Cascade type supercooling method ice storage system
A cascading, ice-storage technology, applied in air-conditioning systems, refrigerators, heating methods, etc., can solve the problems of slow melting speed, low heat transfer efficiency, low energy efficiency ratio, etc., to eliminate ice crystals, ensure stability, The effect of preventing ice blockage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
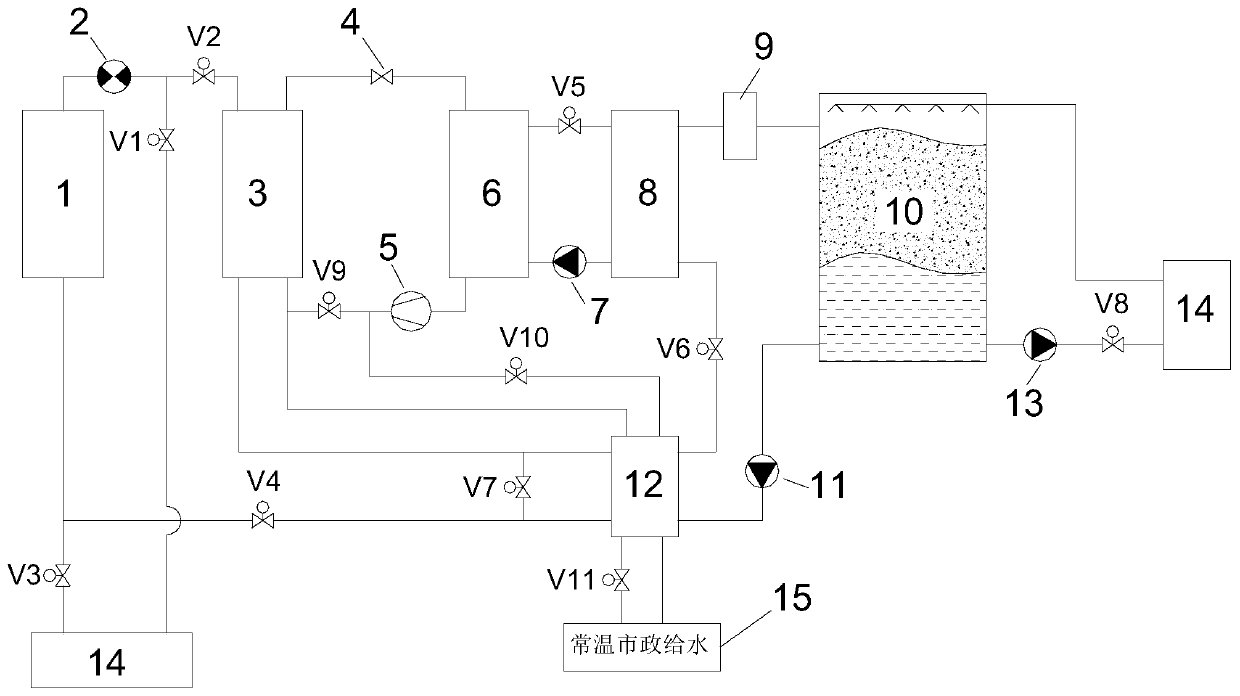
[0032] Such as figure 2 As shown, the two-way pump 2 rotates forward, the upper end of the chiller 1 enters water, and the lower end outputs water. The preheating of the heat exchanger 12 uses 7°C chilled water directly from the chiller 1 .
[0033] During the day, the chiller is used for cooling alone: open valves V1 and V3, close valves V2 and V4, the 7°C chilled water flowing out from the lower end of the chiller 1 enters the terminal equipment 14 through the valve V3 for heat exchange, and the 12°C chilled water flowing out of the terminal equipment 14 is refrigerated The return water is pumped back to the chiller 1 by the bidirectional pump 2 through the valve V1 to complete the cooling cycle.
