Naphthalene-degrading strain applied to sewage treatment and microbial agent and application thereof
A technology for naphthalene-degrading bacteria and sewage treatment, applied in the field of degrading bacteria, can solve the problems of reducing the degradation speed and effect of degrading bacteria, slow screening process of degrading bacteria, and long sewage treatment time, etc., achieving fast treatment speed, easy promotion and use, domestication good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A naphthalene-degrading bacteria used in sewage treatment, naphthalene-degrading bacteria include Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium, Rhodococcus, the cultivation method of naphthalene-degrading bacteria includes the following process steps: s1, screening of degrading bacteria, from oil-polluted seaports Water samples were collected, and degrading bacteria with naphthalene as the sole carbon source were screened out after enrichment and purification; Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium, and Rhodococcus were screened out; Cultivate Rhodococcus strains in phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 4.5-5.8 to achieve primary domestication of the strains, and then cultivate the screened strains under high-concentration naphthalene conditions to achieve secondary domestication of the strains and obtain domestication The final degrading bacteria include Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium and Rhodococcus.
[0024] In this embodiment, the screening process of the s1 strain is as fol...
Embodiment 2
[0027] A naphthalene-degrading bacterial agent used in sewage treatment, the bacterial agent includes: Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium, Rhodococcus, the total number of viable bacteria is 1.5×10 8 -6.0×10 8 cfu / mL. The Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium and Rhodococcus were cultivated by the cultivation method in Example 1.
[0028] In the present embodiment, the number of live bacteria of Bacillus subtilis in the bacterial agent is 0.5×10 8 -2.5×10 8 cfu / mL, the number of viable coryneform bacteria is 1×10 8 -1.5×10 8 cfu / mL, the viable count of Rhodococcus is 0.5×10 8 -2.0×10 8 cfu / mL.
[0029] In the present embodiment, the preparation method of bacterial agent comprises the following steps: the first step, the above-mentioned purified Bacillus subtilis, coryneform bacteria, and Rhodococcus strains are respectively inoculated on the test tube slant medium, and its test tube slant medium is inverted In the incubator, cultivate until colonies grow on the medium to ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] An application of naphthalene-degrading bacteria in sewage treatment. Naphthalene-degrading bacteria are used to biodegrade naphthalene in sewage. The naphthalene-degrading bacteria agent of Example 2 is inoculated into fillers, and the fillers are used in biodegradation tanks to degrade naphthalene in sewage.
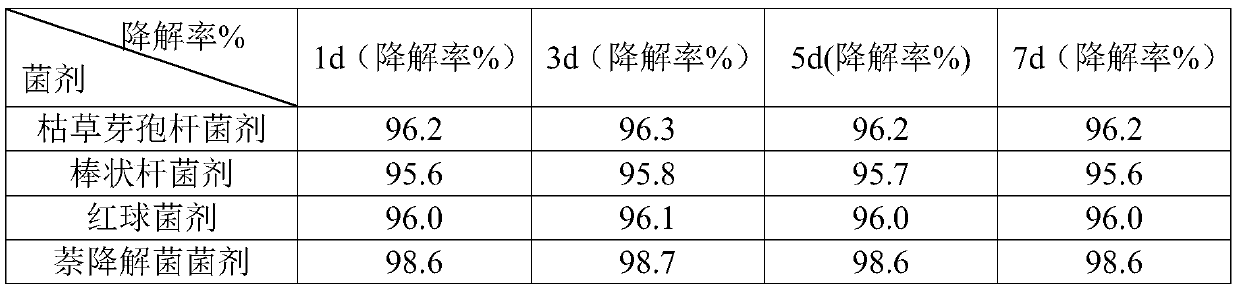
[0032] In this embodiment, the temperature is 25-35 degrees Celsius, the pH is 5.0-5.5, and the naphthalene concentration is 100 mg / L, which is the best degradation condition. The degradation rate of the bacterial agent to naphthalene is as high as 97%-98%. Naphthalene degradation in sewage wastewater shows high application value.
[0033] In this embodiment, the filler is a biodegradable fiber filler, and the preparation process of the fiber filler is as follows: active treatment of recycled waste animal hair to obtain active keratin fibers, and then active treatment of recycled straw to obtain active keratin fibers. Plant fibers, mixing active keratin fibers a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com