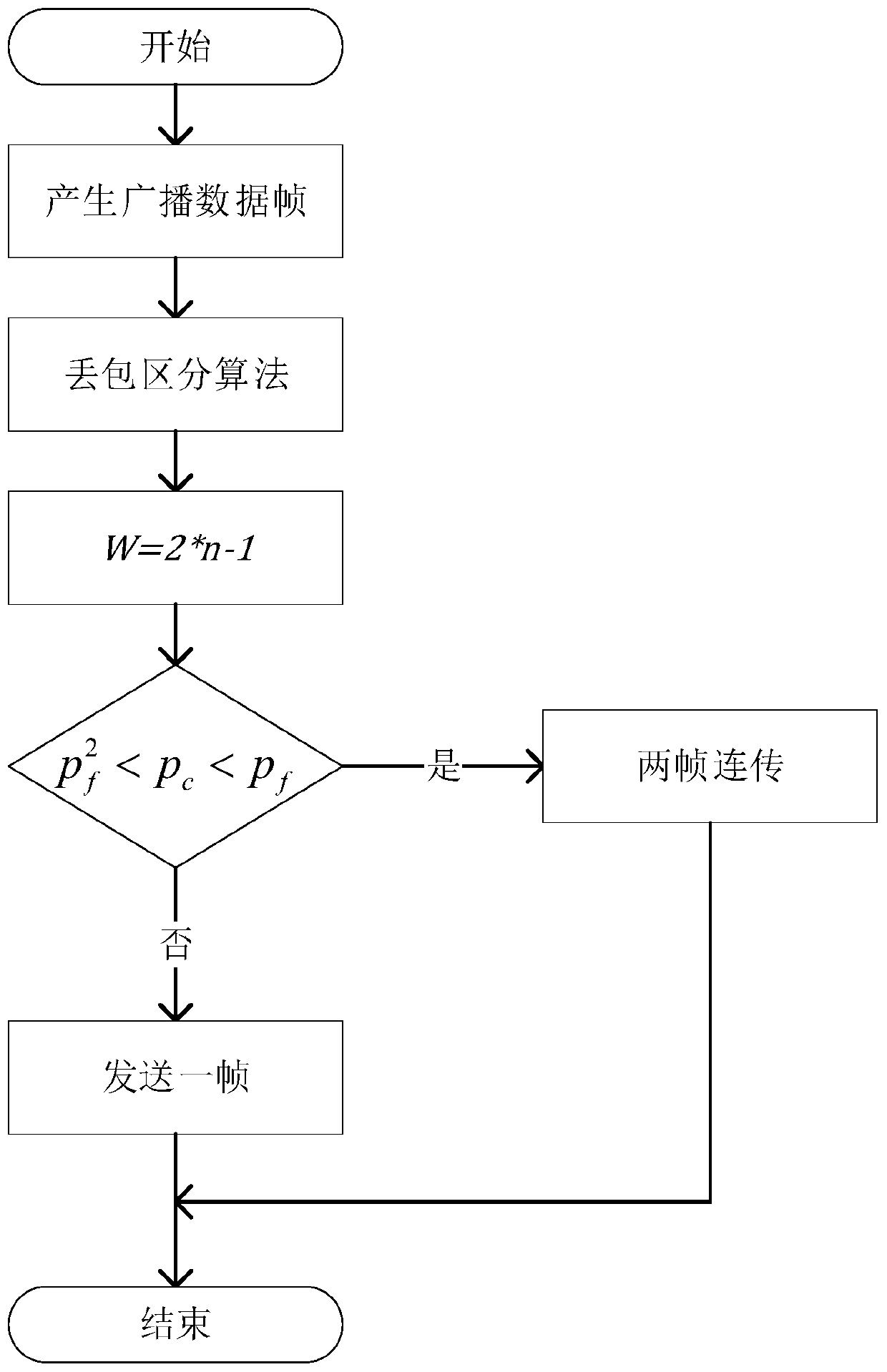
[0105] see figure 1 , figure 2 as well as image 3 , this embodiment provides a vehicle networking back-off method based on the sender packet loss discrimination mechanism, which can be applied in the vehicle networking environment based on the IEEE802.11 protocol. Wherein, the vehicle networking avoidance method includes the following steps (steps 1-4).
[0106] Step 1. According to the vehicle speed, dynamically adjust the observation interval so that the vehicle speed and the observation interval change inversely, and take the average value of the current observation interval and the last observation interval as the number of surrounding nodes. The traditional traffic density detection method is to calculate the number of surrounding nodes periodically by receiving information such as MAC addresses and GPS messages in broadcast frames in a circle with the vehicle as the center and the transmission range as the radius. The core of the algorithm is to record the MAC addre...
Embodiment 2
[0162] This embodiment provides a vehicle networking back-off method based on the packet loss discrimination mechanism of the sender, which is similar to the method in Embodiment 1, except that the model and the calculation method of the probability of packet loss due to collision are different. In this embodiment, in the unicast mode, the method for calculating the probability of packet loss due to collision includes the following steps.
[0163] (2.1) Establish a two-dimensional Markov chain model; see Figure 9 , where the two-dimensional stochastic process of the two-dimensional Markov chain model is {s(t),b(t)}. Among them, s(t) represents the backoff series (0,...,m) of the node at time t, and m is the maximum backoff series. b(t) represents the waiting time in the backoff process at time t. This embodiment adds the situation that the backoff window is not updated. When the data frame fails to be sent through the channel, the probability is p f , the backoff order mai...
Embodiment 3
[0195] This embodiment provides a vehicle networking back-off method based on the senders packet loss discrimination mechanism, which performs simulation analysis on the basis of Embodiment 2, and sets relevant parameters.
[0196] , in order to verify the accuracy of the collision probability prediction model under error channel conditions, this embodiment uses the MATLAB simulation tool to perform Monte-Carlo statistical simulation. Among them, IEEE 802.11p link simulation (including transmitter, receiver and channel model) adopts WLAN System Toolbox 2.0 simulation toolbox, which was added for the first time in the 2015b version, providing models and examples for WLAN design, simulation and testing , relying on the digital computing capability of MATLAB, it provides a complete transceiver model and channel modeling that conform to the 802.11 protocol standard. The specific channel coding, modulation methods (OFDM, DSSS and CCK) and MIMO beamforming are packaged with special ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com