a duplexer
A duplexer and resonator technology, which is applied in the field of semiconductors and micro-electromechanical systems, can solve the problems of limiting the overall performance of the filter, the difficulty of guaranteeing the performance of the resonator, and the limited adjustable range, so as to achieve out-of-band suppression and isolation improvement , wide adjustment range, improve the effect of in-band insertion loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
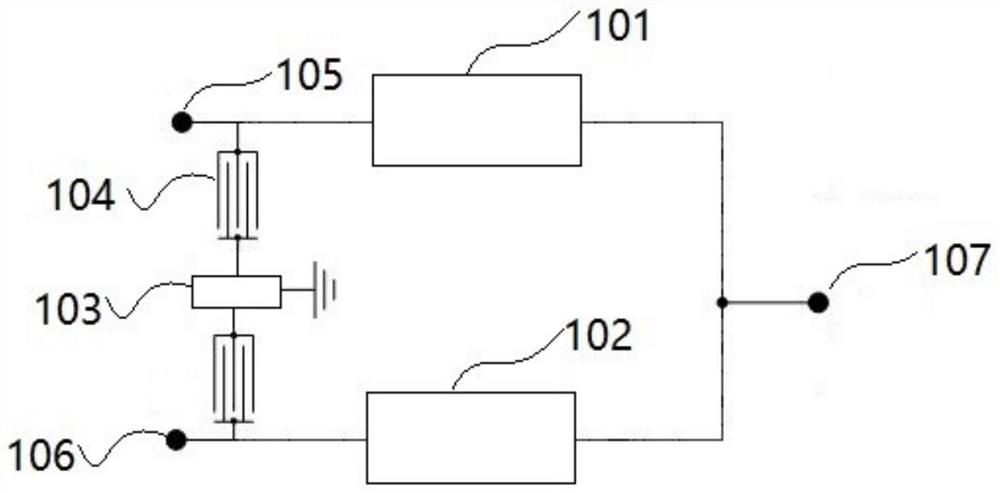
[0057] figure 1 A block diagram of a duplexer according to the first embodiment of the present application is shown. Such as figure 1 As shown, a duplexer includes:
[0058] a transmit filter 101 connected between the transmit terminal 105 and the antenna terminal 107 and comprising series resonators and parallel resonators connected in a trapezoidal form; and
[0059] A receiving filter 102, the receiving filter 102 is connected between the receiving end 106 and the antenna end 107,
[0060] Wherein, the transmitting end 105 and the receiving end 106 respectively lead a branch to the grounding end, and the LWR resonator 104 and the passive device 103 are connected in series in the branch.
[0061] Wherein, each passive device 103 may be a capacitor, an inductor or a resonator. The structure of the passive device 103 may be T-type, pi-type or L-type.
[0062] The above duplexer increases the LWR resonator path between the transmitting end 105 and the receiving end 106, wh...
Embodiment 2
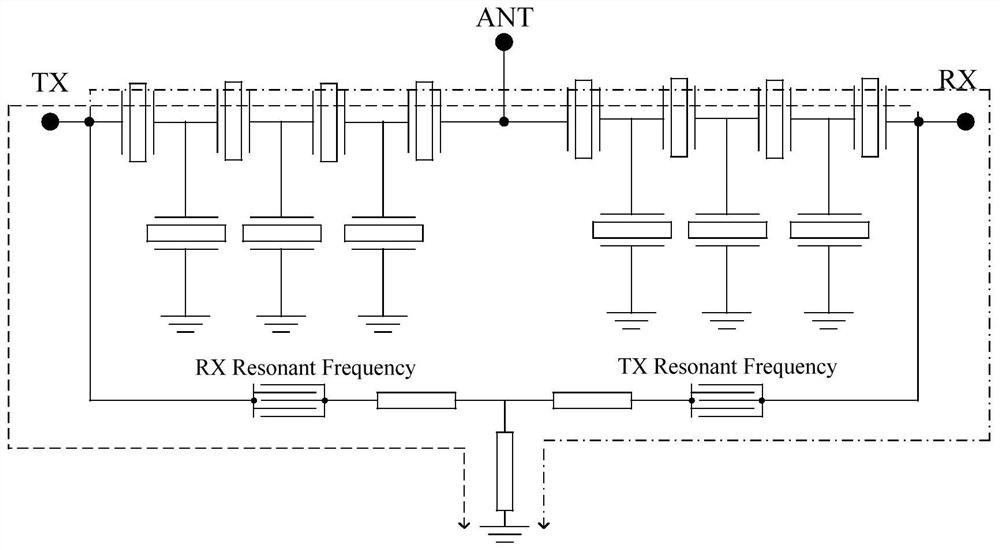
[0091] Figure 7 A block diagram of a duplexer according to the second embodiment of the present application is shown. Such as Figure 7 As shown, a duplexer includes:
[0092] a transmit filter 101 connected between the transmit terminal 105 and the antenna terminal 107 and comprising series resonators and parallel resonators connected in a trapezoidal form; and
[0093] A receiving filter 102, the receiving filter 102 is connected between the receiving end 106 and the antenna end 107,
[0094] Wherein, the transmitting terminal 105 leads a branch to the ground terminal, and the LWR resonator 104 and the passive device 103 are connected in series in the branch.
