A strain of Lactobacillus plantarum with antibacterial properties and its application in the prevention of diarrhea
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and characteristics, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of serious strain homogeneity and lack of functional subdivision products, etc., and achieve good adhesion characteristics, reduce adhesion rate, and excellent antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
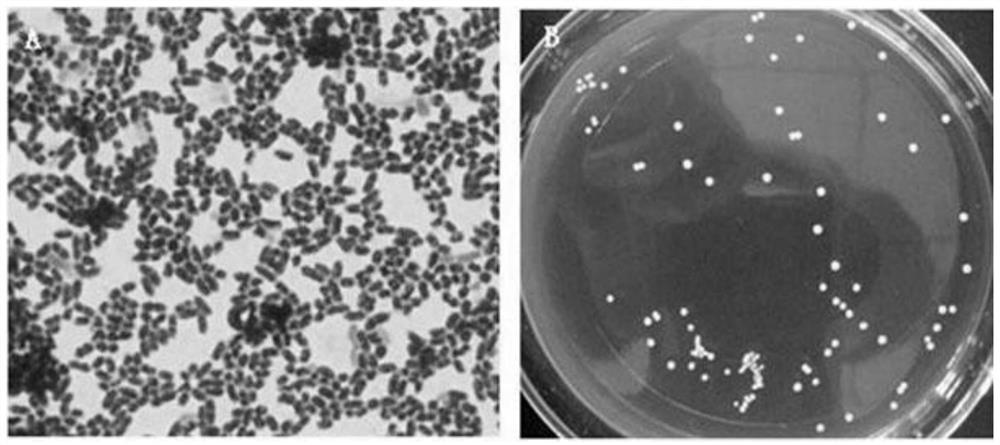
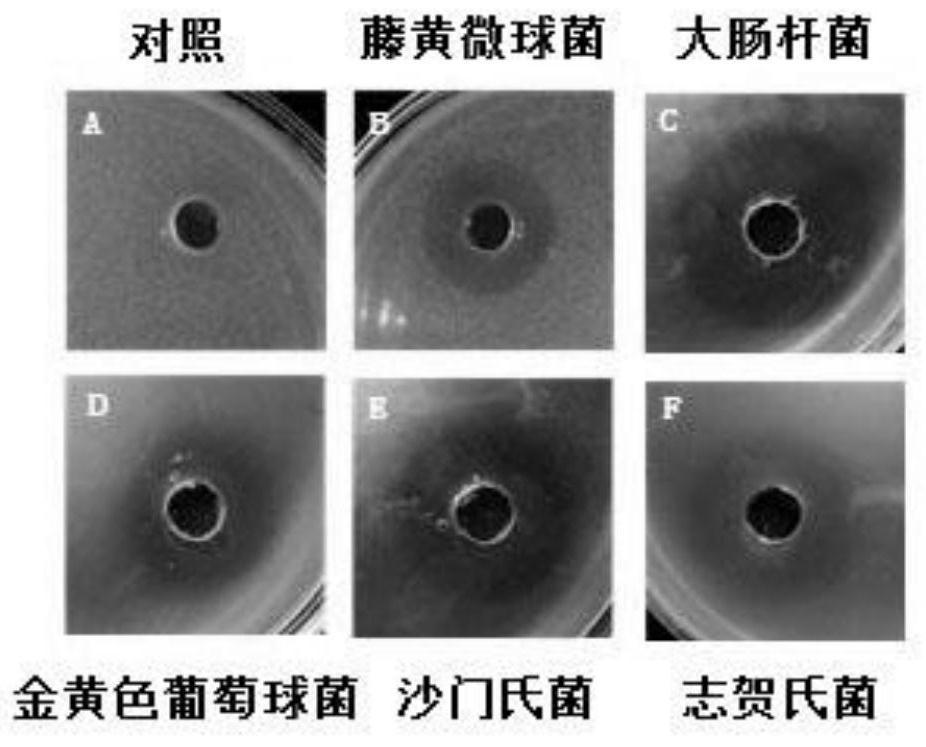
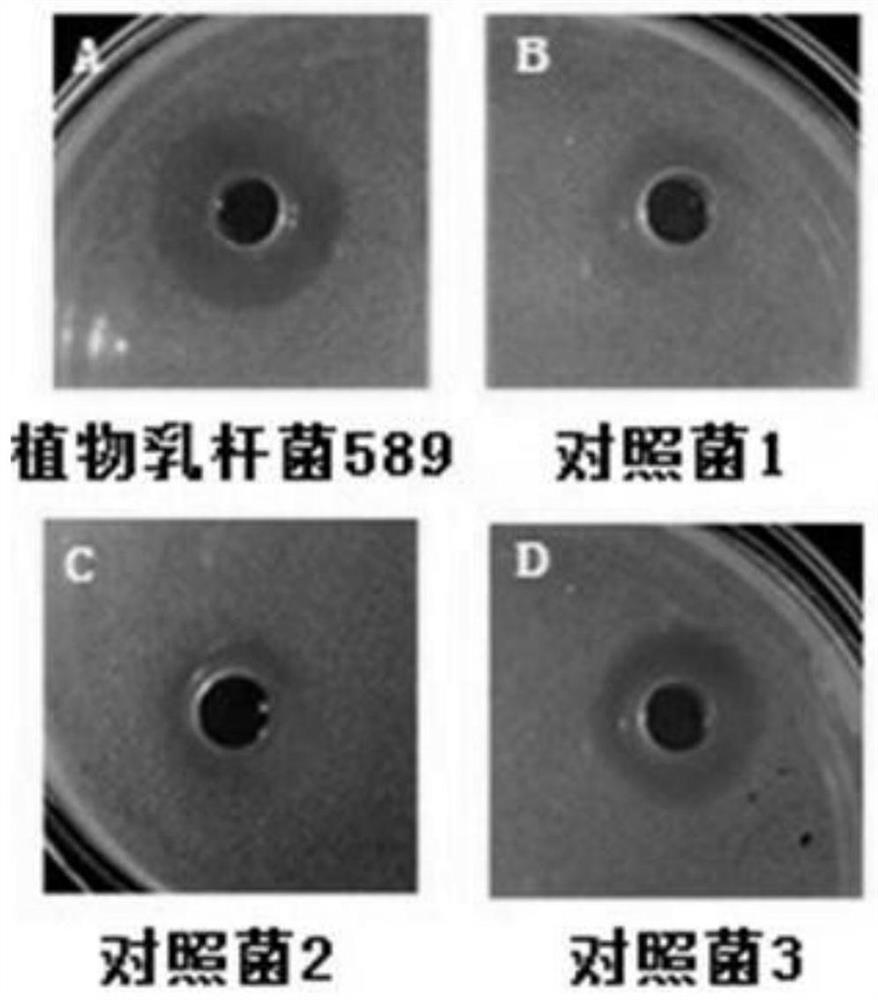
[0031] Antibacterial properties of Lactobacillus plantarum 589
[0032]The indicator bacteria were Micrococcus luteus, Escherchia coli CICC 23689, Staphylococcus aureus CICC 10301, Salmonella typhimurium CICC 10437, Shigella flexneri CICC 21534 ) four common intestinal infection pathogens. Using NB medium, under the condition of 37 ℃ culture, after three generations of continuous activation, it was used for antibacterial experiment. The antibacterial properties of the bacterial strains of the present invention were measured by a double-layer plate punching diffusion method. Pour the sterilized 1.5% agar into a sterile petri dish. After solidification, cool down the sterilized solid medium (containing 1.1% agar) to a certain temperature, mix it with the indicator bacteria and pour it into Placed on top of the agar layer in an Oxford cup. The indicator bacteria should be adjusted to a reasonable concentration according to the growth conditions. After the upper layer is solid...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Tolerance Characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum 589
[0042] After culturing the strains of the present invention and commercially available commercial strains to the end of logarithmic growth, the bacterial suspension was obtained, and the bacterial suspension was divided into two groups, and the acid resistance and bile salt resistance were measured respectively. The operation is as follows. (1) Take a certain amount of bacterial liquid, centrifuge at 4000g / 10min and discard the supernatant. Add the same volume of MRS solution with pH=2.5, pipette and mix well, incubate at 37°C, and measure the changes in the number of bacteria at 0 point and after incubation for 1h, 2h, and 3h by the dilution smear counting method. (2) Take a certain amount of bacterial liquid, 4000g, centrifuge for 10min and discard the supernatant. Add the same volume of MRS solution containing 0.3% bile salts, pipette and mix well, incubate at 37°C, and measure the changes in the number of b...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Intestinal adhesion ability of Lactobacillus plantarum 589
[0047] strain Adhesion rate (number of bacteria / number of cells) Lactobacillus plantarum 589 1.96±0.15 control bacteria 1.75±0.30
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com