3D printing method for cell tissue by using bio-ink
A 3D printing, bio-ink technology, used in the field of biomedicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
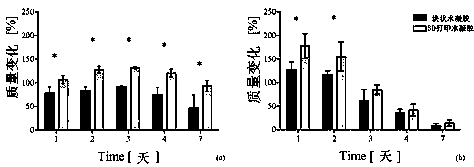
[0012] Preparation of methylcellulose hydrogel
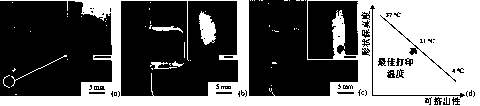
[0013] Briefly, methylcellulose hydrogels containing 8% w / v were obtained by mixing methylcellulose powder (cellulose A4M, ŋ = 4000 mPa, 2% in water at 20 °C, supplied by Dow Chemical Company) into Na2SO4 , 0.05 M saline solution. The resulting polymer suspension was stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C for 24 hours to fully hydrate the methylcellulose-based polymer chains. After repeated testing and demonstration, we confirmed that the methylcellulose-based hydrogel formulation has an optimal transition temperature range (LCST=34-37°C) in cell plate engineering and cell delivery applications.
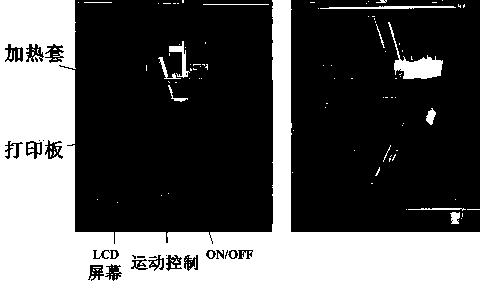
[0014] 3D printer for methylcellulose hydrogel
[0015] Methylcellulose hydrogels are divided into block form and 3D printing form, and their respective preparation methods are shown in Table 1:
[0016] Table 1 Preparation method of methylcellulose-based hydrogel
[0017] name
Methylcellulose-based hydrogel concentration (%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com