Fast magnetic resonance imaging method based on residual U-net convolutional neural network
A convolutional neural network, magnetic resonance imaging technology, applied in biological neural network model, neural architecture, 2D image generation, etc. Convergence speed and other issues to achieve the effect of reducing overfitting, steadily decreasing the learning rate, and preventing the training from ending prematurely
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
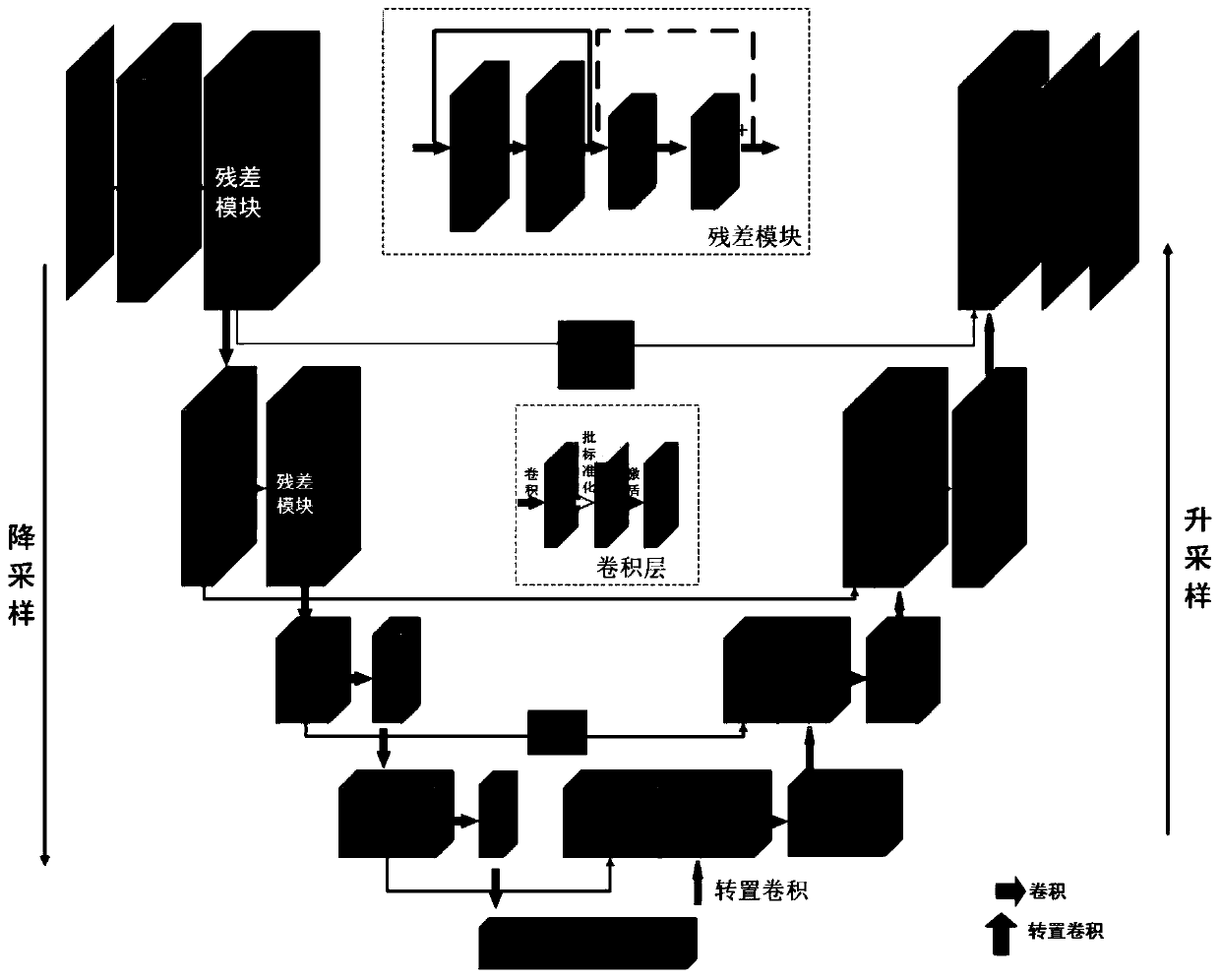
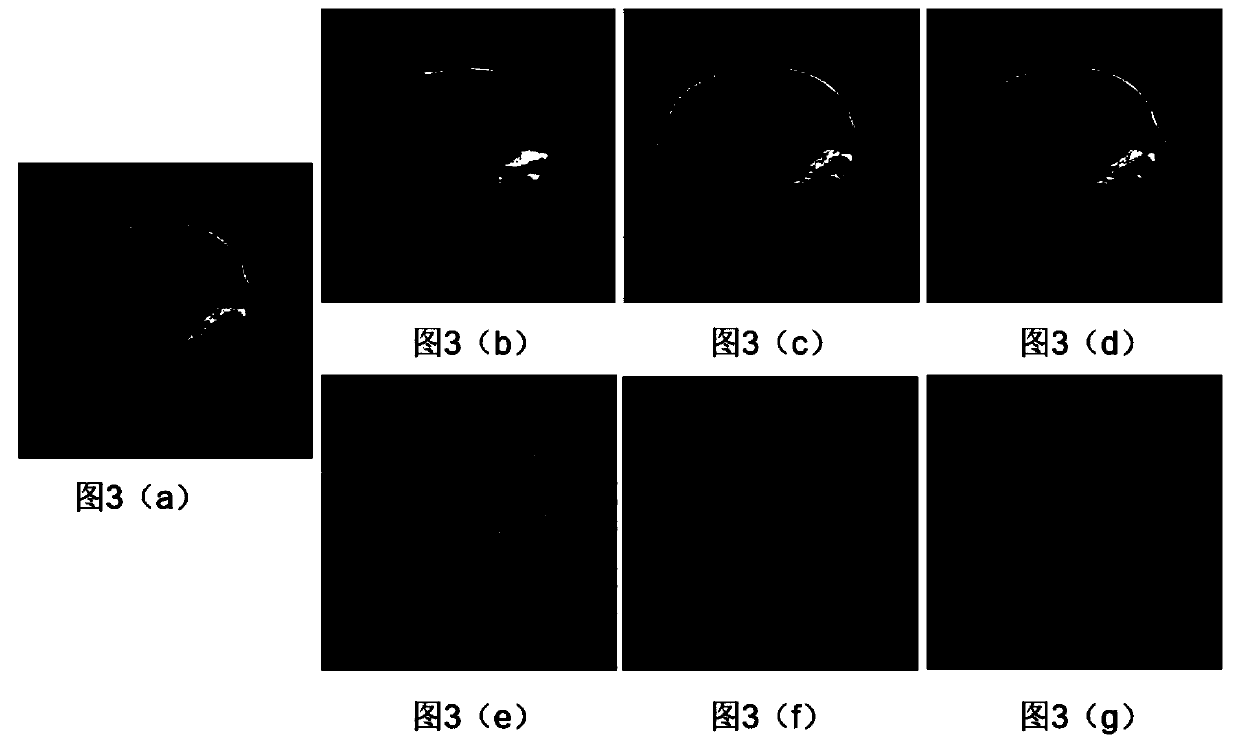
[0089] The invention comprises three steps: preparation of training data, training based on residual U-net convolutional neural network, and image reconstruction based on residual U-net convolutional neural network.
[0090] Step 1: Preparation of training data
