Processing method for sample for detecting bloodstream infection pathogenic bacteria
A treatment method and technology for pathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of clinical detection, can solve the problems of detection methodology failing to achieve positive detection and low detection sensitivity, and achieve the effect of ensuring the positive detection rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1: Sample processing method of the present invention
[0034] 1. Bacteria isolation
[0035] Carry out bacterial cell separation according to the reagent in Table 1;
[0036] Table 1
[0037]
[0038]
[0039] Use red blood cell lysate to lyse the patient's plasma sample, the ratio of blood sample to red blood cell lysate is 1:3, incubate at 4 degrees for about 10 minutes, and centrifuge the lysed sample to obtain the precipitate containing bacteria and white blood cells;
[0040] The precipitate was added to the blood cell lysate at a ratio of 1:1, 20-50 microliters of fluorinated oil was added, and the mixture was fully shaken and mixed.
[0041] Add proteinase K to cleavage the protein, incubate at 55°C for 5-10 minutes, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10 minutes, and separate the bacteria.
[0042] The centrifuged sample was carefully removed to obtain the fluorinated oil and the precipitate of the lower layer to obtain an isolated sample.
[0043] 2...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Comparison between the sample processing method of the present invention and the conventional blood culture method
[0053] Escherichia coli artificially mixed with 5-10 CFU into the blood as a simulated sample, respectively processed according to the sample processing method of the present invention (Example 1) and the conventional blood culture method, and then amplified under the same droplet digital PCR conditions , the results are shown in Table 2;
[0054] Table 2
[0055]
[0056] The above experimental results show that under the same trace bacterial concentration conditions, the samples obtained by the sample processing method of the present invention can obtain more positive points after testing, while the conventional blood culture method cannot obtain positive points, indicating that the method of the present invention can obtain more positive points. Ensure the positive detection rate of trace pathogenic bacteria.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3: Comparison of different blood cell lysates
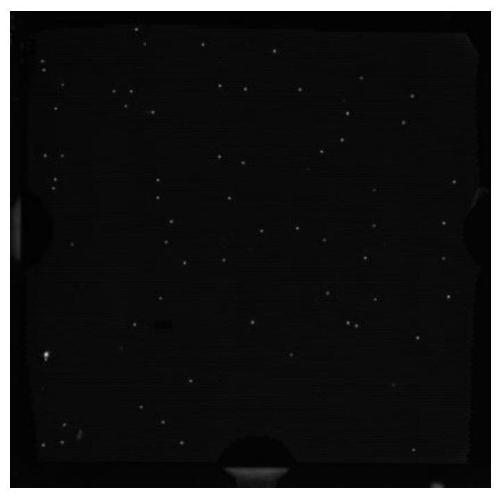
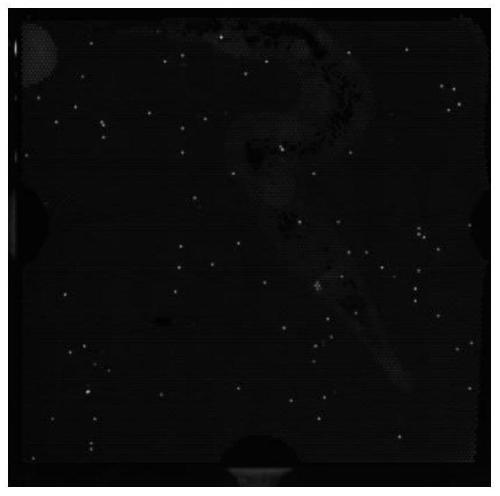
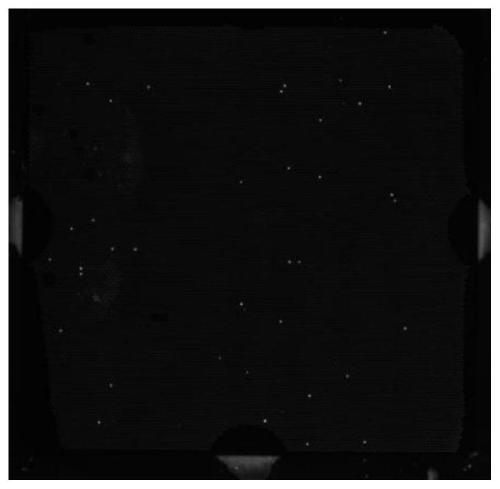
[0058] Escherichia coli (9CFU) mixed in the blood is still used as a simulated sample in the past, and the simulated sample is divided into three parts, and processed with reference to the method of Example 1. The difference is that the blood cell lysate is different, and then under the same droplet digital PCR conditions Amplification, the results are shown in Table 3 and Figure 1-3 ;
[0059] table 3
[0060] group blood cell lysate Number of positive amplification points 1 2.74% sorbitol in RNase-free aqueous solution 61 2 5M guanidine hydrochloride in RNase-free aqueous solution 73 3 5% SDS in RNase-free aqueous solution 34
[0061] Depend on Figure 1-3 As can be seen from the results in Table 3, under the premise of the same trace concentration of pathogenic bacteria, more positive amplification points can be obtained by using guanidine hydrochloride and sorbit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com