Absolute linear displacement sensor based on decimal shift coding
A linear displacement and decimal system technology, which is applied in the direction of instruments, measuring devices, optical devices, etc., can solve the problems that the sensor is not easy to miniaturize and the method is complicated
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
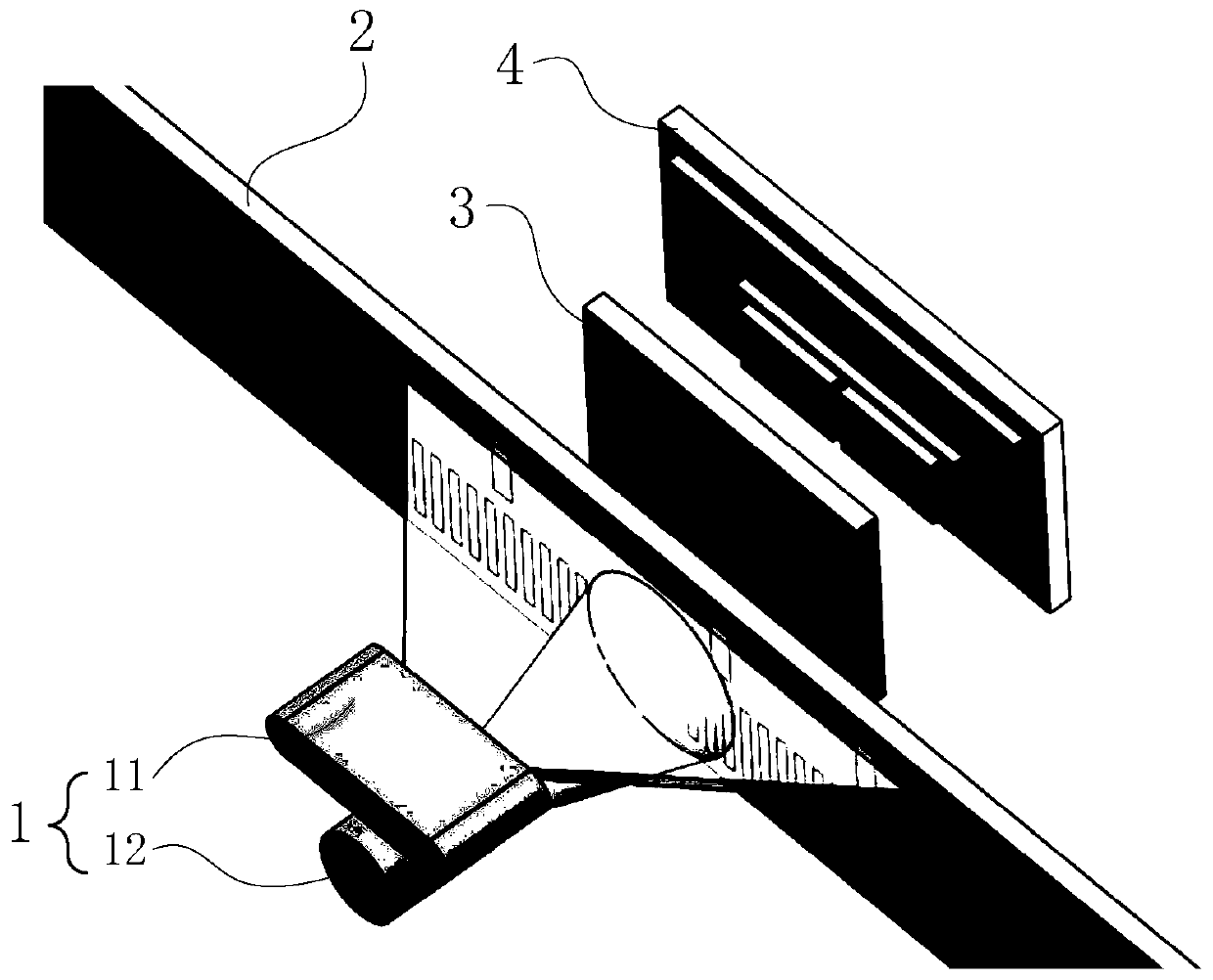
[0032] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1 to Figure 6 The shown absolute linear displacement sensor based on decimal displacement coding includes a light emitting element 1, a moving scale base 2, a fixed scale base 3, a photodetector 4 and a signal processing circuit.
