Substituted azole derivatives for generation, proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
A technology for hematopoietic stem cells and peripheral blood stem cells, applied in the field of substituted azole derivatives for the generation, proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells, capable of solving the problem of opportunistic microbial and viral infections that increase whole blood cell reduction receptors Risk and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0241] method
[0242] UCB collection, processing, thawing and inoculation
[0243] UCB were obtained from donor units (not meeting clinical storage criteria) through the Singapore Cord Blood Bank (SCBB). The donor mothers and the Research Advisory Ethics Committee of the SCBB and the Institutional Review Boards of the National University of Singapore (NUS) and the Singapore General Hospital (SGH) were consulted in advance. Agreed, the use of the sample is approved. Using Ficoll-Histopaque TM Premium (GE Healthcare, UK) isolated mononuclear cells (MNC) from fresh UCB by density gradient centrifugation. Enumerated UCB-MNCs were cryopreserved in 90% v / v autologous plasma containing 10% v / v dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma Aldrich, USA) for subsequent use. A brief summary of the method is as follows image 3 shown. UCB-MNCs were thawed using human serum albumin (25% v / v) (HealthSciences Authority, Singapore) and Dextran 40 (75% v / v) (Hospira, USA). UCB-MNC empirically deter...
Embodiment 2
[0268] Main method steps
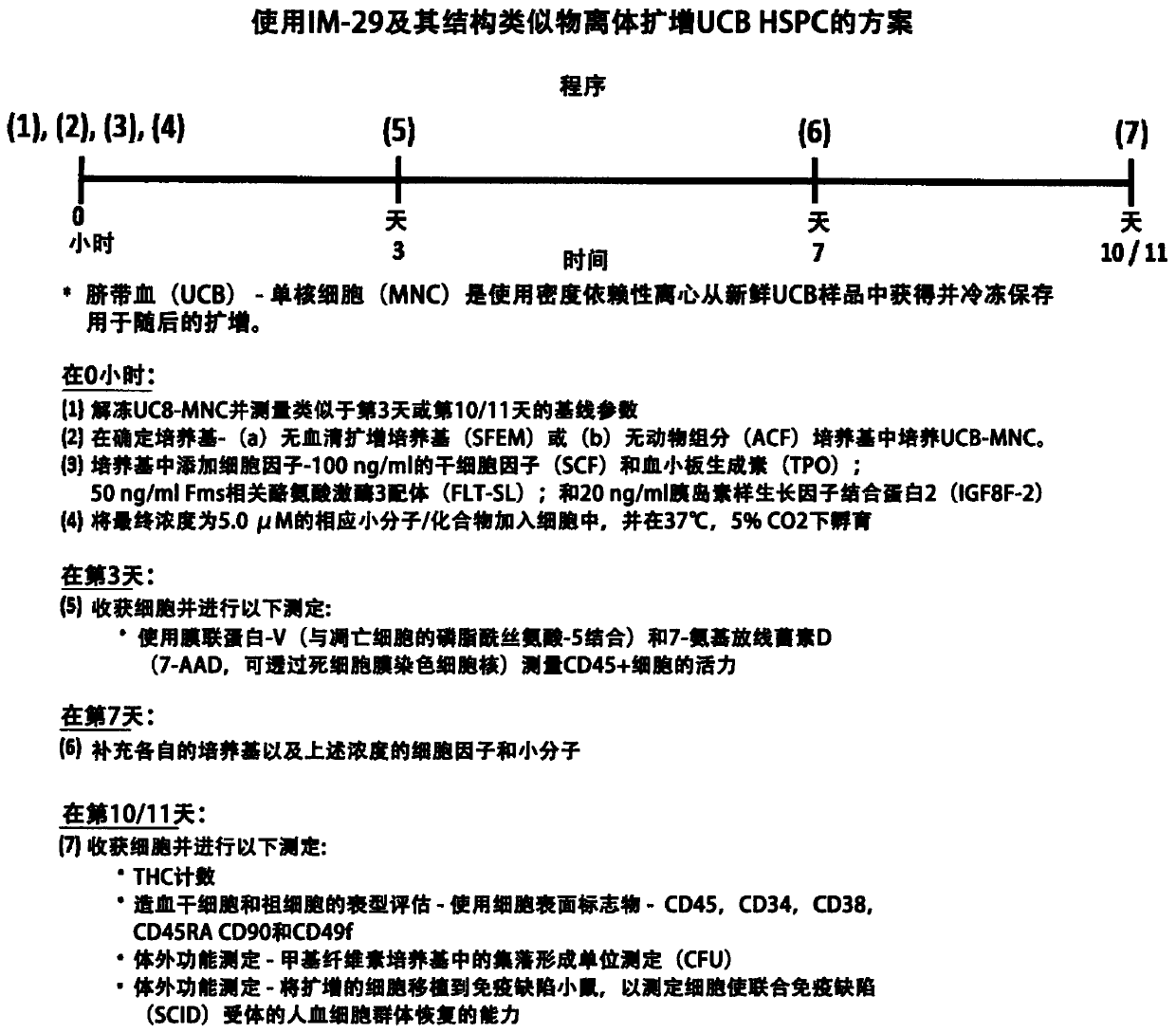
[0269] In an embodiment of the present invention, the main steps involved in the method of using IM-29 to amplify HSPC from freeze-thawed UCB-MNC are as follows: figure 2 Shown:
