Magnetic nanocomposite, and preparation and application thereof
A composite material, magnetic nanotechnology, applied in the field of heavy metal detection in food samples, can solve the problems of difficult separation of GO and solution, and achieve the effects of high accuracy, high sensitivity and good adsorption performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] (1) Synthesis of silica-modified magnetic graphene oxide
[0056] (1.1) Synthesis of Magnetic Graphene Oxide
[0057] 0.5 g of graphene oxide (GO) powder and 100 mL of distilled water were added to a three-necked round-bottom flask, followed by mechanical stirring until the bath temperature rose to 70 °C. A total of 2.16g of FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 0.80 g FeCl 2 4H 2 O was dissolved in 40 mL of distilled water in a beaker to obtain a clear solution. The mixture was then added to the dispersion at 70°C with vigorous stirring. Afterwards, ammonia solution was added to adjust the pH of the suspension to 12 in order to modify Fe on the surface of GO materials. 3 o 4 Nanoparticles. The mixture was stirred mechanically at 70°C for 60 minutes. Throughout the process, the reaction was protected with pure nitrogen to prevent complete growth and oxidation of the nanoparticle crystals. After the reaction, the magnetic material is separated from the mixture with a magnet. The...
Embodiment 2
[0063] For MGO / SiO 2 Characterization of @coPPy-An nanocomposites
[0064] The size and morphology of the nanocomposites were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) X-ray diffraction (XRD).
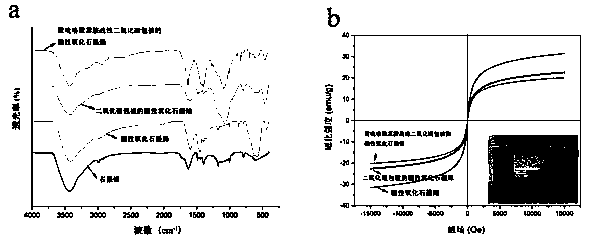
[0065] Observation of GO, MGO, MGO / SiO by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) 2 and MGO / SiO 2 @coPPy-An's surface morphology as figure 1 shown. figure 1 a shows that its surface morphology is a smooth, disorderly folded sheet structure, which is a typical structure of GO structure. figure 1 The SEM image of MGO shown in b has a rougher surface compared to GO because of Fe with a diameter of about 30 nm 3 o 4 Nanoparticles (NPs) were attached to the GO surface, and this also confirmed the successful modification of magnetic nanoparticles on the GO surface. According to MGO / SiO 2 SEM image of ( figure 1 c), it can be clearly seen that the surface of the MGO nanocomposite is covered ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Optimization of MSPE (Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction) Conditions
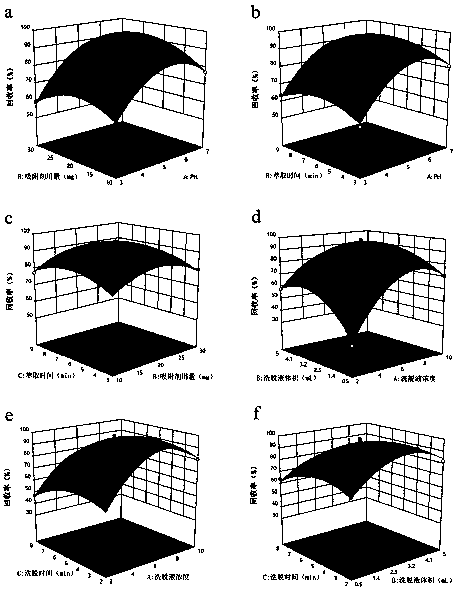
[0071] In order to understand the influence of experimental variables on the MSPE process, the interaction between the main parameters must be fully considered and each parameter should be optimized. We obtained the optimal conditions of each parameter through the Box-Behnken design (BBD) method of response surface fitting. On the basis of preliminary experiments, the influence of six factors was studied from two levels of extraction process and elution process. like Figure 4 As shown in the results, the optimum operating condition is that the pH value is 5.7, the amount of adsorbent is 19.2mg, and the adsorption time is 6.3min; the eluent volume is 2.9mL, and the eluent concentration is 6.8% (v / v). The desorption time is 3.7min, which can obtain the best adsorption recovery rate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com