Method for automatically parsing stable isotope labeled sugar chain quantification mass spectrum data
A stable isotope and automatic analysis technology, applied in the field of protein analysis, can solve the problems of quantitative error, easy omission of low-abundance sugar component quantitative results, weak response of sugar chain mass spectrometry, etc., to achieve high quantitative accuracy and robustness, Good application prospect, convenient calculation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
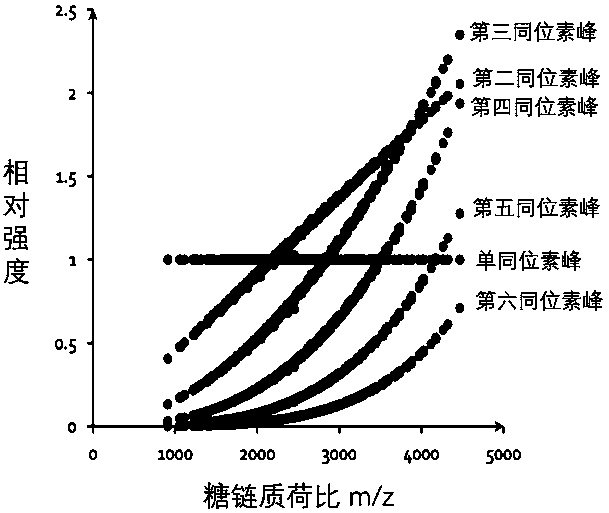
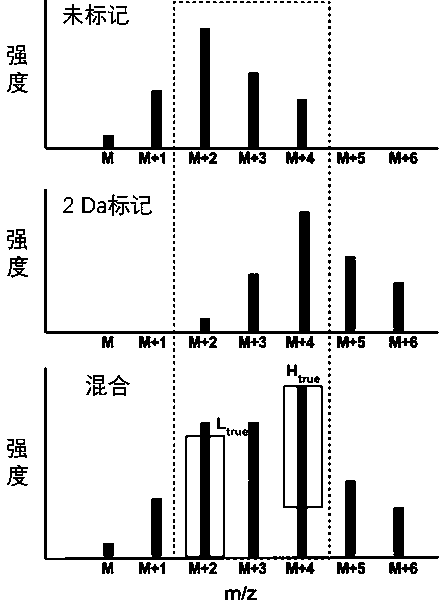
[0026] Asialofetuin (ASF) was divided into two parts, one part was added with 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate and PNGase F enzyme; the other part was added with 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate and PNGase F enzyme dissolved in oxygen 18 water, 37 After incubation at ℃ for 16 hours, 10K ultrafiltration, PGC desalination, and freeze-drying were performed respectively to obtain the sugar chains of ASF. The obtained sugar chains were mixed according to two ratios of 1:1 and 1:5, and then detected by MALDI mass spectrometry, and then the data was analyzed by gquant. When the m / z of the sugar chain is greater than 2250, gGuant shows advantages, such as image 3 For the sugar chains shown in , gQuant reported that the quantitative ratios of the two were 1.084 and 4.816, which were close to the theoretical values, while the quantitative results of hand-picked but calculated isotope peaks were 1.4649 and 10.607, respectively. The serious deviation of the second ratio is caused by the severe in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com