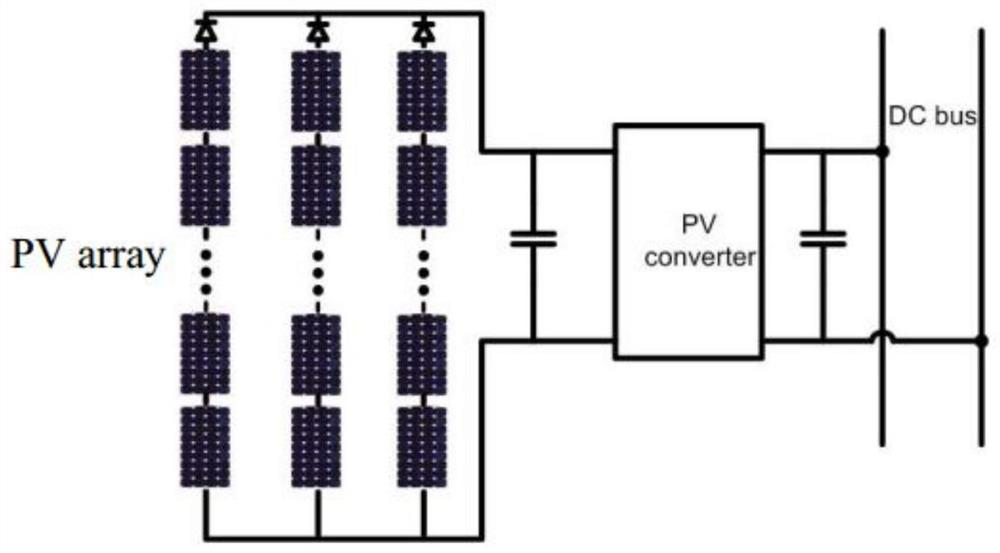
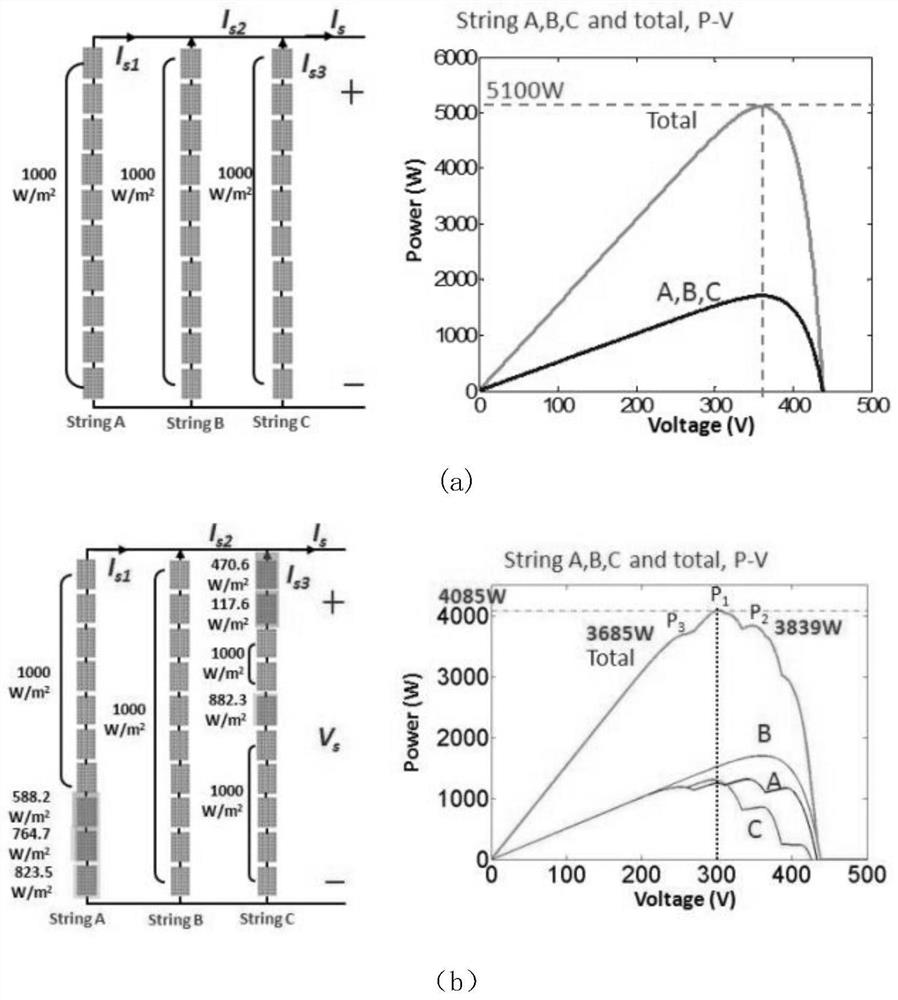
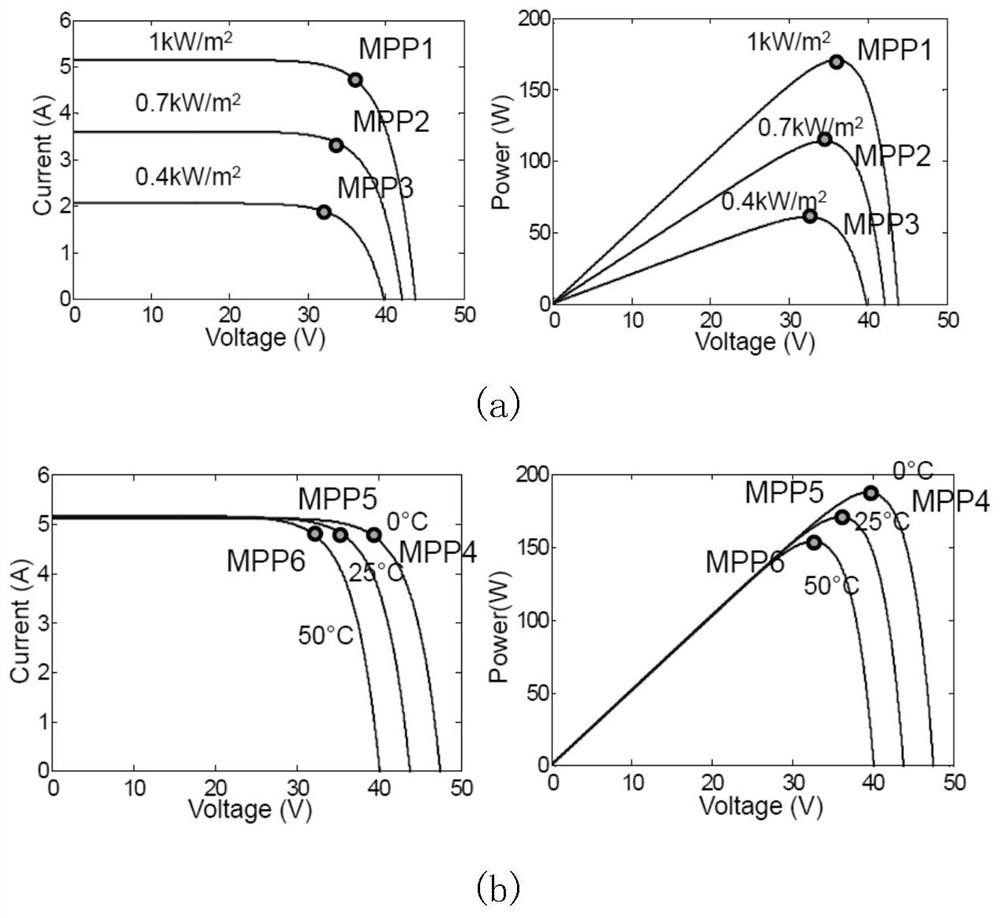
Operation control method and system for a solar inverter of a vehicle-mounted photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system and operation control technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, control/regulation systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to adapt to vehicle-mounted photovoltaic systems, and achieve both tracking speed, improved energy utilization, and output voltage stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0191] 1. For family cars such as Figure 18 As shown, the areas where photovoltaic cells can be installed are divided into three groups according to the different illumination conditions on the surface. Among them, group a has the largest area. Assuming STC, the installed photovoltaic cells have an open-circuit voltage of 109V and a short-circuit current of 6.1A. The areas of groups b and c are the same, assuming that the installed photovoltaic cells have an open-circuit voltage of 70V and a short-circuit current of 5.08A.
[0192] 2. According to formula (10), using the Newton iteration method, after four iterations, calculate the equivalent series internal resistance RSNA=0.427Ω of the photovoltaic cells of group a under the condition of STC when the photovoltaic cells leave the factory, and the equivalent series of photovoltaic cells of group b and c are equivalent to 0.427Ω. Series internal resistance RSNB, C=0.279Ω.
[0193] 3. Suppose the acceptable time extension coe...
Embodiment 2
