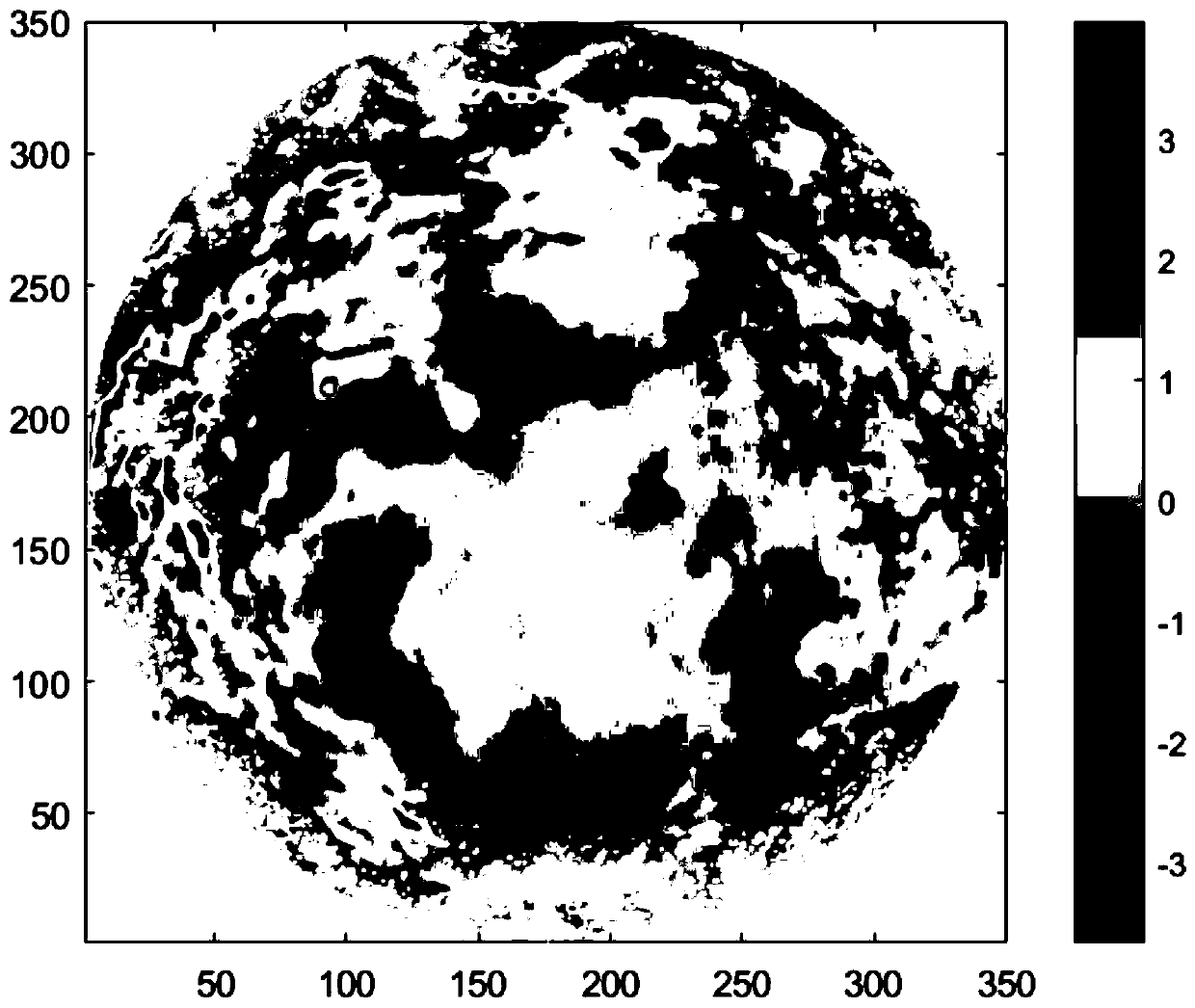
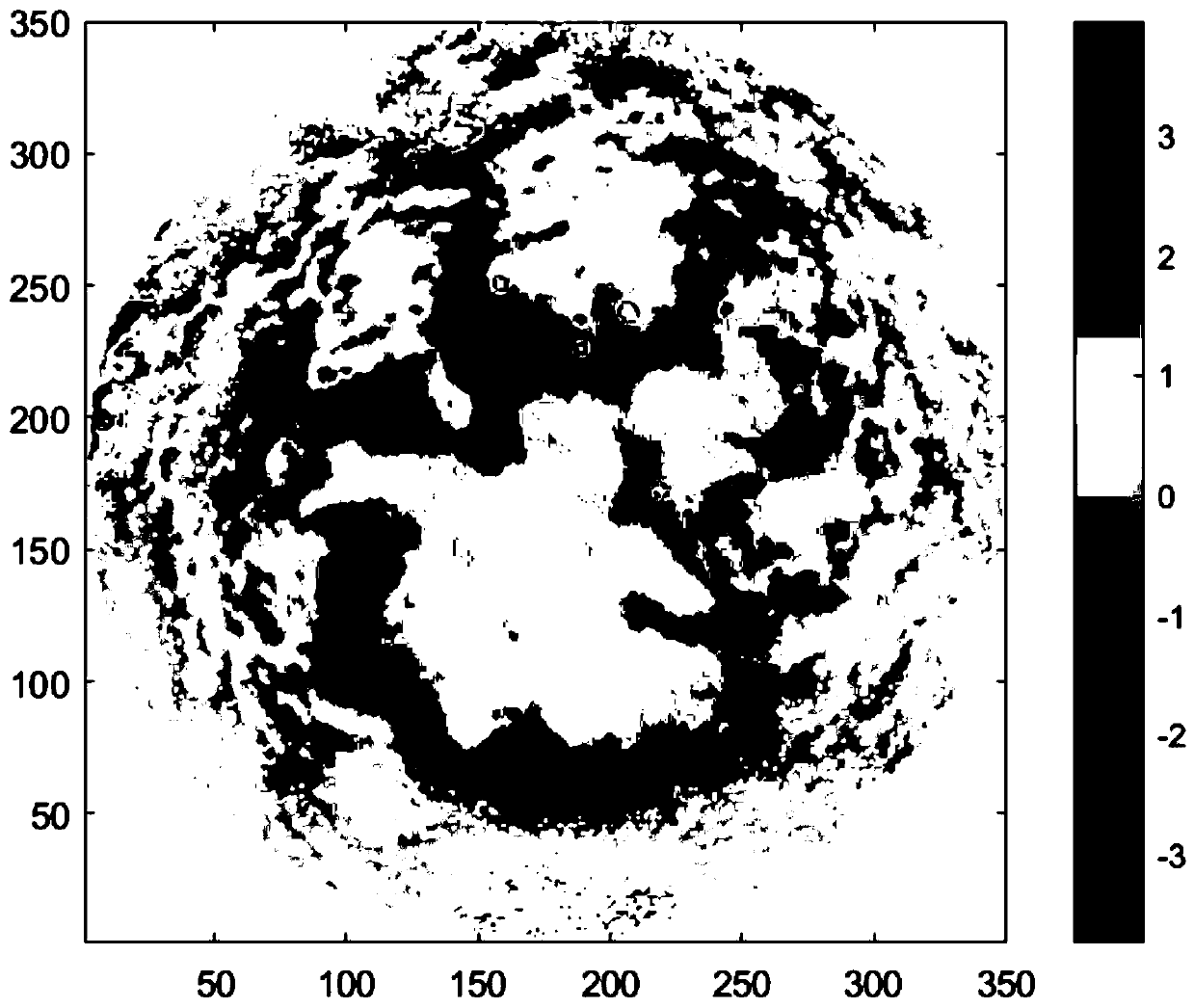
A two-dimensional normalized Gaussian filtering method for three-dimensional surface topography feature extraction
A topographic feature and three-dimensional surface technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problem of low accuracy of topographic feature recognition and achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] Specific implementation manner 1: The specific process of the two-dimensional normalized Gaussian filtering method for extracting three-dimensional surface topography features in this embodiment is:
[0023] Step 1. Set the input of the filter as the three-dimensional image f(u, v) and the cutting length λ c , Based on the cut length λ of the three-dimensional topographic features of the image to be extracted c , Calculate the Gaussian weight function g(x,y) of the two-dimensional Gaussian filter;
[0024] Step 2: Establish the template function bf(u, v) of the three-dimensional image shape f(u, v) to avoid the edge distortion problem of the filtering result;
[0025] Step 3: Make the Gaussian weight function g(x, y) of the two-dimensional Gaussian filter move point by point on the three-dimensional shape of the input image f(u, v), and calculate the normalized filter when moving to (u, v) As a result t(u, v), after moving all the positions, the matrix of normalized filtering ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one in that in the step one, the input of the filter is assumed to be the three-dimensional image f(u, v) and the cut length λ c , Based on the cut length λ of the three-dimensional topographic features of the image to be extracted c , Calculate the Gaussian weight function g(x, y) of the two-dimensional Gaussian filter, the specific process is:
[0027] The Gaussian weight function g(x, y) of the two-dimensional Gaussian filter is expressed as:
[0028]
[0029] Where α is the Gaussian filter constant, According to the Gaussian distribution, the range of (x, y) is The number of matrix points after the value is recorded as N x With N y ; (X, y) is the point of the Gaussian weight function.
[0030] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0031] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is different from specific embodiments one or two in that in the second step, the template function bf(u, v) of the three-dimensional image f(u, v) is established to avoid the edge of the filtering result The distortion problem, the specific process is:
[0032]
[0033] The boundary is (u, v) is the topographic feature point to be filtered.
[0034] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com