[0034]Ice storage at night: Turn on the low-temperature condenser 3, throttle valve 4, compressor 5, and evaporator 6, and the refrigerant liquid evaporates in the evaporator 6, taking away the -0.5°C brine pumped by the brine pump 7 of heat, cooling the brine to an outlet tem...
Embodiment 2
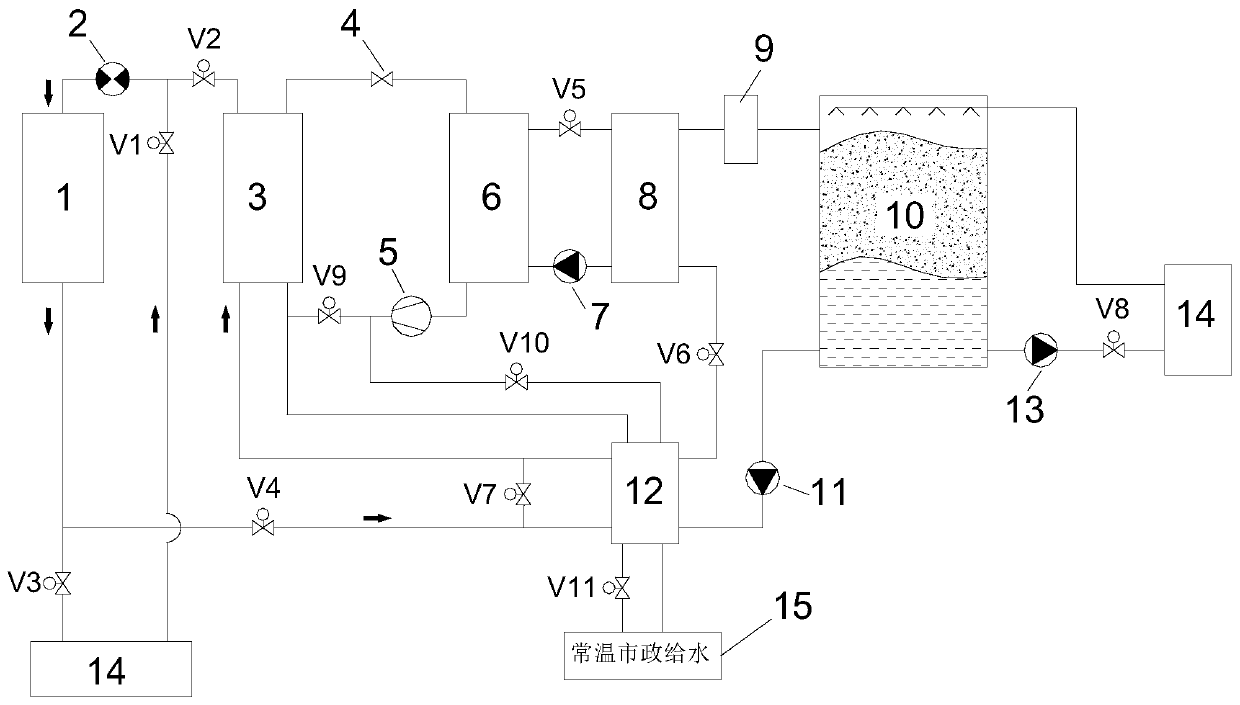
[0039] Such as image 3 As shown, the two-way pump 2 is reversed, water is discharged from the upper end of the chiller 1, and water is fed from the lower end. The preheating of the heat exchanger 12 uses the 7°C chilled water of the chiller 1 that is heated by the low-temperature condenser 3 and returns to the chilled water.
[0040] The working process of independent cooling by the water chiller during the day, independent cooling by the ice storage tank during the day, and joint cooling by the chiller and the ice storage tank during the day is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0041] Ice storage at night: Different from the first embodiment, the 7°C chilled water flowing out from the chiller 1 cools down the low-temperature condenser 3 first. Specifically, the 7°C chilled water flowing out from the upper end of the chiller 1 enters the low-temperature condenser 3 through the valve V2 to cool down the high-temperature refrigerant steam, and t...
