Electric-pneumatic composite braking control method for train
A hybrid braking and braking control technology, applied in the field of rail transit vehicles, can solve the problems of reduced braking reliability, increased brake shoe wear, large brake shoe wear, etc., to reduce signal delay, prevent braking force superposition, The effect of reducing maintenance costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
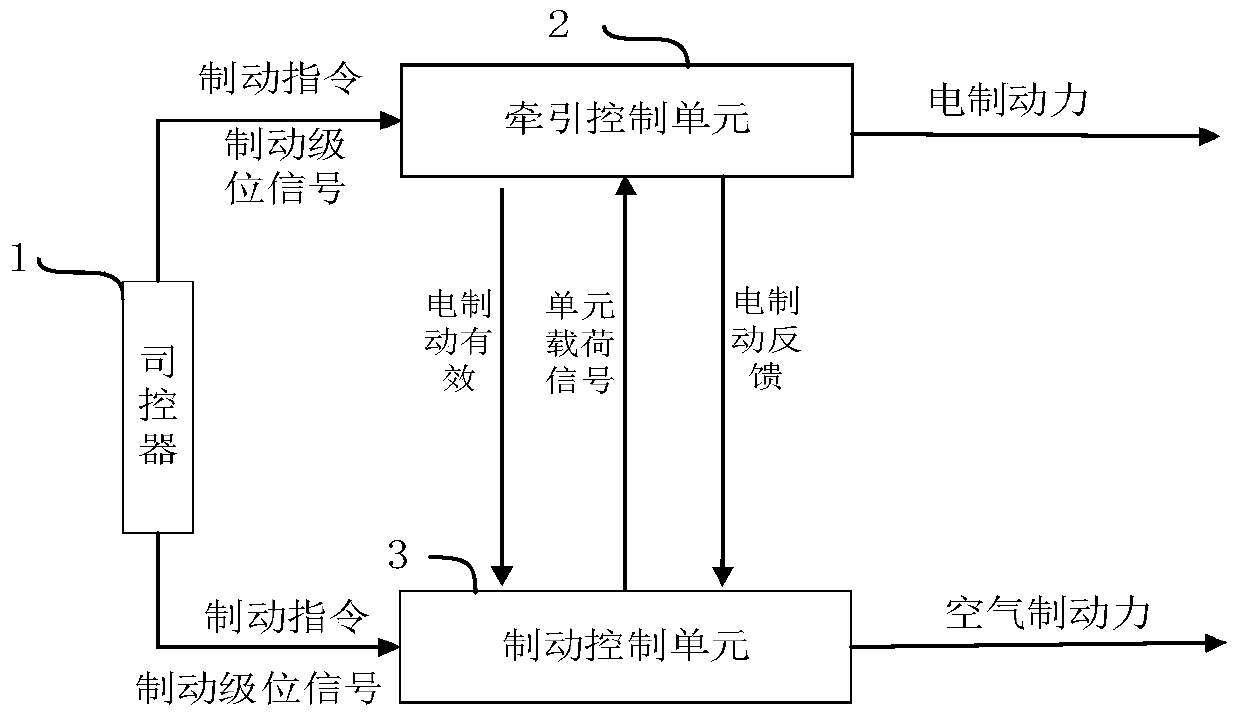
[0072] see figure 1 , the train is provided with a controller 1, and the train is divided into several motor car trailer units, and electro-pneumatic hybrid braking is carried out in each motor car trailer unit; the motor car trailer unit is provided with a traction system and a braking system; The traction system includes a traction control unit 2 (TCU), and the braking system includes a brake control unit 3 (EBCU); the controller 1 sends the traction control unit 2 (TCU) and the brake control unit 3 (EBCU) Braking command and braking level signal; the traction control unit 2 (TCU) and braking control unit 3 (EBCU) receive the braking command and braking level signal, and perform the next step of operation. Preferably, in this embodiment, the traction control unit 2 (TCU) and the brake control unit 3 (EBCU) directly perform signal interaction through electrical hard wires to realize real-time data transmission.
[0073] In this embodiment, TCU represents the traction control...
Embodiment 2
[0093] The principle of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment, which is a further specific implementation of the first embodiment, and the specific content is as follows:
[0094] Such as Figure 4-Figure 5 , the traction control unit 2 (TCU) includes an electric brake controller and an electric brake applicator coupled thereto, the traction control unit 2 (TCU) transmits information through the electric brake controller, and is controlled by the electric brake controller The brake applicator executes the relevant commands to apply the electric brake.
[0095] In this embodiment, the motor car EBCU represents the motor car brake control unit 31 , and the trailer EBCU represents the trailer brake control unit 32 .
[0096] The braking control unit 3 (EBCU) includes a motor vehicle braking control unit 31 (motor vehicle EBCU) and a trailer braking control unit 32 (trailer EBCU), and the motor vehicle braking control unit 31 (motor vehicle EBCU) inclu...
Embodiment 3
[0128] The principle of the third embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment to the second embodiment, and the main difference is that: Figure 9-Figure 10 , in this embodiment, the motor vehicle braking control unit 31 presets the normal range of the electric braking force feedback value, and the electric braking force feedback value Fe exceeds the preset normal range of the electric braking force feedback value (below or higher than the normal range) , and last for a preset time, it indicates that the feedback signal is abnormal. That is, when the electric brake feedback signal exceeds the physical limit (lower or higher than the normal range) for a certain period of time, it indicates that the feedback signal is abnormal. At this time, the motor vehicle brake control unit 31 (motor vehicle EBCU) sends an electric brake removal signal to the traction control Unit 2 (TCU), the traction control unit 2 (TCU) receives the electric brake removal signal, and cuts off t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com