Two-dimensional blade modeling method for directly controlling channel
A technology for controlling channels and blades, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical and digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as poor effectiveness, low design efficiency, and poor channel shape control capabilities, to improve flexibility and design. The effect of efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
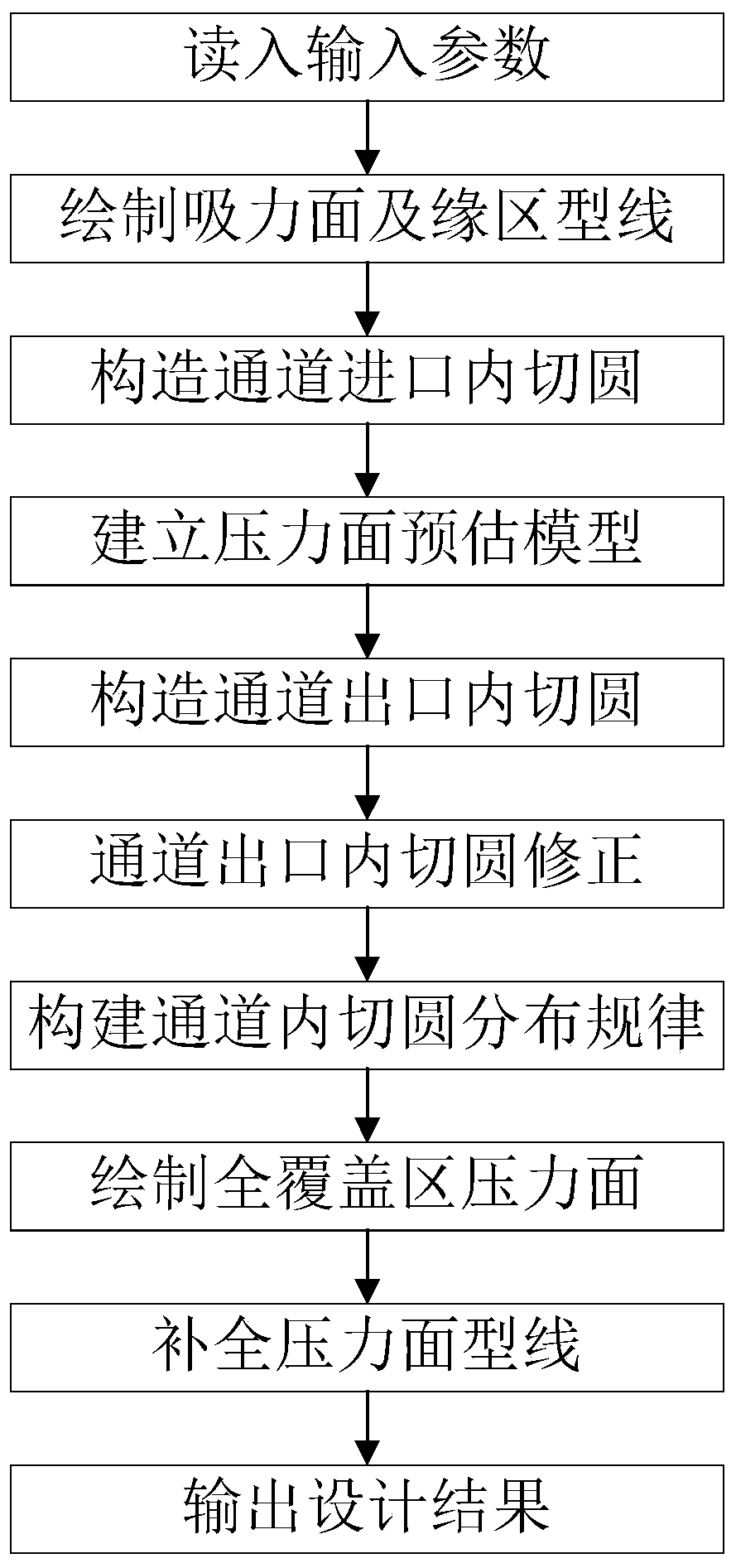
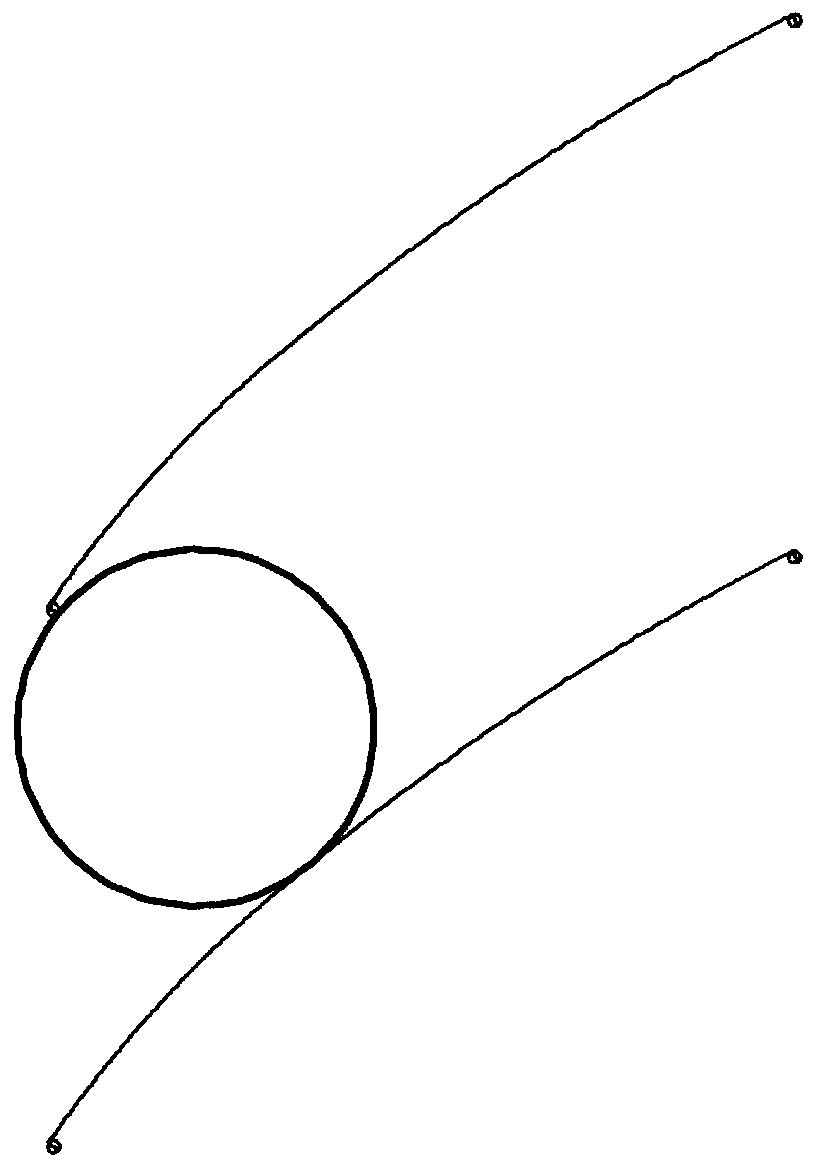
[0052] This example describes the specific implementation of a two-dimensional blade modeling method using a direct control channel according to the present invention.
[0053] The application scenario of this embodiment is that in an axial-flow aeroengine whose design state is subsonic cruising, the two-dimensional span section design at the root of the first-stage moving blade of the compressor is designed, the inlet Mach number is 0.85, and the pressure ratio is 1.3. The original blade shape adopts the conventional design method of double-arc middle arc + thickness distribution, and does not pay attention to the shape of the channel between the blades and the flow performance of the channel. Multiple geometric shapes are required to obtain a cross-sectional shape with better aerodynamic performance. In this embodiment, according to the subsonic flow condition, the spanwise position of the blade and the input parameters, the airfoil is reconstructed from the perspective of di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com