Embodiment 3
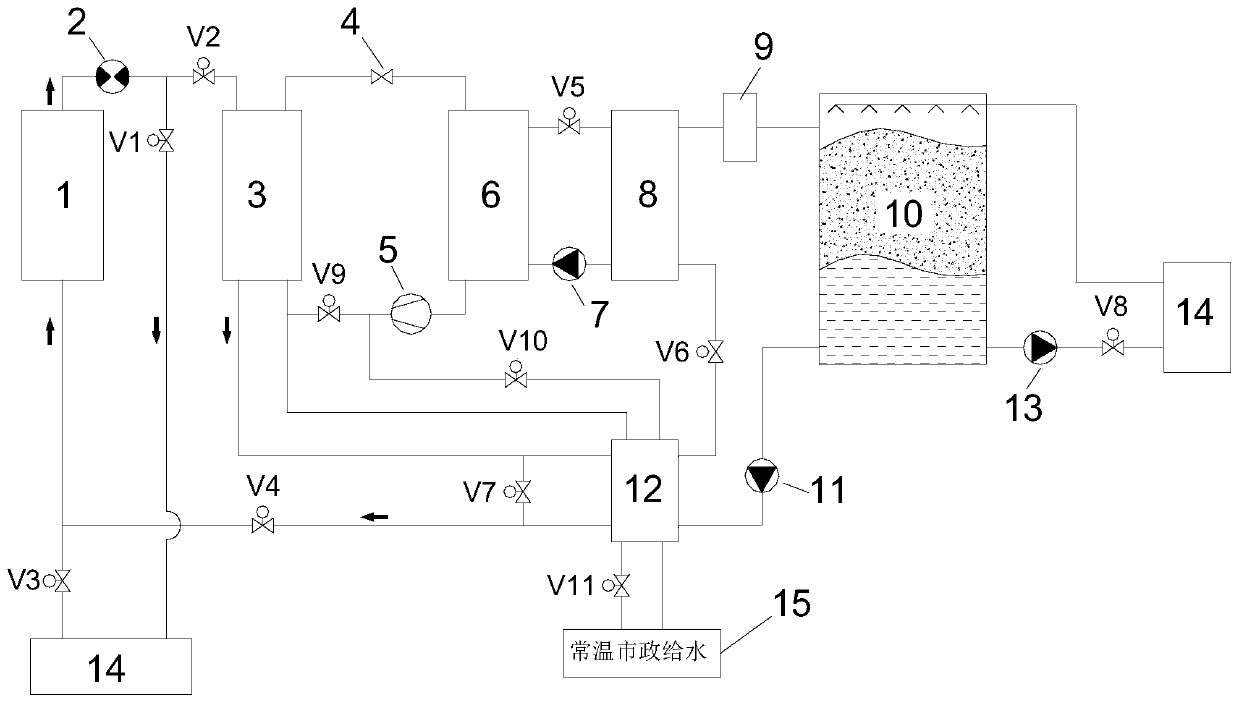
[0044] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference from the first and second embodiments is that the preheating of the heat exchanger 12 uses the high-temperature refrigerant vapor split from the outlet of the compressor 5 .
[0045] The working process of independent cooling by the water chiller during the day, independent cooling by the ice storage tank during the day, and joint cooling by the chiller and the ice storage tank during the day is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0046] Ice storage at night: The two-way pump 2 can be reversed. The 7°C chilled water flowing out of the chiller 1 enters the low-temperature condenser 3 to cool down the refrigerant steam, and then flows back to the chiller 1 through the valve V7 to complete the cycle. A part of the high-temperature refrigerant steam coming out of the compressor 5 enters the second heat side of the heat exchanger 12 through the valve V10 to exchange heat with the low-temperature water,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com