Production technology of coated modified polyethylene fibers
A polyethylene fiber and production process technology, which is applied in the field of chemical fiber production, can solve the problems of slow water dispersion, poor moisture permeability, and decreased air permeability, and achieve high production efficiency, improved modification effect, and weight reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
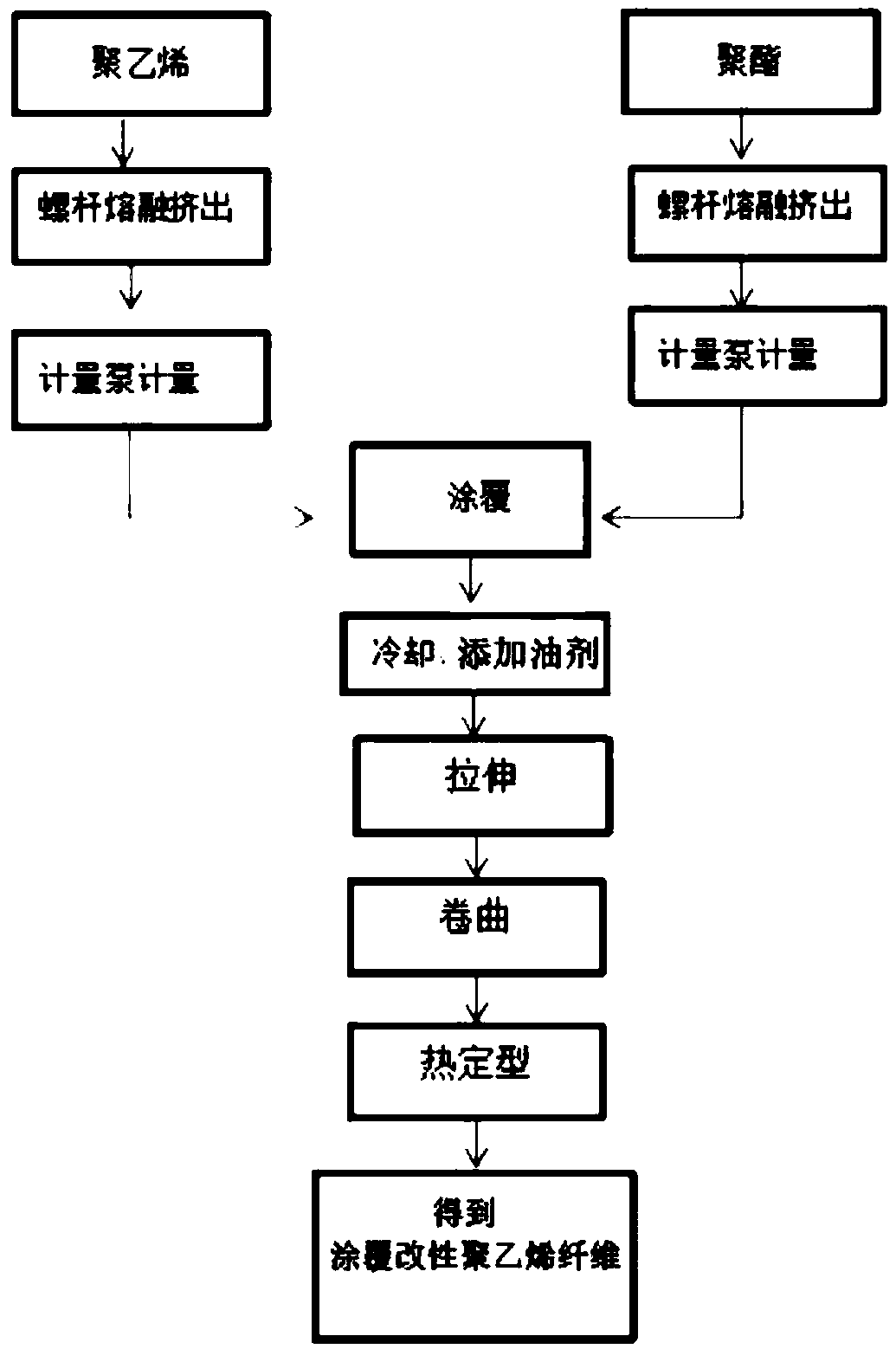
[0022] A production process for coating modified polyethylene fibers, comprising the following steps:
[0023] (1) polyethylene and polyethylene terephthalate are respectively melted and extruded by a screw to obtain molten polyethylene material and molten polyethylene terephthalate material;
[0024] (2) In a mass ratio of 55:45, the molten polyethylene material is coated on the surface of the molten polyethylene terephthalate material to obtain polyester-modified polyethylene; The ethylene glycol phthalate material is realized by a bath tank loaded with molten polyethylene material with a flow rate of 0.5g / min per hole;
[0025] (3) cooling the polyester-modified polyethylene, adding an oil agent to the surface of the polyethylene to obtain a semi-finished product coated with modified polyethylene fibers;
[0026] (4) The coated modified polyethylene fiber semi-finished product is stretched in hot water at a temperature of 70°C, steam stretched at a temperature of 125°C, st...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A production process for coating modified polyethylene fibers, comprising the following steps:
[0029] (1) Polyethylene and polytrimethylene terephthalate are melted and extruded by screw respectively to obtain molten polyethylene material and molten polytrimethylene terephthalate material;
