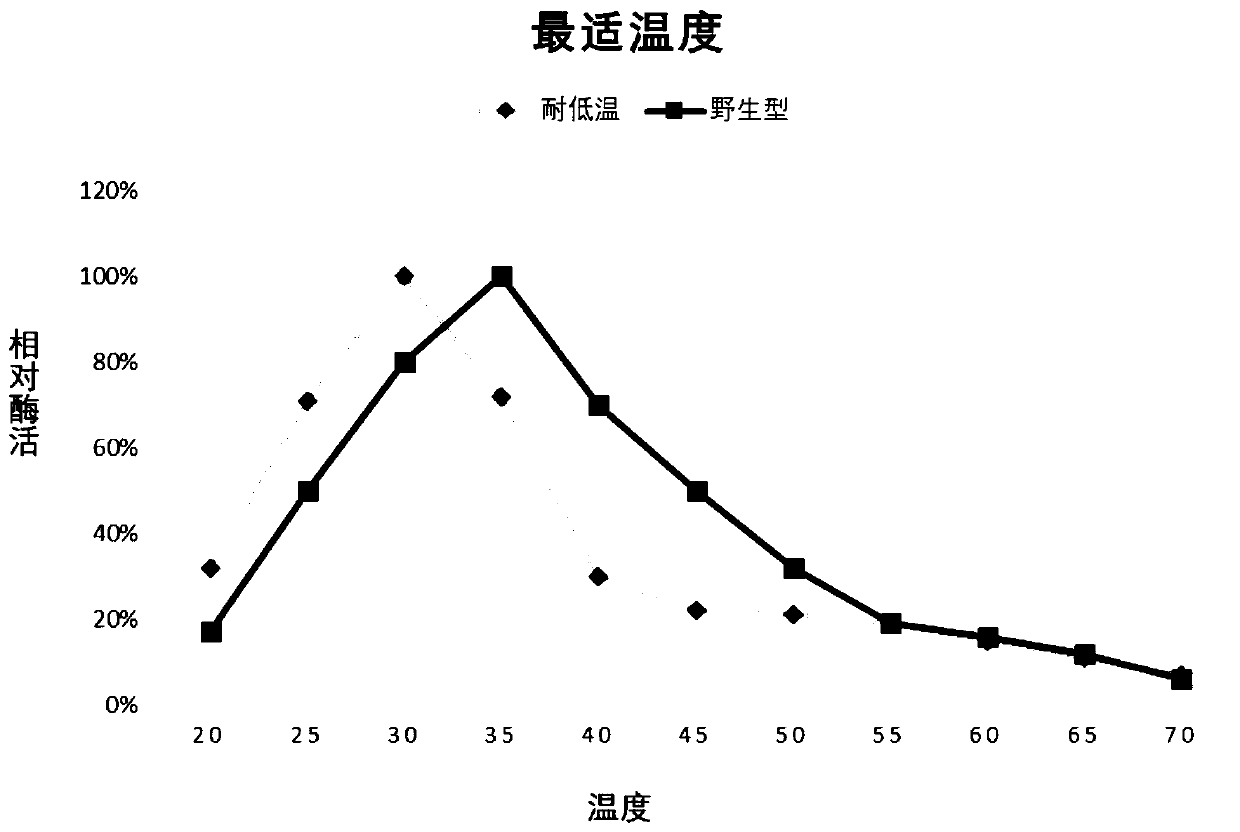
Chitinase low temperature resistant mutant and application thereof
A technology of chitinase and chitin, which is applied in the direction of application, enzyme, and introduction of foreign genetic material by using vectors, etc., can solve the problem of not many low-temperature chitinases, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023]The gene cloning of embodiment 1 wild-type chitinase
[0024] The inventors have discovered that a chitinase screened from the amino acid sequence of Pseudoalteromonas sp. as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 is disclosed in the prior art, and its encoded nucleotide is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. ID NO: 2, expressed and prepared in Escherichia coli. In short, the gene was entrusted to Shanghai Jierui Biotechnology Co., Ltd. to artificially synthesize, then ligated into pET-28(+) vector (New England Biolabs) between the restriction sites of EcoR I and HindIII, and transformed into the large intestine Bacillus DH5α was screened on an LB plate containing 50 mg / L ampicillin. The expression vector contained in the screened positive bacteria was named pET-chi, and the plasmid was extracted and identified correctly by sequencing.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2 mutation screening
[0026] In order to further improve the low temperature resistance of the above-mentioned chitinase (the amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO: 1), the applicant used the recombinant plasmid pET-chi constructed in Example 1 as a template to design random mutation primers respectively for error-prone PCR, carried out multi-point random mutations on the target gene, and found that some mutations had no effect on its low temperature resistance, some mutations even made the low temperature resistance worse, and some mutations, although they could improve heat resistance, were not affected by the mutation. The scope of application of pH narrowed, and none of them met the requirements. In the end, the applicant obtained a combination of mutation sites that can not only significantly improve the low temperature performance, but also expand the scope of application under acidic conditions: R501L, Y555W, F635P, A673S, E689T; specifically, the Arg muta...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3 Expression Purification
[0030] Competent cells of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) were prepared by methods known in the art, and the wild-type expression vectors constructed in Example 1 and Example 2 and the expression vectors of mutants were respectively transformed into competent cells by the heat shock method, and positive screening results were obtained. The clones were verified by PCR and sequencing for later use.
[0031] Pick up the positive bacteria with the inoculation needle and inoculate them in 5mL LB medium, culture them at 30°C and 200r / min for 12h, then inoculate them in 400mL LB containing 50ug / mL kanamycin with 2% (V / V) inoculum. culture medium at 30°C, 200r / min for 8h. When the bacterial density OD600 reached 0.7, 0.5 mM IPTG was added to induce expression; 16 ° C 170 rpm shaking culture overnight.
[0032] Bacteria were collected by centrifugation, washed with PBS, sterilized by ultrasonication in ice, and the supernatant was collected by c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com