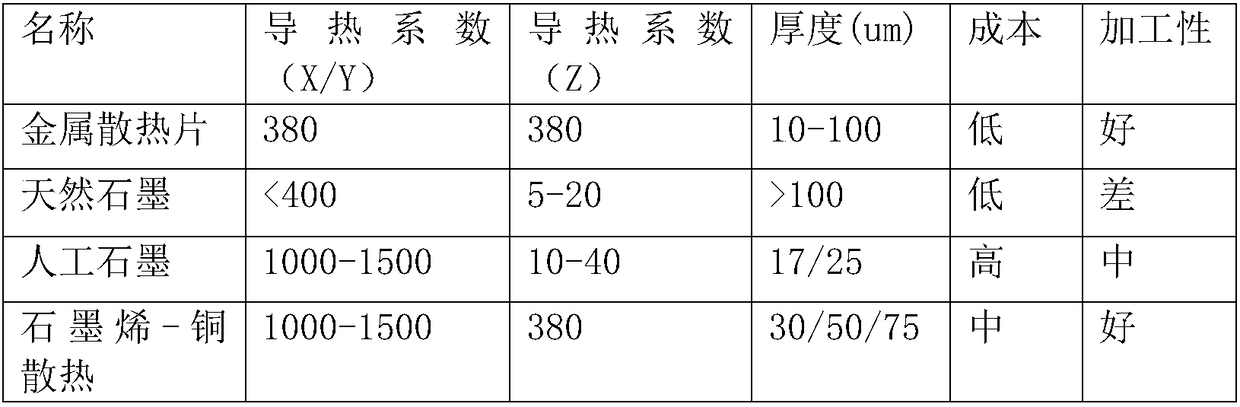
Graphene-copper composite heat-dissipating film as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of composite heat dissipation film and graphene film, applied in the direction of graphene, applications, other household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of many defects, poor thermal conductivity and flexibility of macro-materials, etc. Outstanding cooling performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Embodiment 1 proposes a kind of graphene-copper composite cooling film, and its preparation method comprises the steps:
[0016] S101: first pretreating natural graphite, and then sequentially undergoing high-speed shearing, ultrasonic stripping and emulsification to obtain graphene.
[0017] S102: The graphene mixture obtained in the step S101 is prepared into a film and dried to obtain a graphene film, and then the graphene film is heated at a temperature of 2900° C. to prepare micro-airbags, and then mechanically The micro-airbags were rolled to produce micro-folds.
[0018] S103: Compacting the graphene film treated in step S102 with the copper foil, and then pasting the thermally conductive black film on the other side of the copper foil to obtain a graphene-copper composite heat dissipation film with a thickness of 25 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0020] Embodiment 2 proposes a kind of graphene-copper composite cooling film, and its preparation method comprises the steps:
[0021] S101: first pretreating natural graphite, and then sequentially undergoing high-speed shearing, ultrasonic stripping and emulsification to obtain graphene.
[0022] S102: The graphene mixture obtained in the step S101 is prepared into a film and dried to obtain a graphene film, and then the graphene film is heated at a temperature of 3100° C. The micro-airbags were rolled to produce micro-folds.
[0023] S103: compacting the graphene film treated in step S102 with the copper foil, and then pasting the thermally conductive black film on the other side of the copper foil to obtain a graphene-copper composite heat dissipation film with a thickness of 150 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Embodiment 3 proposes a kind of graphene-copper composite cooling film, and its preparation method comprises the steps:
[0026] S101: first pretreating natural graphite, and then sequentially undergoing high-speed shearing, ultrasonic stripping and emulsification to obtain graphene.
[0027] S102: The graphene obtained in the step S101 is mixed, then prepared into a film and dried to obtain a graphene film, and then the graphene film is heated at a temperature of 3000°C to prepare a micro-airbag, and then mechanically The micro-airbags were rolled to produce micro-folds.
[0028] S103: Compacting the graphene film treated in step S102 with the copper foil, and then pasting the thermally conductive black film on the other side of the copper foil to obtain a graphene-copper composite heat dissipation film with a thickness of 80 μm.
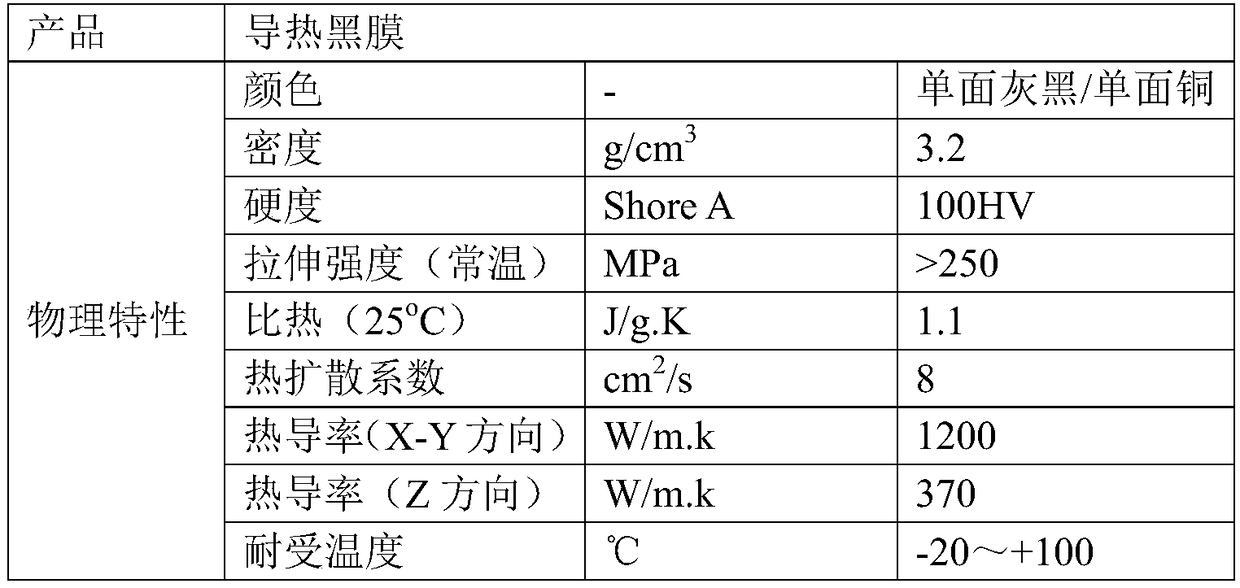
[0029] Table 1: Parameters of thermally conductive black film
[0030]
[0031] In the new material laboratory of the Yangpu District ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electron mobility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com