Laser beam splitter
A laser beam splitter and laser technology, applied in optics, instruments, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult processing, large vector, etc., and achieve the effects of easy fabrication, shallow processing depth, and overcoming the limitation of feature size.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
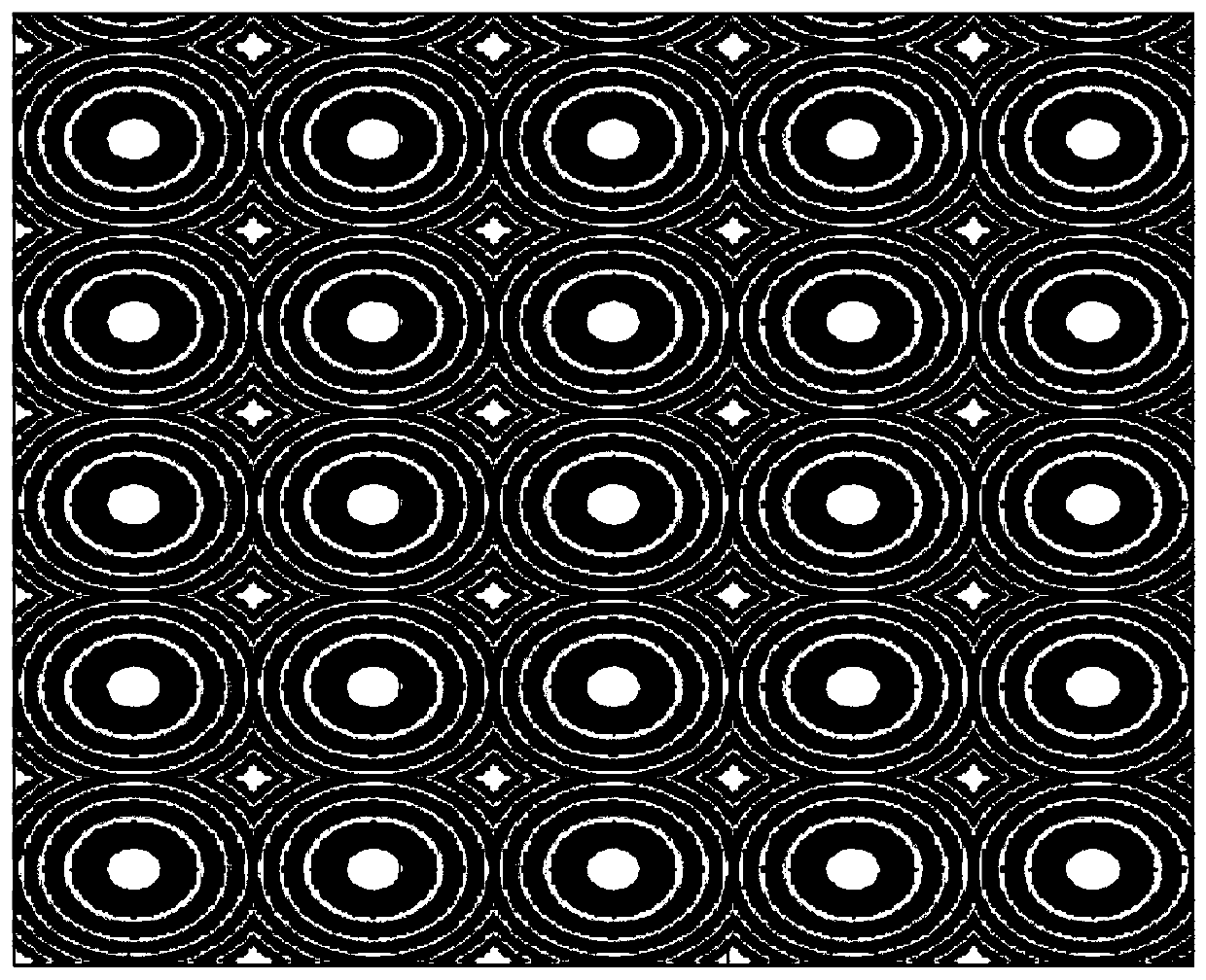
[0032] see figure 1 , is a schematic structural diagram of the laser beam splitter provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0033] In this embodiment, the internal structure of the laser beam splitter is a Fresnel periodic array, and the array period is 6 microns; the structure and array arrangement of the Fresnel periodic array are figure 1 The rectangular arrangement is shown; the Fresnel periodic array is obtained by the corresponding microlens through 2π phase folding; when the laser wavelength is 830nm, the far-field beam splitting lattice generated at a distance of 100mm is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the energy distribution of the beam splitting lattice is uniform, there is no central zero order with obvious brightness difference, and the lattice satisfies the rectangular arrangement.
