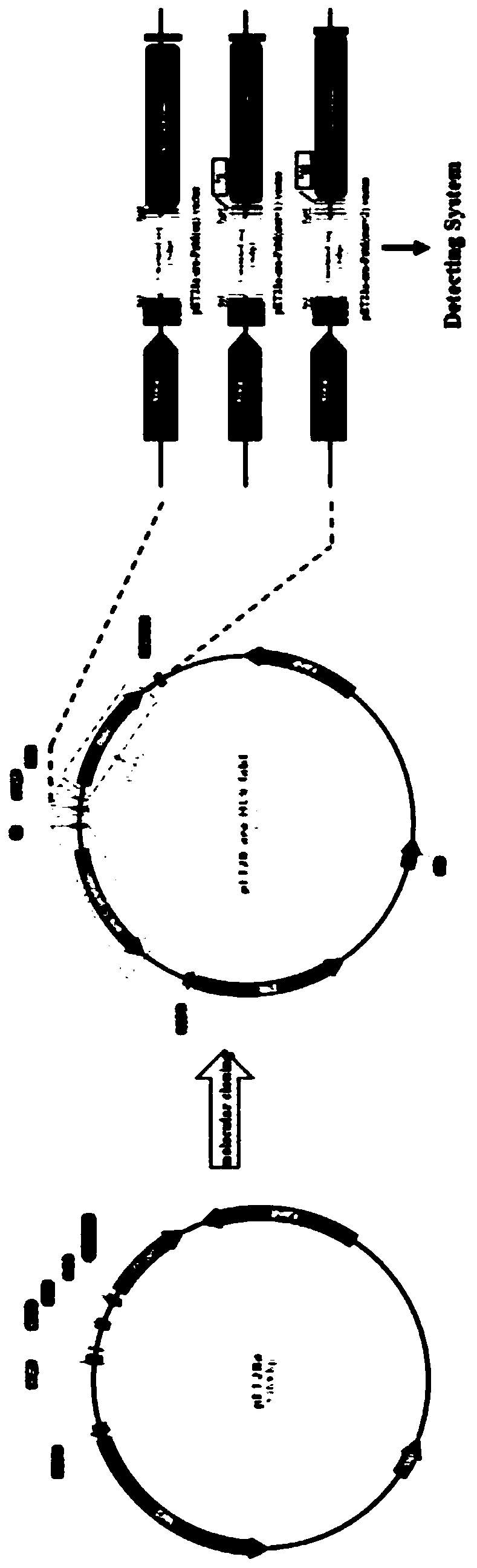
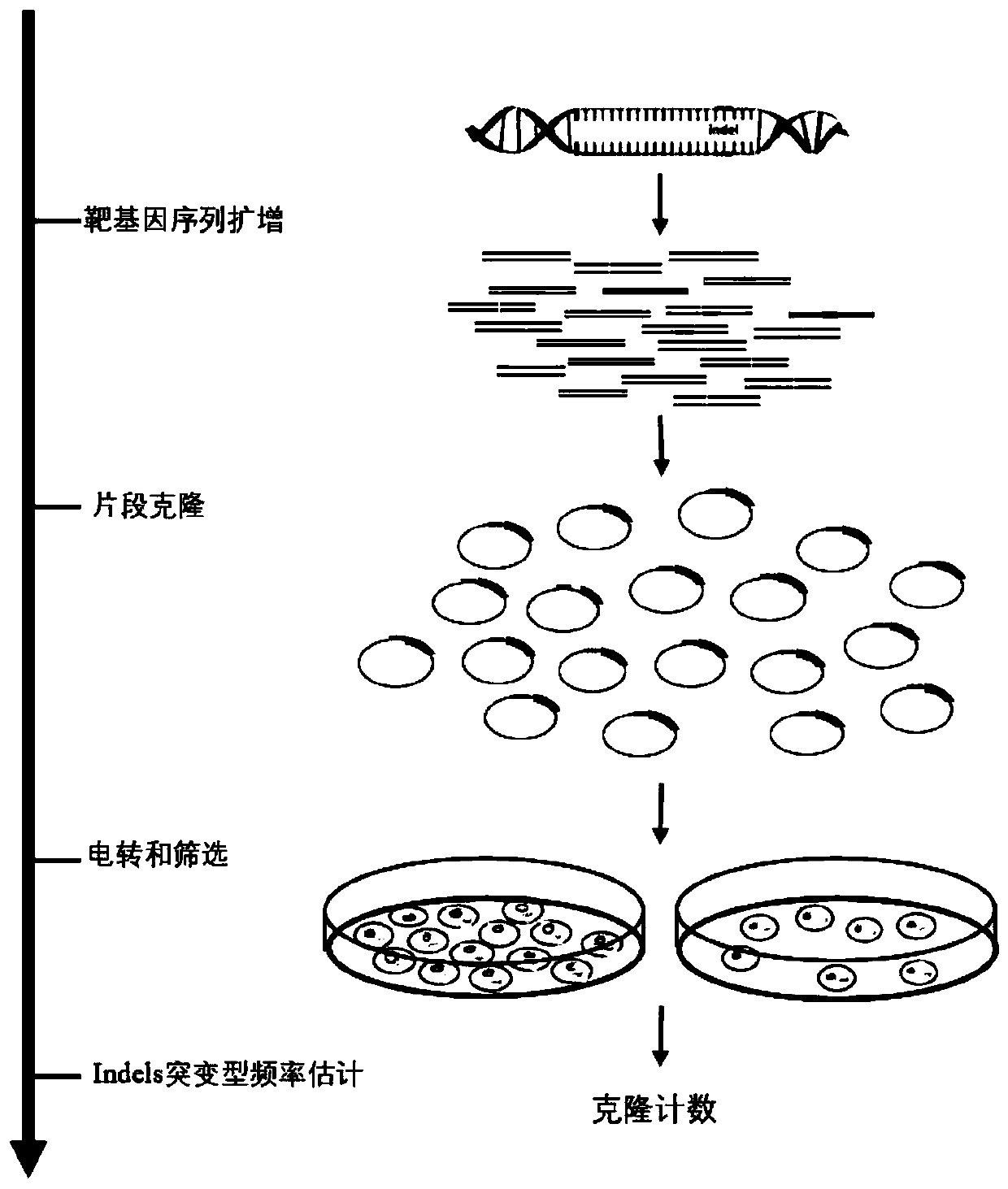
Construction and application of high-flux detection system for nuclease induced insertion and deletions (Indels)
A nuclease, a technology to be detected, applied in the field of genetic engineering, which can solve problems such as destroying the function of proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1: Detection of Indels mutations on the genome of 293T cells after CRISPR / Cas9 action --- different target gene loci (Indels mutation efficiency > 20%)
[0052] 1. Construct a CRISPR / Cas9 system specifically targeting EMX1, HPRT1, and CCR5 genes and transfect 293T cells (human embryonic kidney cells). The sequences of each target gene are shown in Table 2.
[0053] Table 2 Comparison table of target gene sequences
[0054]
[0055] Specifically include the following steps:
[0056] (1) The sgRNA sequence and gene target sequence amplified by Annealing PCR were cloned into the sgRNA-Cas9 expression vector and the NHEJ-RPG reporter vector (the carrier owned by the applicant's laboratory, The specific construction process will not be described in detail), and the sgRNA.EMX1-Cas9 expression vector, NHEJ-RPG.EMX1 reporter vector, sgRNA.HPRT1-Cas9 expression vector, NHEJ-RPG.HPRT1 reporter vector, sgRNA.CCR5-Cas9 expression vector and NHEJ -RPG.CCR5 reporter vec...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2: Indels mutation detection for different target gene loci of unscreened 293T cells
