Single-round kernel value maintenance method for multilateral updating under dynamic graph
A dynamic graph and core value technology, applied in the direction of instruments, relational databases, database models, etc., can solve the problem of high time overhead, achieve the effects of improving calculation speed, good scalability and stability, and reducing time overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
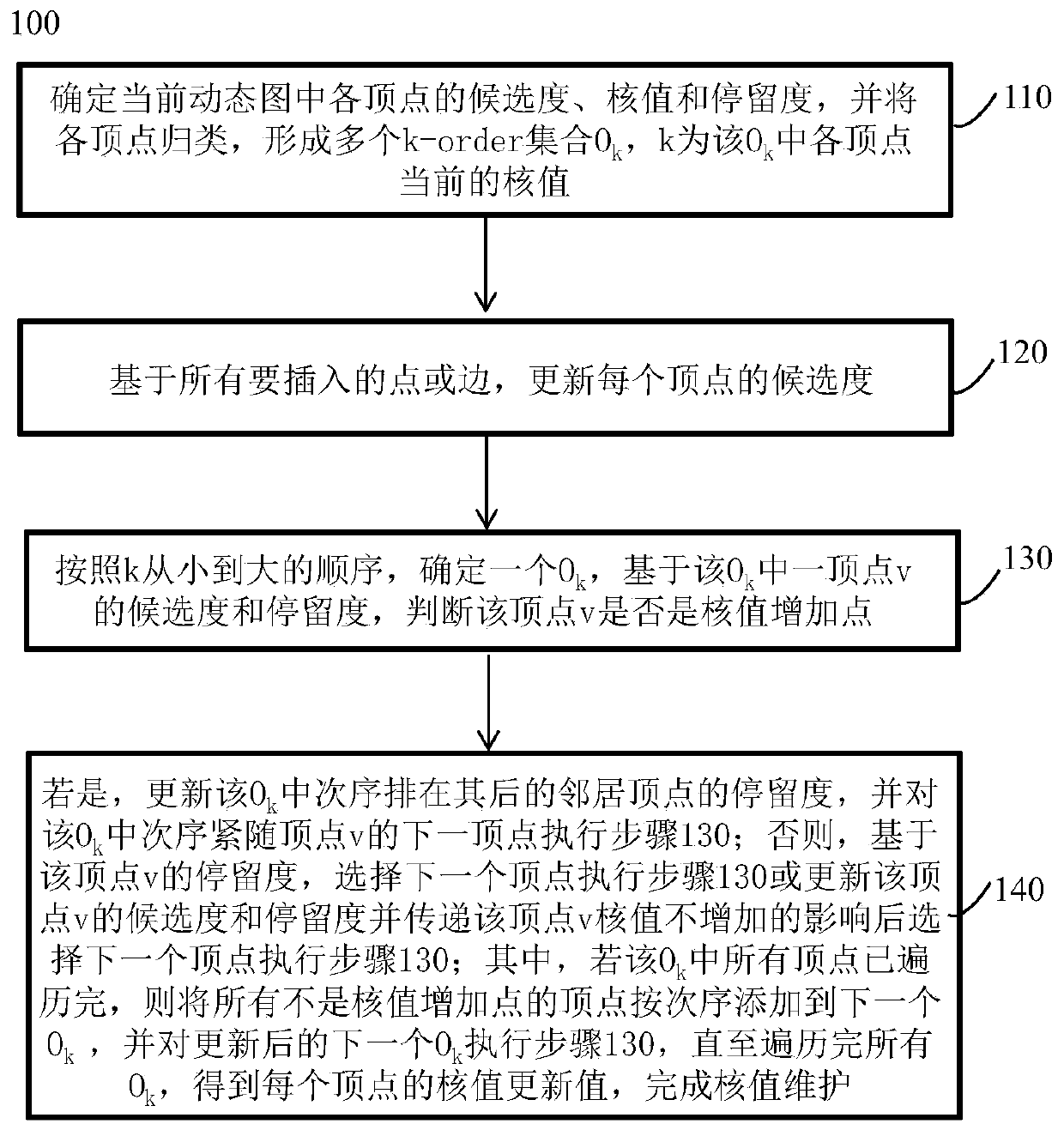
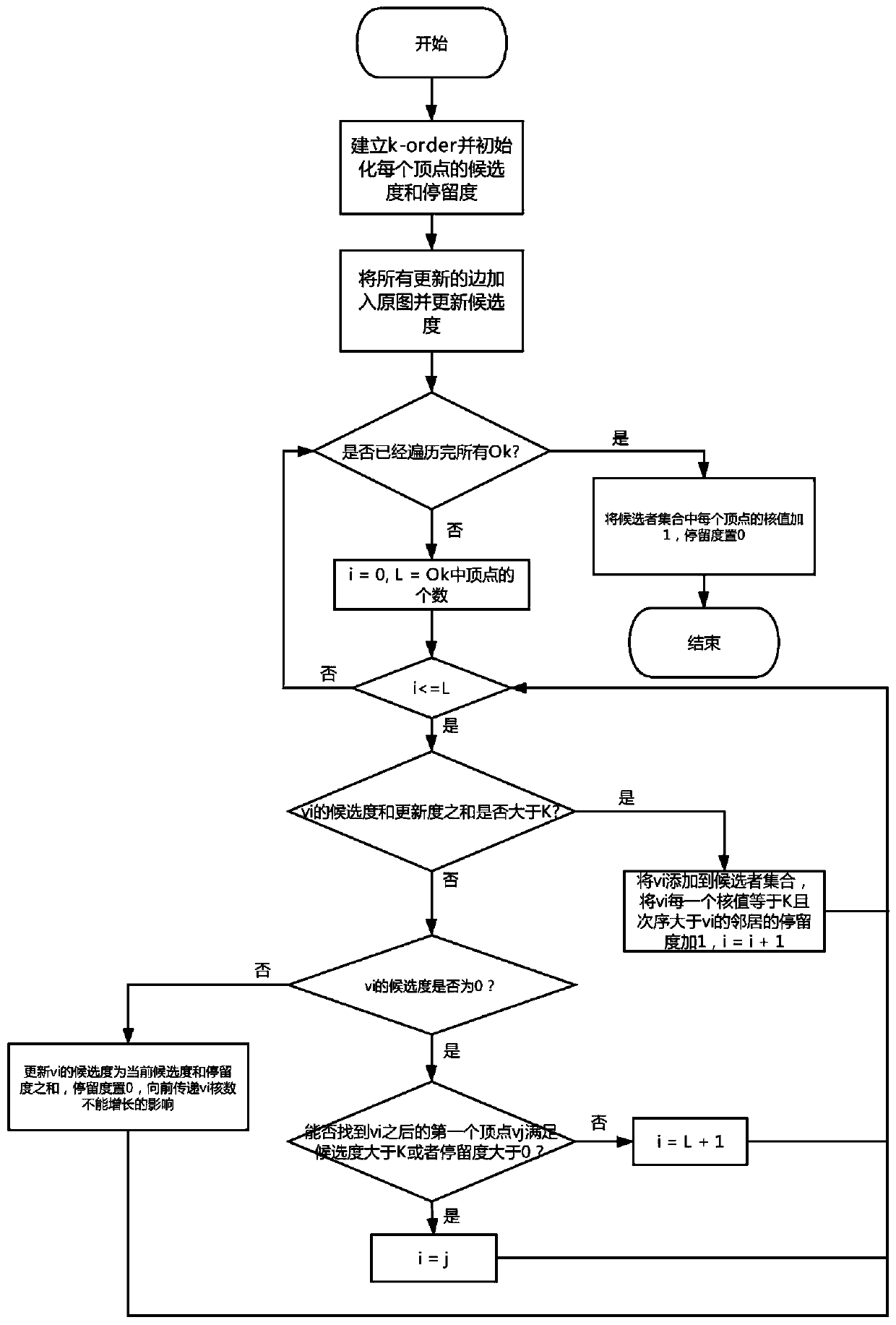
[0053] A single-round core value maintenance method for multi-edge update under a dynamic graph. When inserting a point or an edge under a dynamic graph of a social network, the vertex core value maintenance sub-method 100 is adopted when inserting a point or an edge under a dynamic graph, such as figure 1 As shown, the vertex core value maintenance sub-method includes:
[0054] Step 110, determine the candidate degree, core value and stay degree of each vertex in the current dynamic graph, and classify each vertex to form a plurality of k-order sets. k , k is the O k The current kernel value of each vertex in
[0055] Step 120, based on all points or edges to be inserted, update the candidate degree of each vertex;
[0056] Step 130, according to the order of k from small to large, determine an O k , based on the O k According to the candidate degree and stay degree of a vertex v, judge whether the vertex v is a core value increase point;
[0057] Step 140, if yes, updat...
Embodiment 2
[0105] A single-round core value maintenance method for multi-edge update under a dynamic graph. When deleting a point or an edge under a dynamic graph of a social network, the vertex core value maintenance sub-method 200 is adopted when a point or an edge is deleted under a dynamic graph, such as Figure 5 As shown, the vertex core value maintenance sub-method includes:
[0106] Step 210, determine the superiority number and kernel value of each vertex in the current dynamic graph;
[0107] Step 220, based on all vertices or edges to be deleted, update the degree of excellence of each vertex;
[0108] Step 230, each vertex whose goodness number is smaller than its kernel value is determined as a kernel value reduction point;
[0109] Step 240, based on the kernel value of each kernel value reduction point, determine other missing kernel value reduction points from all vertices;
[0110] Step 250 , update the kernel value and goodness of each kernel value reduction point, an...
Embodiment 3
[0134] A storage medium, in which instructions are stored, and when the computer reads the instructions, the computer is made to execute any sub-method for maintaining vertex core values when inserting points or edges under a dynamic graph as described in Embodiment 1 And / or any sub-method for maintaining vertex core values when deleting points or edges under the dynamic graph as described in the second embodiment.
[0135] The relevant technical solutions are the same as those in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com