[0206] 1. For urban buses, the roof, left side, right side, front and rear of the vehicle that can be installed with photovoltaic cells are divided into 5 groups a, b, c, d, and e according to the different light conditions on the surface. In the case of STC, group a has the largest area, assuming that the installed photovoltaic cells have an open-circuit voltage of 200V and a short-circuit current of 6A. The areas of group b and group c are the same, assuming that the installed photovoltaic cells have an open-circuit voltage of 100V and a short-circuit current of 5A. The open-circuit voltage of group d is 40V, and the short-circuit current is 4A. The open-circuit voltage of group e is 30V, and the short-circuit current is 4A.
[0207] 2 is the same as the first embodiment.
[0208] 3. Set the acceptable time extension factor γ as 190%, the first-level reference voltage step size Δλ(k) as 5V, and the proportionality factor Taking 0.75, the value of the adjustment factor Ca...
Embodiment 3
[0216] For such as Figure 21 For the home photovoltaic system shown, the feasible implementation steps are:
[0217] 1. According to the different lighting conditions on the surface, the two sides of the roof are divided into two groups. Because the roof area is much larger than that of a single photovoltaic cell, two sets of photovoltaic cell groups are formed by cascading multiple sets of photovoltaic cells.
[0218] 2 to 9 are the same as in the first embodiment, and the maximum power point tracking of the home photovoltaic system can still be performed to maximize the power output efficiency.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com