Embodiment 2
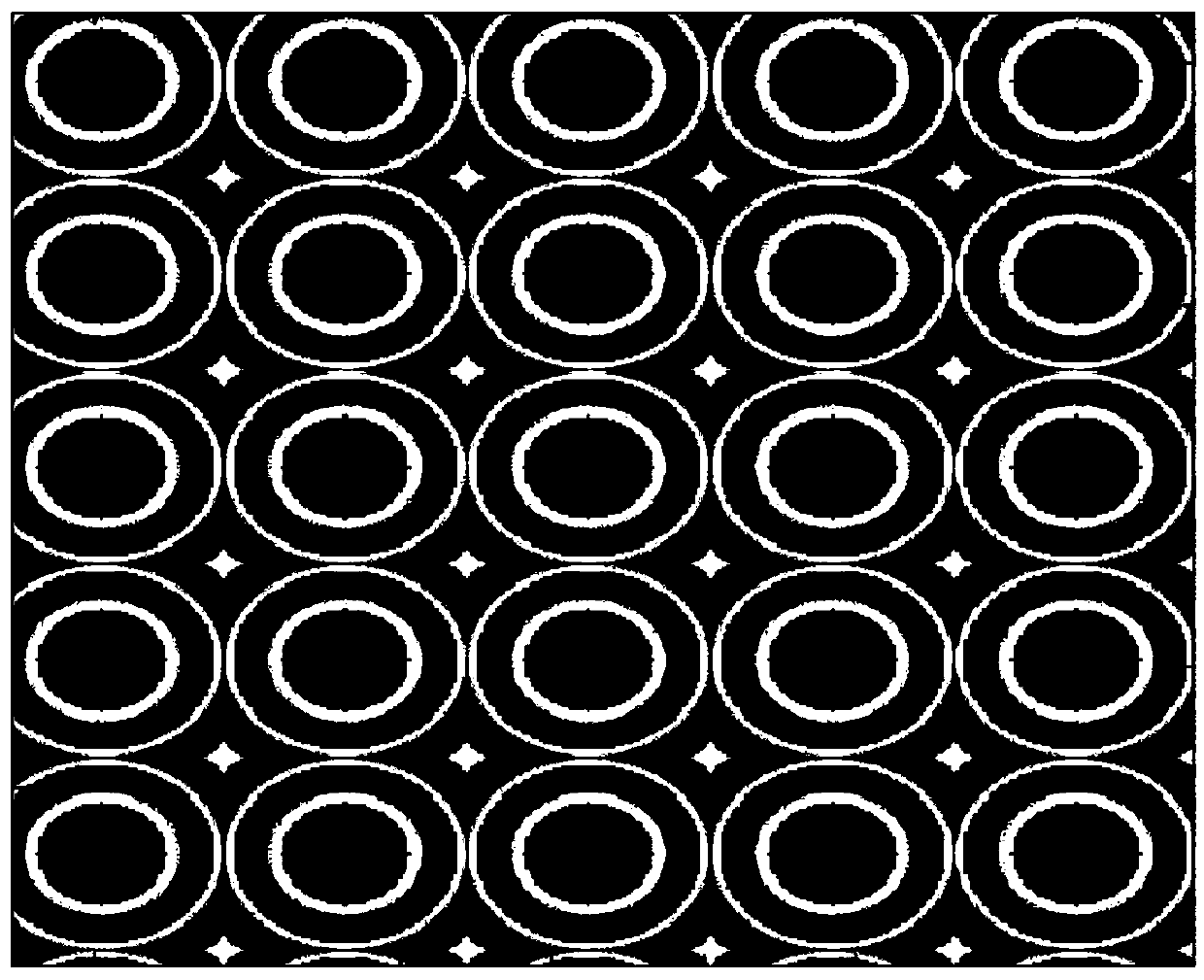
[0035] see figure 2 , is a schematic structural diagram of the laser beam splitter provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0036] In this embodiment, the internal structure of the laser beam splitter is a Fresnel ring array, and the array period is 6 microns; the structure and array arrangement of the Fresnel ring array are figure 2 The rectangular arrangement shown; the Fresnel ring array is obtained by the corresponding microlens through 4π phase folding; at the laser wavelength of 830nm, the far-field beam splitting lattice generated at a distance of 100mm is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the energy distribution of the beam splitting lattice is uniform, there is no central zero order with obvious brightness difference, and the lattice satisfies the rectangular arrangement.
