Slope stability limit balance calculation method based on inter-strip normal force distribution characteristics
A technology of limit balance and calculation method, which is applied in the field foundation soil survey, excavation, foundation structure engineering, etc., to achieve the effect of improving project economic benefits, improving project safety, and saving construction costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: A method for calculating the limit equilibrium of slope stability based on the distribution characteristics of the normal force between strips, the specific steps are as follows:
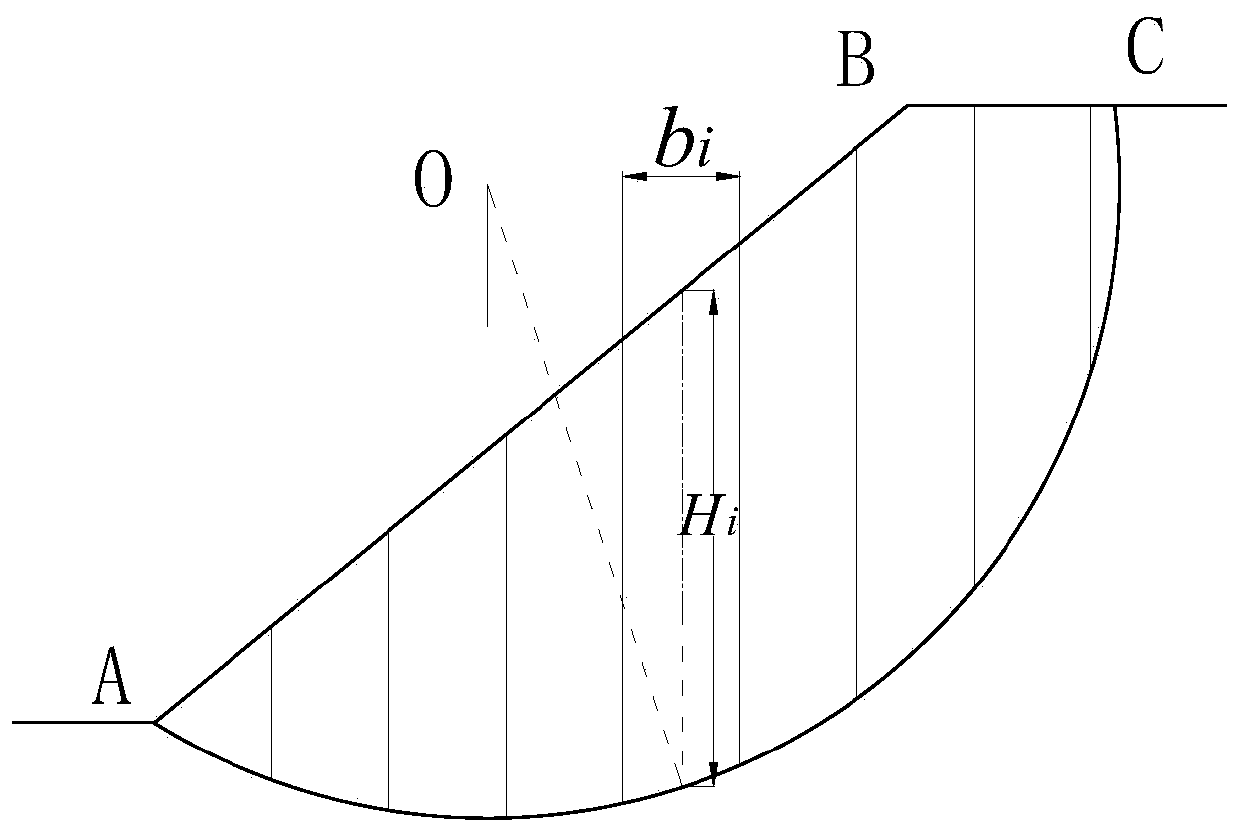
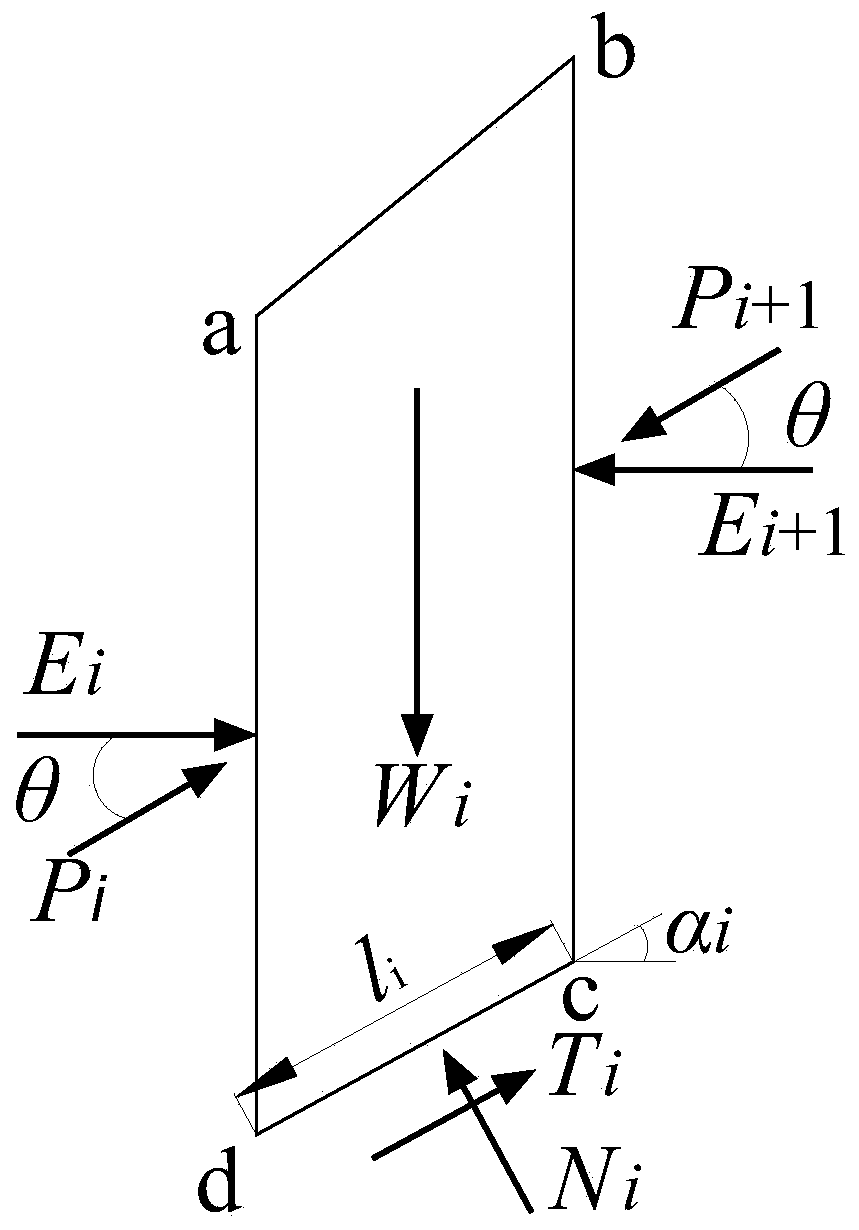
[0045](1) For a given sliding body, it is vertically divided into several bars of equal width (see figure 1 ), in the traditional limit equilibrium Spencer method, the force diagram of the i-th block in the Spencer method calculation model is shown in figure 2 , assuming that the forces between the blocks are parallel to each other, that is, θ i = θ is a constant, the resultant force △P between the bars on both sides of the bar, that is, the difference between the bars on both sides of the bar, is:
[0046]
[0047] (2) When the sliding surface is a circular-arc sliding surface, for the entire slope, the sum of the forces between each block is 0, that is:
[0048] ∑(P i+1 -P i )=0 (2)
[0049] (3) In the process of solving the bar moment balance, the resultant force △P ...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Embodiment 2: A method for calculating the limit equilibrium of slope stability based on the distribution characteristics of the normal force between strips, the specific steps are as follows:
[0074] (1) For a given sliding body, it is vertically divided into several bars of equal width (see figure 1 ), in the traditional limit equilibrium Spencer method, the force diagram of the i-th block in the Spencer method calculation model is shown in figure 2 , assuming that the forces between the blocks are parallel to each other, that is, θ i = θ is a constant, the resultant force △P between the bars on both sides of the bar, that is, the difference between the bars on both sides of the bar, is:
[0075]
[0076] (2) When the sliding surface is a circular-arc sliding surface, for the entire slope, the sum of the forces between each block is 0, that is:
[0077] ∑(P i+1 -P i )=0 (2)
[0078] (3) In the process of solving the bar moment balance, the resultant force △P...
Embodiment 3
[0087]Embodiment 3: A method for calculating the limit equilibrium of slope stability based on the distribution characteristics of the normal force between strips, the specific steps are as follows:
[0088] (1) For a given sliding body, it is vertically divided into several bars of equal width (see figure 1 ), in the traditional limit equilibrium Spencer method, the force diagram of the i-th block in the Spencer method calculation model is shown in figure 2 , assuming that the forces between the blocks are parallel to each other, that is, θ i = θ is a constant, the resultant force △P between the bars on both sides of the bar, that is, the difference between the bars on both sides of the bar, is:
[0089]
[0090] (2) When the sliding surface is a circular-arc sliding surface, for the entire slope, the sum of the forces between each block is 0, that is:
[0091] ∑(P i+1 -P i )=0 (2)
[0092] (3) In the process of solving the bar moment balance, the resultant force △P ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com