Model for evaluating different degradation degrees of meadow grassland and an establishing method and application thereof
A degraded, grass-landed technology, used in data processing applications, character and pattern recognition, systems based on fuzzy logic, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
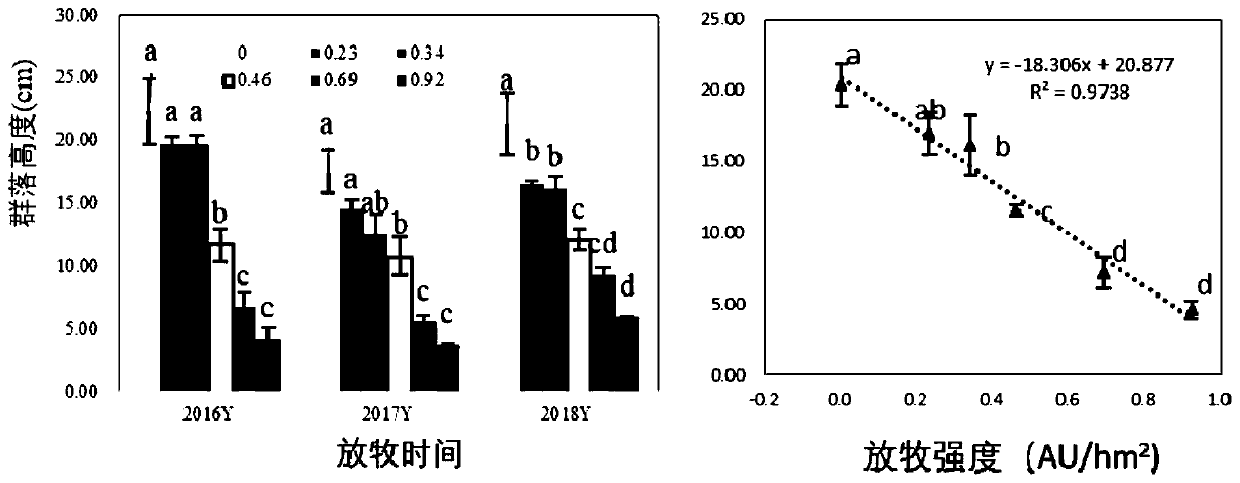
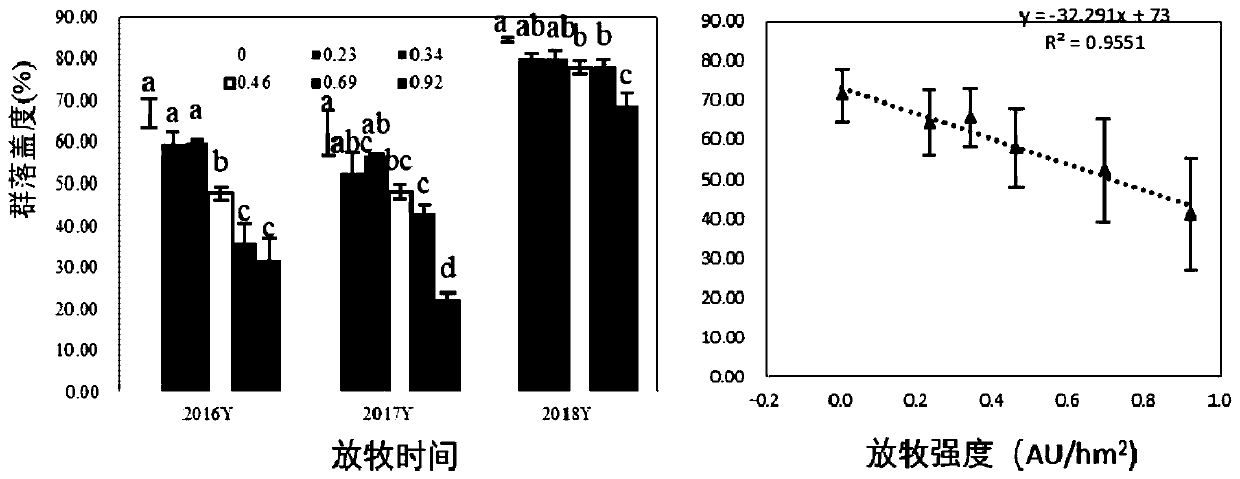
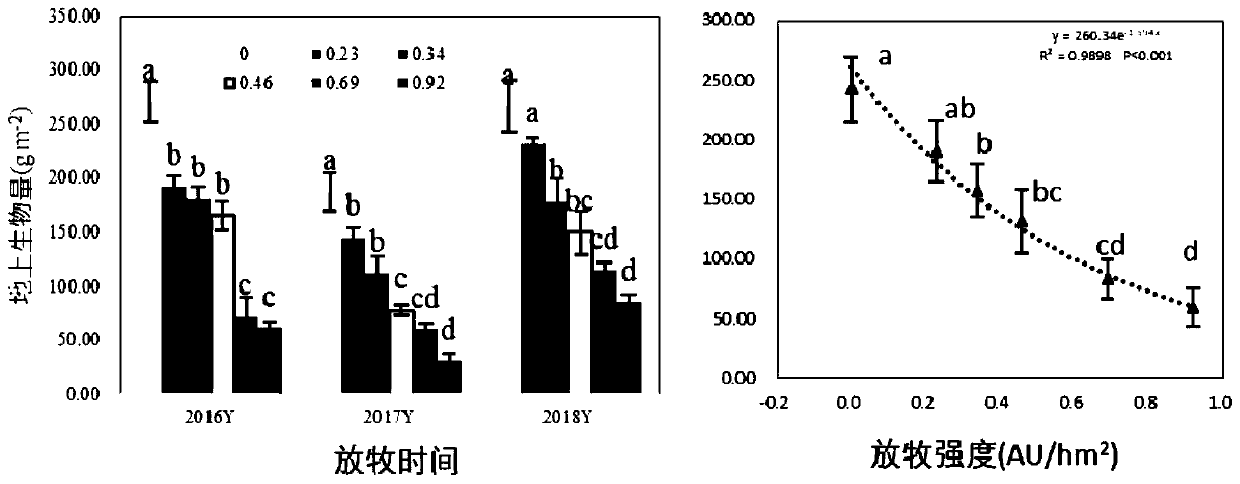
[0081] Embodiment 1, grazing intensity causes the impact of different degradation degrees on meadow grassland
[0082] Experimental design: The natural grassland with the community type of Leymus chinensis + forb community was used as the grazing sample plot, and a total of 6 levels of grazing intensity gradient treatments were set up, and the stocking rates were: G 0.00 :0.00Au / hm 2 , G 0.23 :0.23Au / hm 2 , G 0.34 :0.34Au / hm 2 , G 0.46 :0.46Au / hm 2 , G 0.69 :0.69Au / hm 2 , G 0.92 :0.92Au / hm 2 .
[0083] After ten years (2009-2018) of grazing experiments, with the continuation of grazing time, different grazing intensities have gradually produced significant changes in the characteristics of vegetation communities and soil characteristics, resulting in a series of obvious mildly degraded, moderately degraded and severely degraded areas . The specific data are as follows:
[0084] 1. Changes in community characteristics after continuous control of grazing intensity f...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Embodiment 2. Establishing a model for assessing different degrees of degradation of meadow grassland
[0097] In order to study the interaction between plant communities and soil factors under different grazing degradation degrees of meadow grassland and select the index system for diagnosing the degradation degree of meadow grassland, the Leymus chinensis + forb community non-grazing area (G0, That is, the grazing intensity is G 0.00 ), light grazing use area (G1, that is, the grazing intensity is G 0.23 ), moderate grazing utilization area (G2, that is, the grazing intensity is G 0.46 ), the extreme grazing utilization area (G3, that is, the grazing intensity is G 0.69 ) using the "Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA)" method to analyze the correlation between plant communities and soil factors.
[0098] In each degree of degradation, the plant community variable group (i.e. the first vegetation characteristic group) consists of variables or vegetation indicators:...
Embodiment 3
[0285] Embodiment 3, method inspection
[0286] Taking the data that is not used in the establishment of the model of Example 2 in Example 1 as the data of the meadow grassland to be evaluated, calculate the indicator degree d according to the method of Example 2 i According to the threshold value of Example 2, the degradation level of the meadow grassland to be evaluated is judged, and the result is completely consistent with the actual situation. It proves that the method of this application is very accurate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com