Moving target detection method based on low-rank and sparse decomposition under dynamic background
A technology of moving target detection and dynamic background, applied to instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer components, etc., can solve problems such as biased estimation, reduced performance of moving target detection, sparseness and spatial discontinuity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0117] Attached below figure 1 The implementation steps of the present invention are further described in detail:
[0118] Step 1: RPCA detection model
[0119] image sequence Where m is the height of the image, n is the width of the image, and s is the number of frames. Reconstruct this sequence of images as Then moving target detection can be modeled as the following RPCA problem:
[0120]
[0121] in, are the low-rank background and sparse foreground matrices respectively, ||·|| * Indicates the nuclear norm, ||·|| 1 for L 1 Norm, λ is a regularization factor that balances low rank and sparsity.
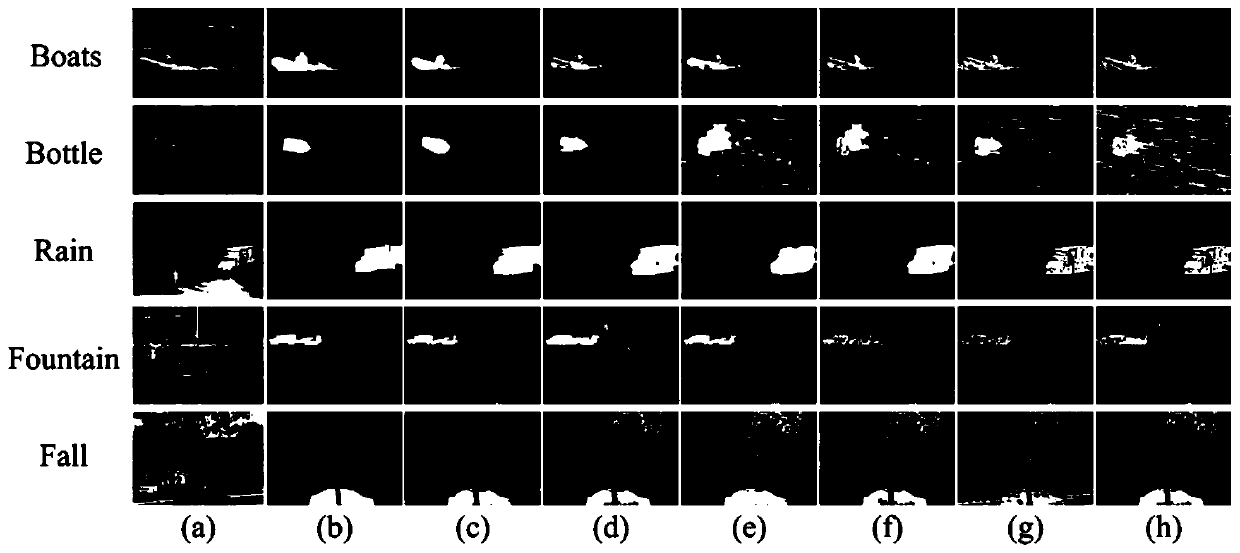
[0122] Although the RPCA model can achieve moving target detection well in some simple scenes, it is difficult for the model to accurately extract foreground targets when the foreground is affected by noise and dynamic background in real video sequences. The Fountain01 and Canoe video sequences containing dynamic backgrounds in the CDnet-2014 dataset are used to ver...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com