Improved interlocking tibia intramedullary nail
An intramedullary nail and tibial bone marrow technology, which is applied in the field of orthopedic surgical medical devices, can solve the problems of increasing the damage to the cortical bone in the head area of the locking nail, the high notch of the head of the intramedullary nail, and increasing the operation time. The effect of reducing the risk of bleeding and infection, reducing the risk of intervention, saving operation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
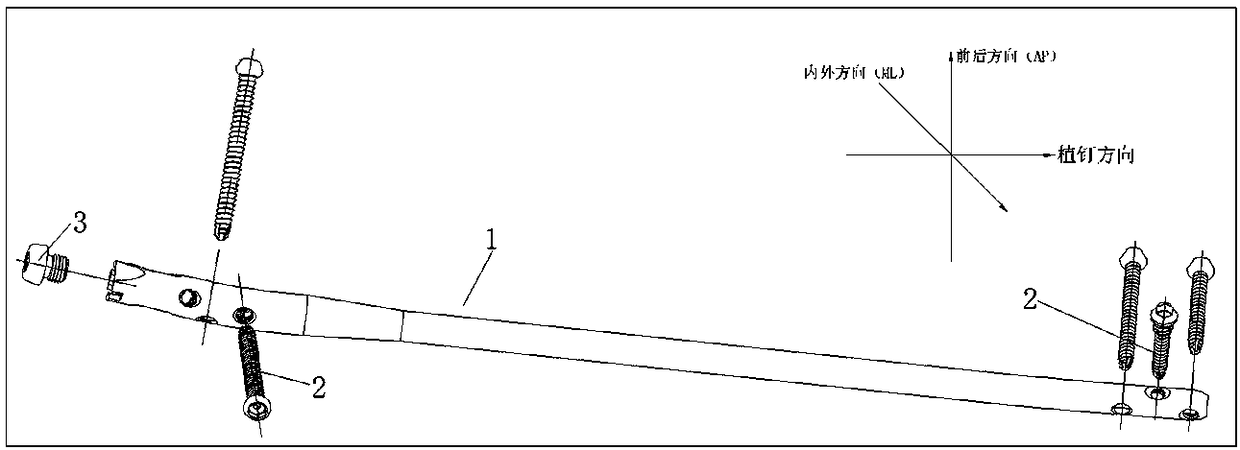
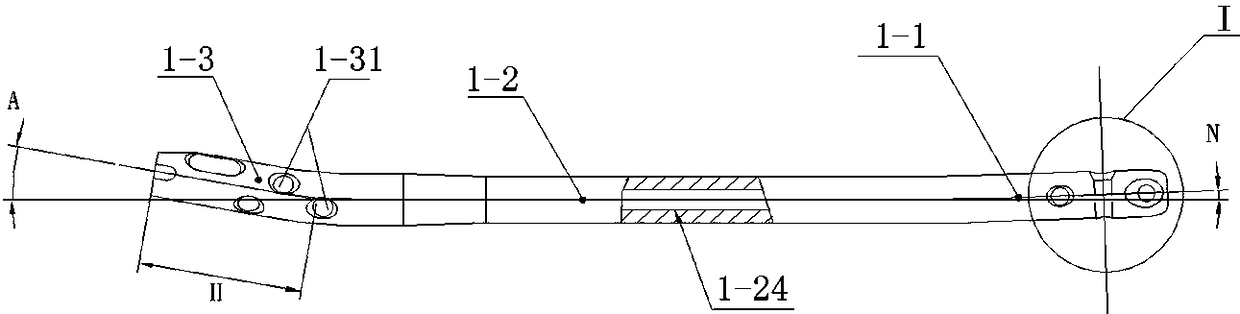
[0094] like figure 1 As shown, an improved interlocking tibial intramedullary nail is inserted into the tibia along the nailing channel, and the design of the distal forward bending zone 1-1 can guide the smooth implantation of the medullary nail along the medullary cavity.
[0095] The middle vertical area 1-2 is the axial load-bearing area of the intramedullary nail. After fracture reconstruction, the axial mechanical demand of the affected limb bone is mainly borne by the middle vertical area.
[0096] Proximal forward bending zone 1-3, the proximal forward bending angle A ranges from 8 degrees to 12 degrees, and the proximal bending distance H ranges within 40mm from the top end surface. The forward bending design meets clinical needs. Choose the necessary design on the tibial anterior condyle surface, do not invade the knee joint cavity, and reduce the impact on the knee joint function.
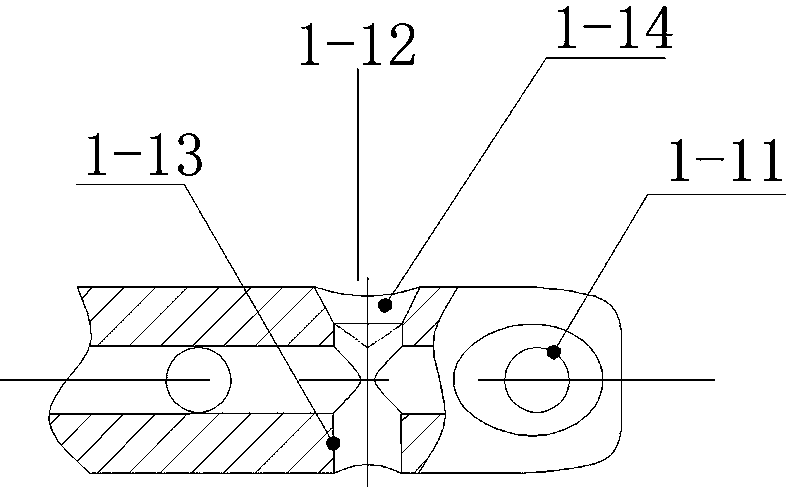
[0097] The first locking nail hole 1-11 at the extreme distal end is 5mm away fro...
Embodiment 2
[0113] like Figure 6 , Figure 7 As shown, after the fixed tail cap is rotated and screwed into the center hole at the top of the main nail, the height H of the exposed part of the tail cap head 3-1 can be used as a supplement to the length of the main nail. Humeral surface fit ( Figure 18 ), to avoid irritation to the surrounding ligaments and surrounding soft tissues, and realize the invention concept of biological low profile. The threaded part 3-2-1 is used to connect the main nail of the intramedullary nail, the lead-in part 3-2-2 plays the role of correcting the thread installation direction, and prevents wrong teeth, and the screwing mechanism 3-4 is used to fix the tail cap and special for surgery The connection area of the tool is mainly used for rotating and screwing in. The structure can be designed as a multi-faceted counterbore such as hexagonal or quincunx. The holding structure 3-6 This mechanism mainly realizes the holding function of the fixed end cap an...
Embodiment 3
[0121] like Figure 8 , Figure 10 , Figure 12 , Figure 15 As shown, the low-profile intramedullary nail locking screw 2 is screwed into the bone surface along the screw implantation channel, and after being compatible with the locking nail hole on the interlocking intramedullary nail (main nail) 1 with a tapered positioning hole at the distal end, Close to the bone surface to complete the implantation. At this time, the height of the exposed part of the locking screw head 2-1 is H. The head of the trapezoidal cylindrical or hemispherical locking screw, and the side close to the bone surface, all adopt a flat design. It can be closely attached to the physiological tibial surface to the maximum extent. Because there is no traditional arc-shaped bottom surface design of the locking nail, the H height of the exposed part has been significantly reduced, and the low-notch effect required by the clinic has been achieved. The height of the head of the locking nail designed with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com