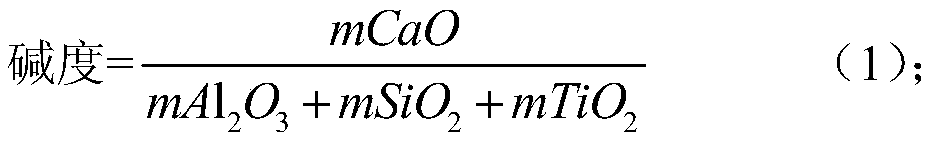Method for recovering iron and titanium from high-iron high-titanium red mud and carrying out direct cementation
A technology for recovering iron and high titanium, which is applied in the field of high-speed iron and high-titanium red mud recovery of iron and titanium and direct cementation, which can solve the problems of poor income, long processing process, and unutilized tailings.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
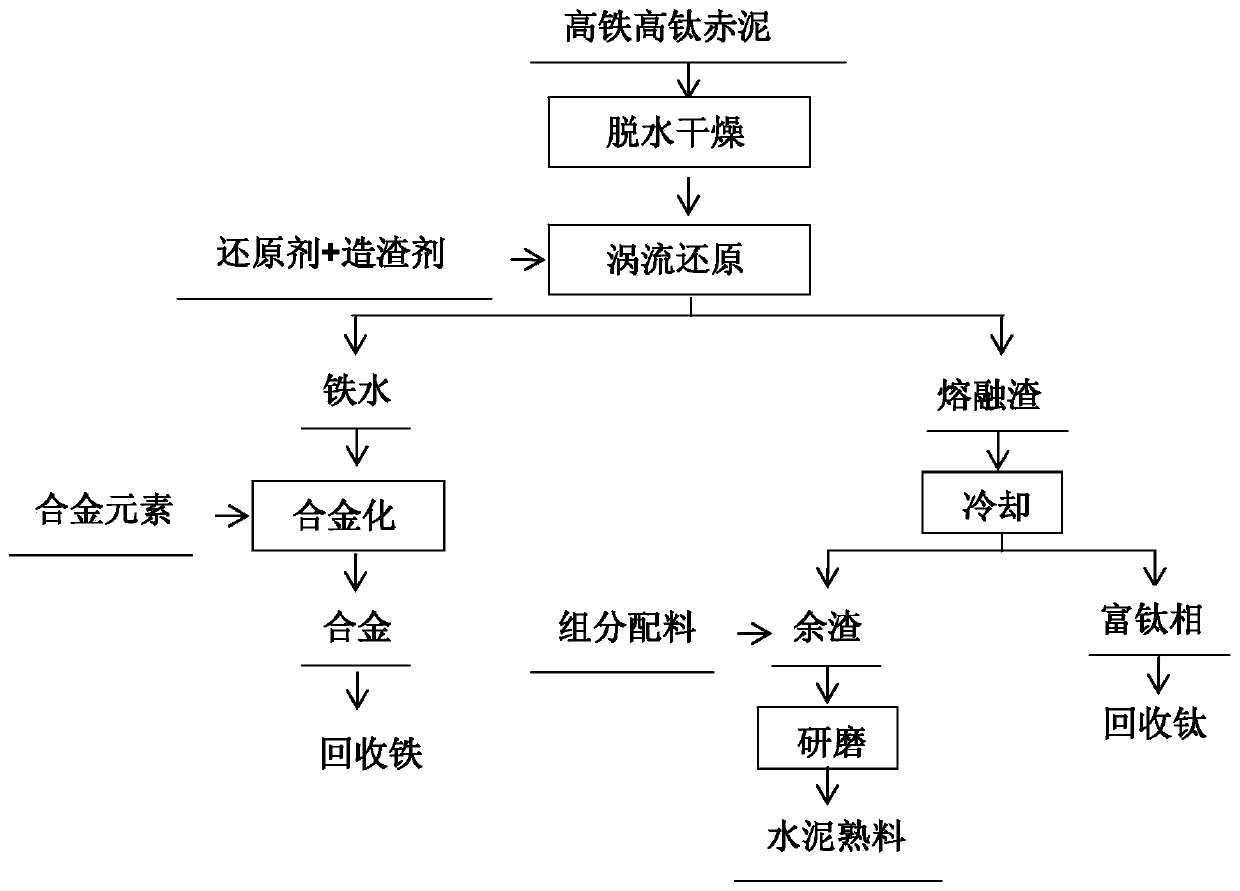
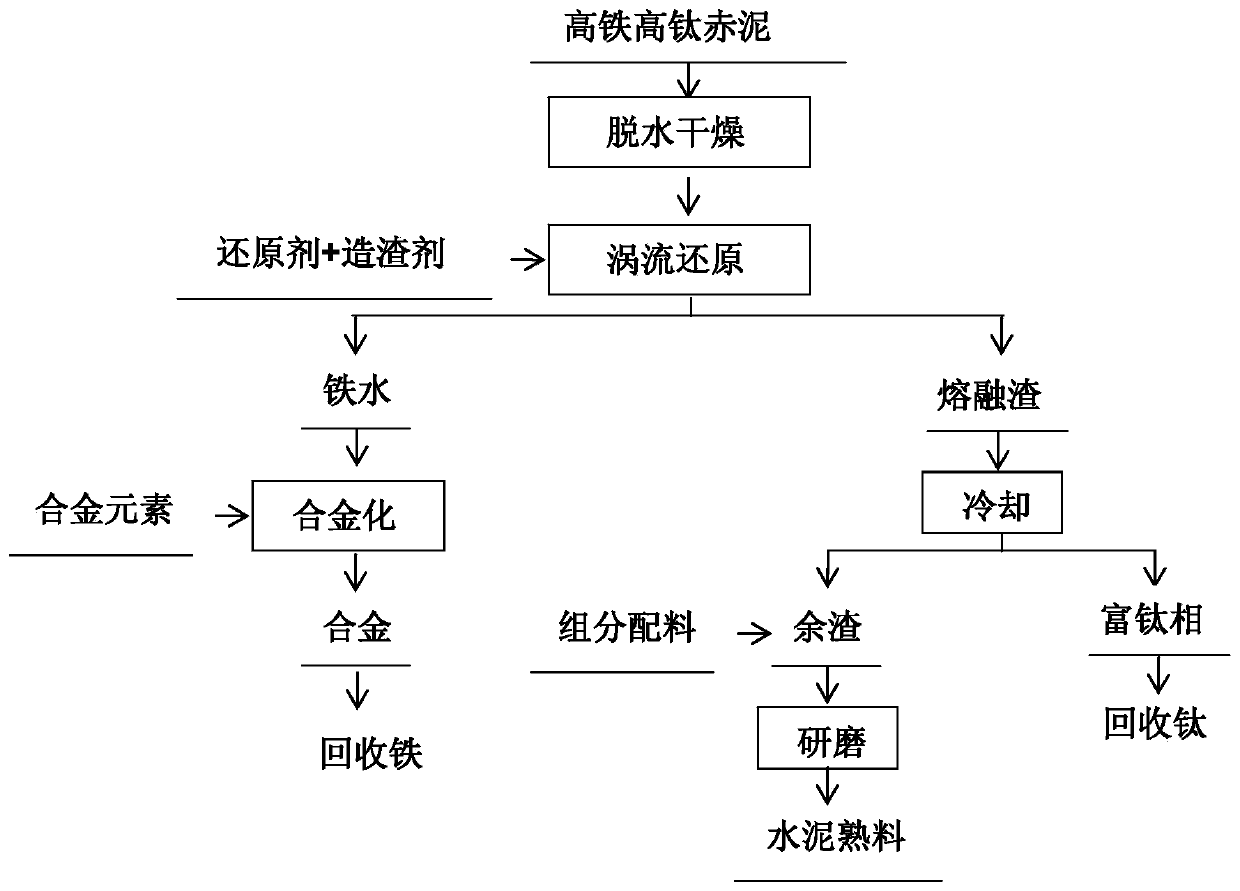
[0040] (1) Prepare the high-iron and high-titanium red mud after the raw material calcification-carbonization process, the raw material is TFe 20% by mass percentage, containing TiO 2 10%; A / S=0.74;
[0041] (2) Dry the raw material until the mass percentage of water is ≤1% to obtain the dehydrated raw material; mix the dehydrated raw material with a solid carbonaceous reducing agent and a slagging agent to make a mixture, and directly spray it into the vortex center of the vortex stirring high-temperature furnace , the mixed material is drawn into the molten pool, and is vortex stirred and reduced at 1300 ° C for 60 minutes; the solid carbonaceous reductant is coking coal, and the molar ratio of the amount of the solid carbonaceous reductant to Fe in the raw material is 1.2, and the slagging agent for CaO and CaF 2 The mixture, in which CaO is added according to the basicity of the mixture is 1.1, CaF 2 Accounting for 10% of the total mass of CaO:
[0042] (3) The molten i...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Prepare the high-iron and high-titanium red mud after the raw material calcification-carbonization process, the raw material is TFe 40% by mass percentage, containing TiO 2 3%; A / S=0.81;