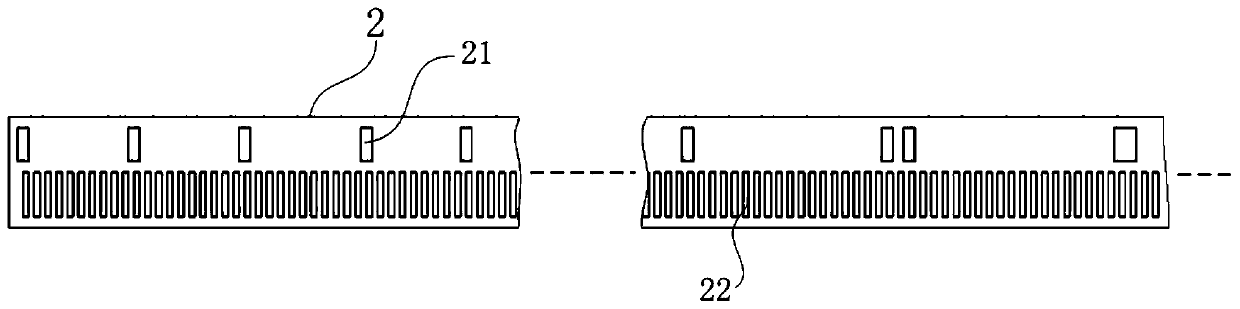
[0033] The moving scale base 2 uses glass as the base material, and covers its upper surface with a light-shielding material, so that a row of rectangular light-transmitting surfaces I that are not covered with light-shielding materials and are evenly spaced at 0.3mm along the measuring direction are left on the moving scale base 2, forming an incremental At the same time, a row of rectangular light-transmitting surfaces II that are not covered with light-shielding materials and distributed along the measurement direction in the order of decimal shift coding are left on the moving scale base 2 to form an absolute code track 21, and the incremental code track 22 is located at Below the absolute code track 21, the width...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: as Figure 8 The shown absolute linear displacement sensor based on decimal shift coding has the same measurement principle as that of Embodiment 1, and most of its structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1. The difference is that in this embodiment, the light-emitting element 1 is a single Semiconductor surface light source (that is, only composed of semiconductor surface light source), the semiconductor surface light source adopts a surface-shaped light-emitting diode, driven by a sinusoidal alternating current signal superimposed with a DC bias, and the emitted light forms an alternating light intensity. The illumination area acts on the incremental code track 22 and the absolute code track 21. The length of the light intensity alternating illumination area formed on the absolute code track 21 is 14mm, and the light intensity alternating light area formed on the incremental code track 22 is The length of the illuminated area is 7mm.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3: as Figure 9 to Figure 12 The shown absolute linear displacement sensor based on decimal shift coding has the same measurement principle as that of Embodiment 1, and most of its structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that:
[0053] In this embodiment, the light-emitting element 1 is a single semiconductor surface light source (that is, only composed of a semiconductor surface light source). driving, the emitted light forms an alternating light intensity area, which acts on the incremental code track 22 and the absolute code track 21, and the length of the light intensity alternating light area formed on the absolute code track 21 is 14mm, and the incremental The length of the illuminated area with alternating light intensity formed on the code track 22 is 7mm.
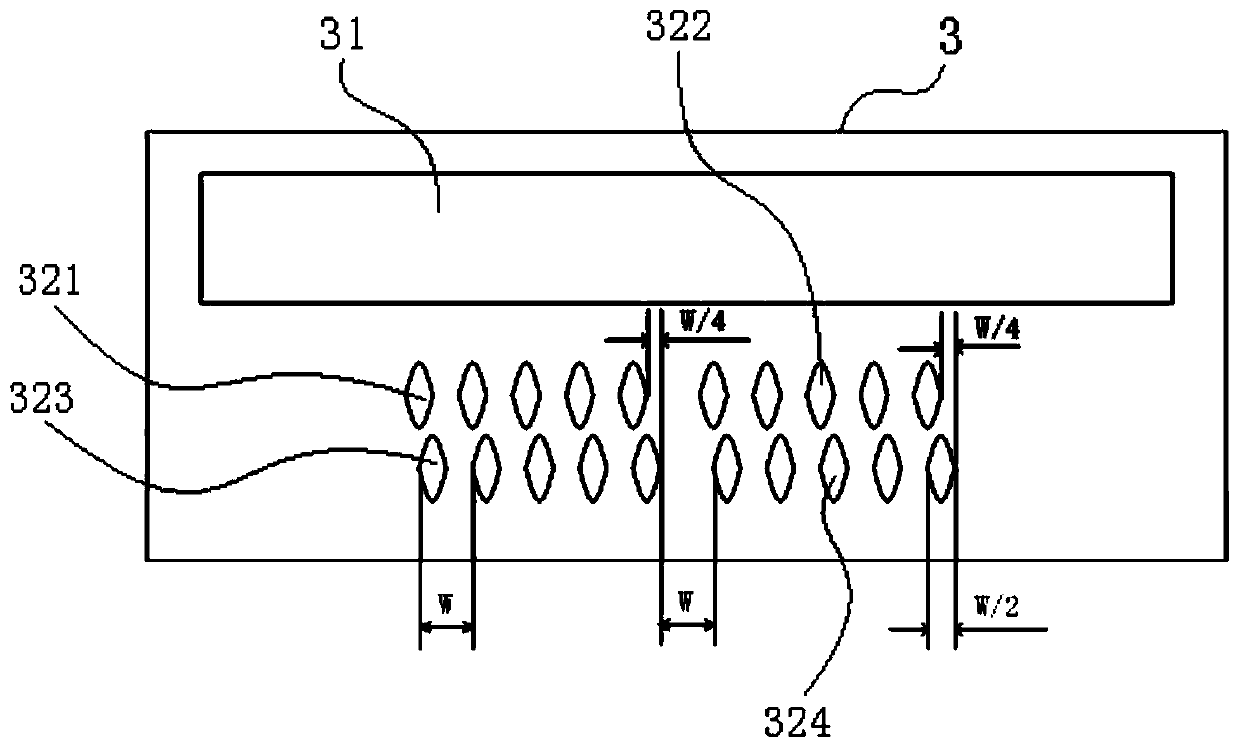
[0054] In this embodiment, there are two rows of rectangular light-transmitting surfaces I that are not covered with light-shielding materials and are evenly spaced by 0.3mm along t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com