Embodiment 3
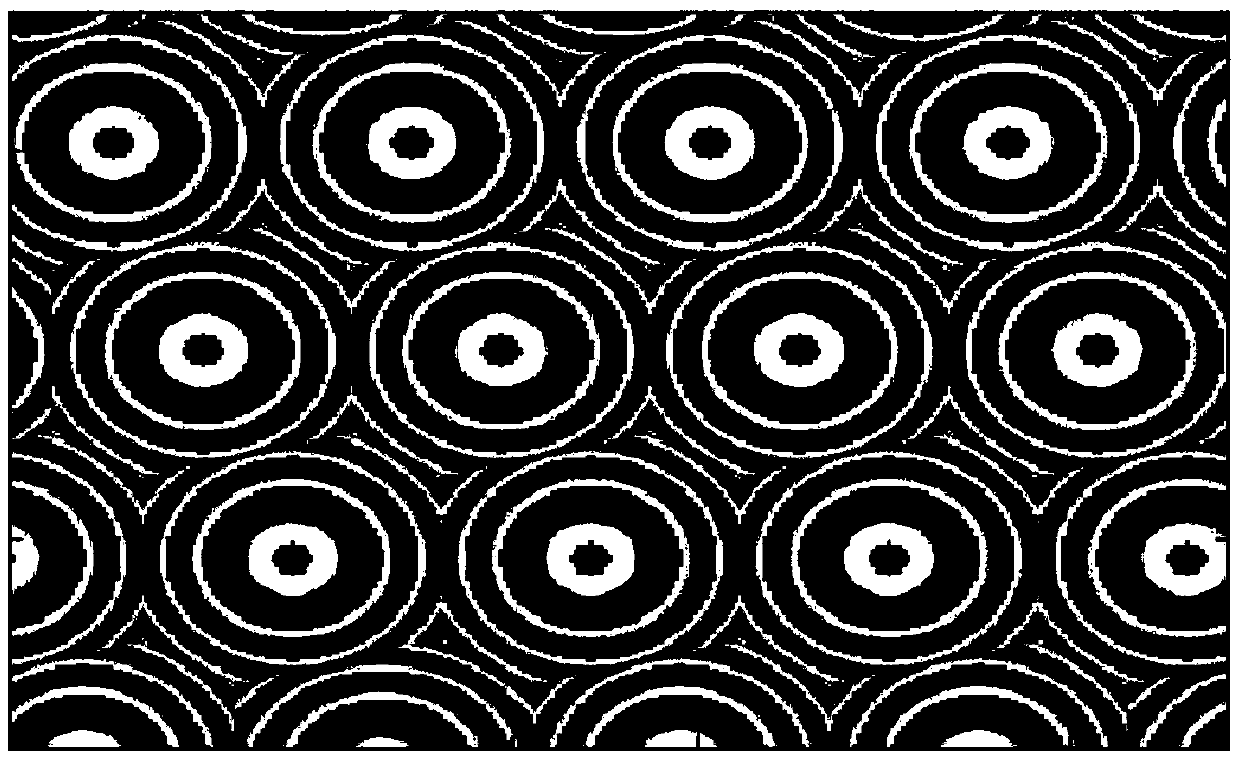
[0038] see image 3 , is a schematic structural diagram of the laser beam splitter provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0039] In this embodiment, the internal structure of the laser beam splitter is a Fresnel ring array, and the array period is 8 microns; the structure and array arrangement of the Fresnel ring array are image 3 The rhombus dislocation arrangement is shown; the Fresnel ring array is obtained by 2π phase folding for the corresponding microlens; at the laser wavelength of 940nm, the far-field beam splitting lattice generated at a distance of 300mm is as follows Image 6 As shown, the energy distribution of the beam-splitting lattice is uniform, there is no central zero order with obvious brightness difference, and the lattice satisfies the dislocation arrangement.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com