[0046] (2) Dry the raw material until the mass percentage of water is ≤1% to obtain the dehydrated raw material; mix the dehydrated raw material with a solid carbonaceous reducing agent and a slagging agent to make a mixture, and directly spray it into the vortex center of the vortex stirring high-temperature furnace , the mixed material is drawn into the molten pool, and is vortex stirred and reduced at 1450° C. for 10 minutes; the solid carbonaceous reductant is coking coal, and the molar ratio of the amount of the solid carbonaceous reductant to Fe in the raw material is 1.4, and the slagging agent for CaO and CaF 2 The mixture, in which CaO is added according to the basicity of the mixture is 1.4, CaF 2 20% of the total mass of CaO:
[0047] (3) The molten iron formed afte...
Embodiment 3
[0050] (1) Prepare the high-iron and high-titanium red mud after the raw material calcification-carbonization process, the raw material is TFe 30% by mass percentage, containing TiO 2 6%; A / S=0.33;
[0051] (2) Dry the raw material until the mass percentage of water is ≤1% to obtain the dehydrated raw material; mix the dehydrated raw material with a solid carbonaceous reducing agent and a slagging agent to make a mixture, and directly spray it into the vortex center of the vortex stirring high-temperature furnace , the mixed material is drawn into the molten pool, and is vortex stirred and reduced at 1400 ° C for 30 minutes; the solid carbonaceous reductant is coking coal, and the molar ratio of the amount of the solid carbonaceous reductant to Fe in the raw material is 1.5, and the slagging agent for CaO and CaF 2 The mixture, in which CaO is added according to the basicity of the mixture is 1.0, CaF 2 Accounting for 10-30% of the total mass of CaO:
[0052] (3) The molte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com