[0087] 1. Construct and obtain 293T cell lines specifically targeting EMX1, HPRT1, and CCR5 genes, and only use a single sgRNA.EMX1-Cas9, sgRNA.HPRT1-Cas9, and sgRNA.CCR5-Cas9 expression vectors to achieve different target gene positions For point genome editing, the cells were harvested 5 to 7 days later and the cell genome was extracted. The subsequent detection methods and steps were the same as in Example 1.
[0088] 2. Indels frequency statistical results are shown in Table 10. Figure 7 shown.
[0089] Table 10 CRISPResso2 analysis and ara-FabI system detection Indels frequency statistics
[0090] Indels frequency (%) CCR5 EMX1 HPRT1 NGS 4.51 15.73 17.96 ara-mFabI 9.11 10.94 25.63
[0091] It can be seen from the above results that the system constructed by the present invention can not only effectively reveal the higher frequency (...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3: Detection of Indels mutations at the CCR5 gene locus on different cell lines
[0093] 1. Construct 293T, A375 (human melanoma cells) and U2OS (human osteosarcoma cells) specifically targeting the CCR5 gene, and transfect the sgRNA.CCR5-Cas9 expression vector to achieve the same target in different cell lines For genome editing of gene loci, the cells were harvested 5 to 7 days later and the cell genome was extracted. The subsequent detection methods and steps were the same as in Example 1.
[0094] 2. Indels frequency statistical results are shown in Table 11. Figure 8 shown.
[0095] Table 11 CRISPResso2 analysis and ara-FabI system detection Indels frequency statistics
[0096] Indels frequency (%) 293T A375 U2OS NGS 4.51 1.29 0.62 ara-mFabI 9.11 1.08 0.4
[0097] It can be seen from the results that the constructed system has a certain revealing effect even for <1% of target gene Indels mutations, and maintains a high ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com