[0270] (i) Fresh UCB was processed using density-dependent centrifugation to isolate the mononuclear (MNC) fraction, which was frozen at -180°C for future expansion;
[0271] (ii) thawing and culturing UCB-MNCs in a defined medium containing a cytokine mixture of SCF, TPO, FLT-3L and IGFBP-2;
[0272] (iii) adding IM-29 with a final concentration of 5.0 μM;
[0273] (iv) Keep the cells at 37°C and 5% CO 2 Incubated in a humidified incubator;
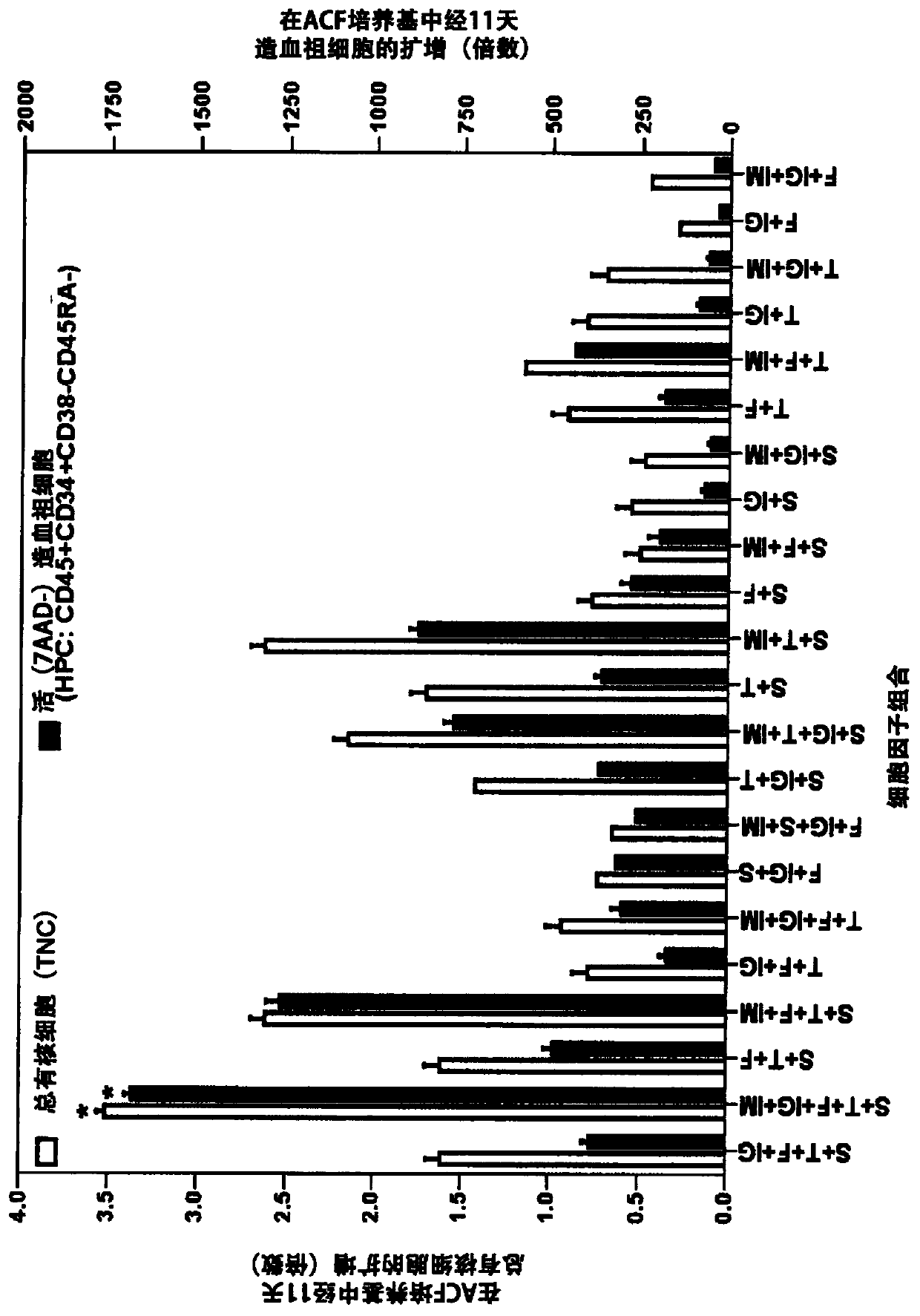
[0274] (v) On day 3, the viability of CD45 expressing white blood cells (WBC) was monitored. HSPCs are a subset of CD45 cells;
[0275] (vi) On day 7, supplement (replenish) growth medium, cytokines and IM-29;
[0276] (vii) On day 10 / 11, cells were harvested for assessment of cell expansion by in vitro phenotypic and function...
Embodiment 3
[0279] Small molecules derived from compound SB203580
[0280] The small molecule library includes several analogs, all of which are derived from the parent compound SB203580 ( Figure 6D ), which is a known inhibitor of p38MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) with optimal activity at working concentrations of 5 to 10 μΜ. have Figure 6A Compound IM-29 of the shown chemical structure was the most potent of the compounds tested. have Figure 6B IM-04 of the shown chemical structure was the second most potent compound. Structural analogs of IM-29 and IM-04 that gave suboptimal effects are shown in Figure 6C middle. A total of 40 SB203580 analogs were generated for this study, which are shown in Figure 6E , and are roughly divided into four groups based on structure and chemical modification. Figure 6E Group 1 examined changes in the substituent at the C-2 position of the imidazole while retaining the pyridin-4-yl / 3-tolyl or pyridin-4-yl / 3 -(trifluoromethyl)phenyl m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com