[0091] The preparation of training data consists of three steps: full sampling data acquisition, simulated undersampling, and zero-fill reconstruction.
[0092] Step 1-1: Full sample data acquisition
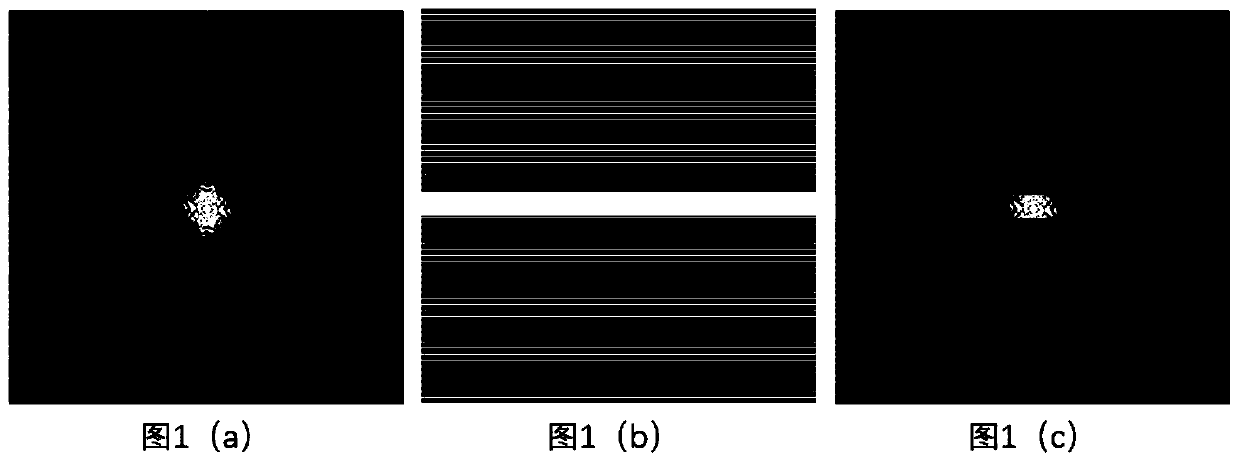
[0093] Fully sampled k-space data with S r (k x ,k y ) means (such as figure 1 (a) shown), where, k x Indicates the position in the direction of k spatial frequency encoding FE (Frequency Encoding), k y Indicates the position in the PE (Phase Encoding) direction, and the reference image I is obtained through the inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) ref (x,y):
[0094] I ref (x,y)=IDFT(S r (k x ,k y )) [1]
[0095] Step 1-2: Simulate undersampling
[0096] Regularly simulate undersampling of k-space d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com