[0095] Wherein, each passive device 103 may be a capacitor, an inductor or a resonator. The structure of the passive device 103 may be T-type, pi-type or L-type.
[0096] Figure 8 A circuit structure diagram of a duplexer according to the second embodiment of the present application is shown. Such as Figure...
Embodiment 3
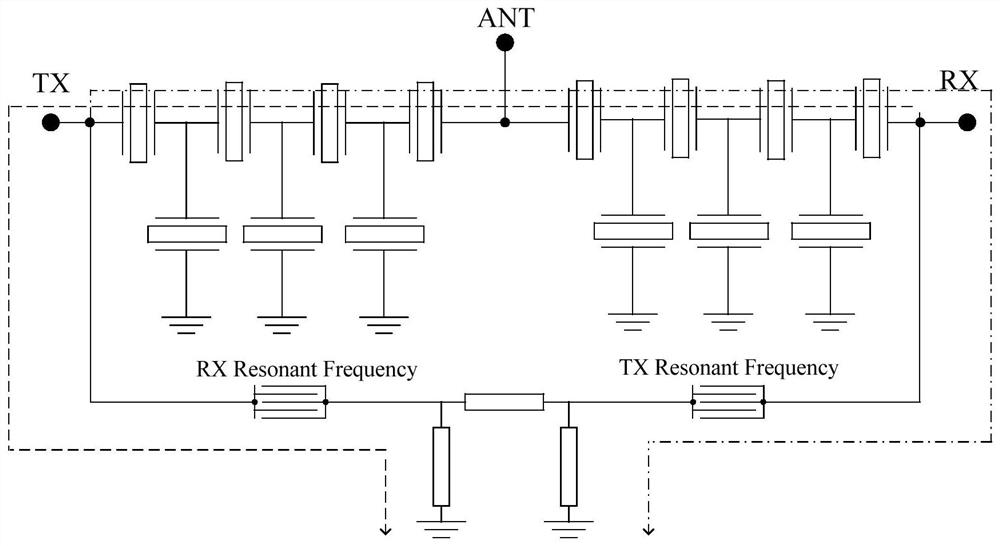
[0105] Figure 11 A block diagram of a duplexer according to the third embodiment of the present application is shown. Such as Figure 11 As shown, a duplexer includes:
[0106] a transmit filter 101 connected between the transmit terminal 105 and the antenna terminal 107 and comprising series resonators and parallel resonators connected in a trapezoidal form; and
[0107] A receiving filter 102, the receiving filter 102 is connected between the receiving end 106 and the antenna end 107,
[0108] Wherein, the receiving terminal 106 leads a branch to the ground terminal, and the LWR resonator 104 and the passive device 103 are connected in series in the branch.
[0109] Wherein, each passive device 103 may be a capacitor, an inductor or a resonator. The structure of the passive device 103 may be T-type, pi-type or L-type.
[0110] Figure 12 A circuit structure diagram of a duplexer according to the third embodiment of the present application is shown. Such as Figure 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com