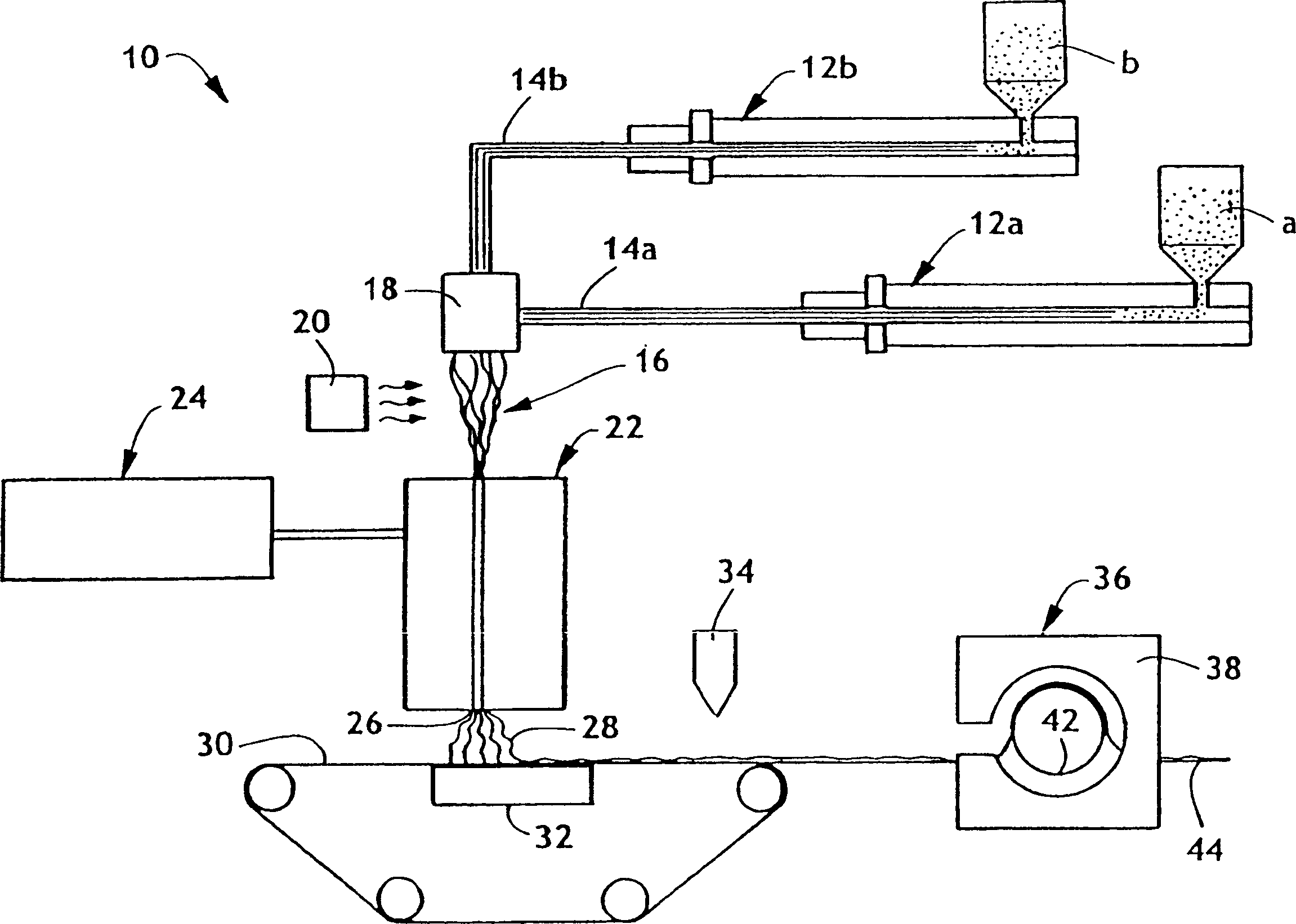
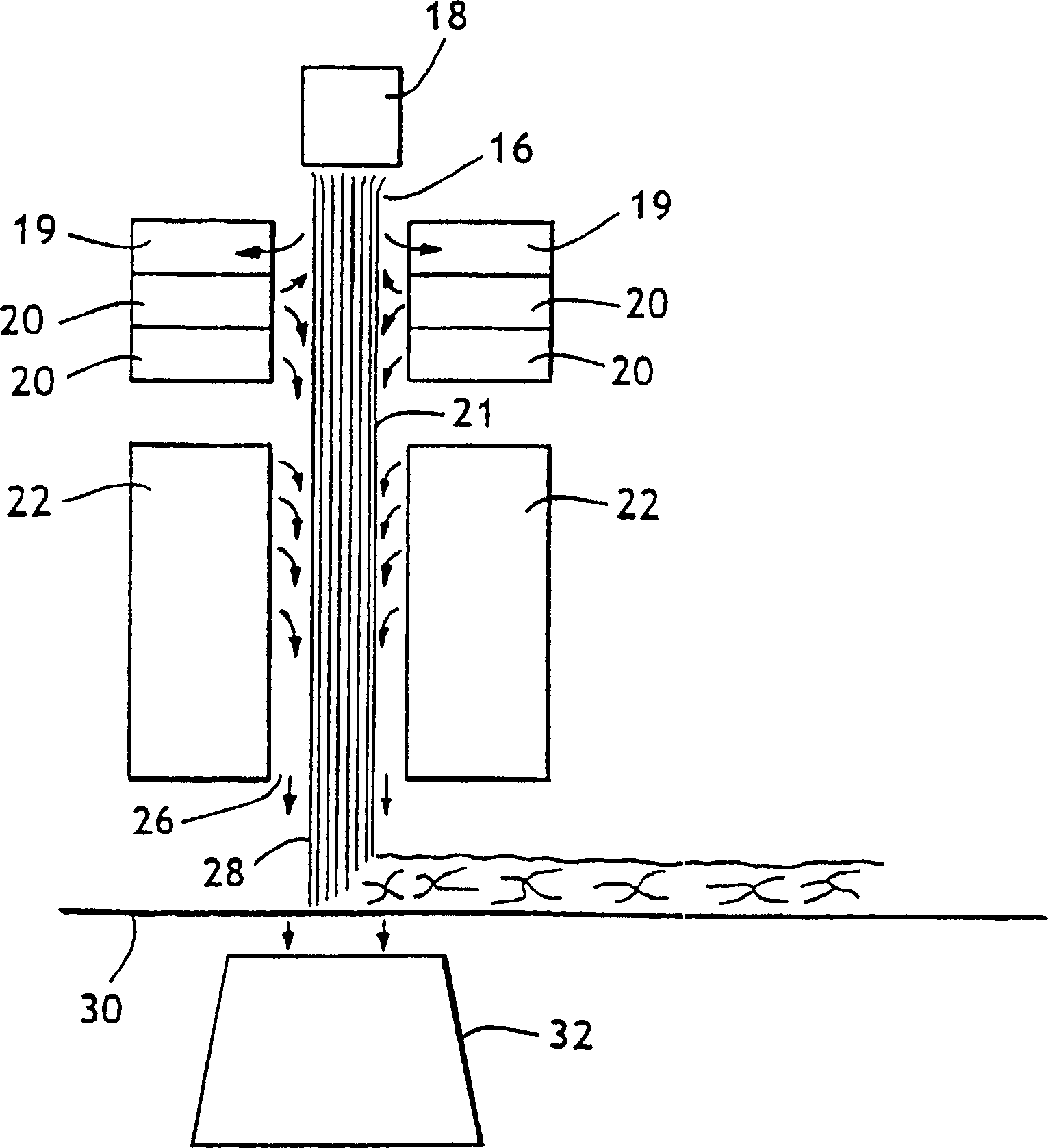
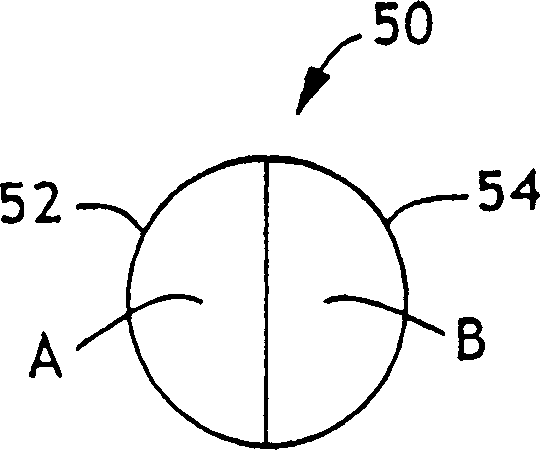
Crimped multicomponent fibers and methods of making same
A technology of multi-component fibers and manufacturing methods, applied in fiber processing, melt spinning, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve the problems of increasing basic investment production costs, bulkiness, basis weight and overall uniformity fluctuations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0061] Example 1: Component 1 comprises a conventional propylene polymer (sold by Exxon Chemical Company under the trade name ESCORENE and under the designation Exxon-3445, which has an MFR equal to 35, a polydispersity index of 3, and a density equal to 0.9 g / cm 3 , flexural modulus 220,000psi, yield tension 5000psi) and 2wt% titanium dioxide. The second component comprised a metallocene catalyzed propylene polymer (sold by Exxon Chemical Company under the tradename ACHIEVE and under the designation Exxon-3854, having a melt flow index equal to 25 and a polydispersity index of 2). The formed spunbond web contains helically crimped fibers.
example 2
[0062] Example 2: Component 1 comprised a conventional propylene polymer as in Example 1 and 2 wt% titanium dioxide. The second component comprises an amorphous propylene / ethylene copolymer (sold by Huntsman under the trade name REXFLEX FLEXIBLE POLYOLEFINS and under the designation W201, with an MFR equal to 19, a tensile modulus of 6, and a density of 0.88 g / cm 3 ). The formed spunbond web comprises helically crimped fibers with excellent "stretch and recover" properties.
example 3
[0063] Example 3: Component 1 comprised a conventional propylene polymer as in Example 1 and 2 wt% titanium dioxide. The second component comprises an amorphous propylene homopolymer (sold by Huntsman under the trade name REXFLEXFLEXIBLE POLYOLEFINS and under the designation W104, with an MFR equal to 30, a tensile modulus of 14, and a density of 0.88 g / cm 3 ). The formed spunbond web contains helically crimped fibers with excellent elongation and recovery properties.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flexural modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| enthalpy of fusion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com