[0030] (2) In terms of a mass ratio of 50:50, the molten polyethylene material is coated on the surface of the molten polytrimethylene terephthalate material to obtain polyester-modified polyethylene; The propylene glycol formate material is realized by a bath tank loaded with molten polyethylene material with a flow rate of 0.45g / min per hole;
[0031] (3) cooling the polyester-modified polyethylene, adding an oil agent to the surface of the polyethylene to obtain a semi-finished product coated with modified polyethylene fibers;
[0032] (4) The coated modified polyethylene fiber semi-finished product is stretched in hot water at a temperature of 80°C, steam stretched at a tempe...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A production process for coating modified polyethylene fibers, comprising the following steps:
[0035] (1) polyethylene and polybutylene terephthalate are respectively melted and extruded by a screw to obtain molten polyethylene material and molten polybutylene terephthalate material;
[0036] (2) In a mass ratio of 45:55, the molten polyethylene material is coated on the surface of the molten polybutylene terephthalate material to obtain polyester-modified polyethylene; Butylene phthalate material is realized by the bath tank that is loaded with molten polyethylene material with flow rate as the trickle of 0.4g / min hole;
[0037] (3) cooling the polyester-modified polyethylene, adding an oil agent to the surface of the polyethylene to obtain a semi-finished product coated with modified polyethylene fibers;
[0038] (4) The coated modified polyethylene fiber semi-finished product is stretched in hot water at a temperature of 90°C, steam stretched at a temperature of 1...
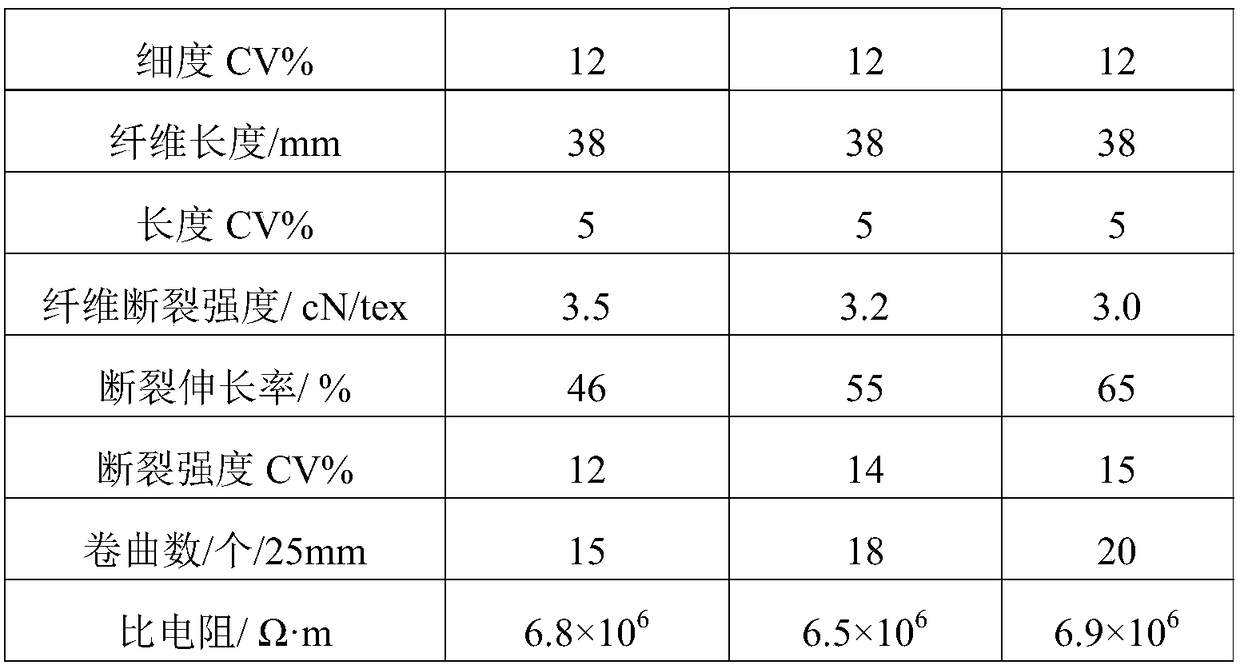
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com