Light-diffusing film and production method therefor, and display device
A light-diffusing film and light-diffusing layer technology, applied in the direction of identification devices, lighting devices, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of reduced visual recognition, low light diffusivity, dimness, etc., and achieve improved visual recognition, high-gloss Diffusion and less yellowness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
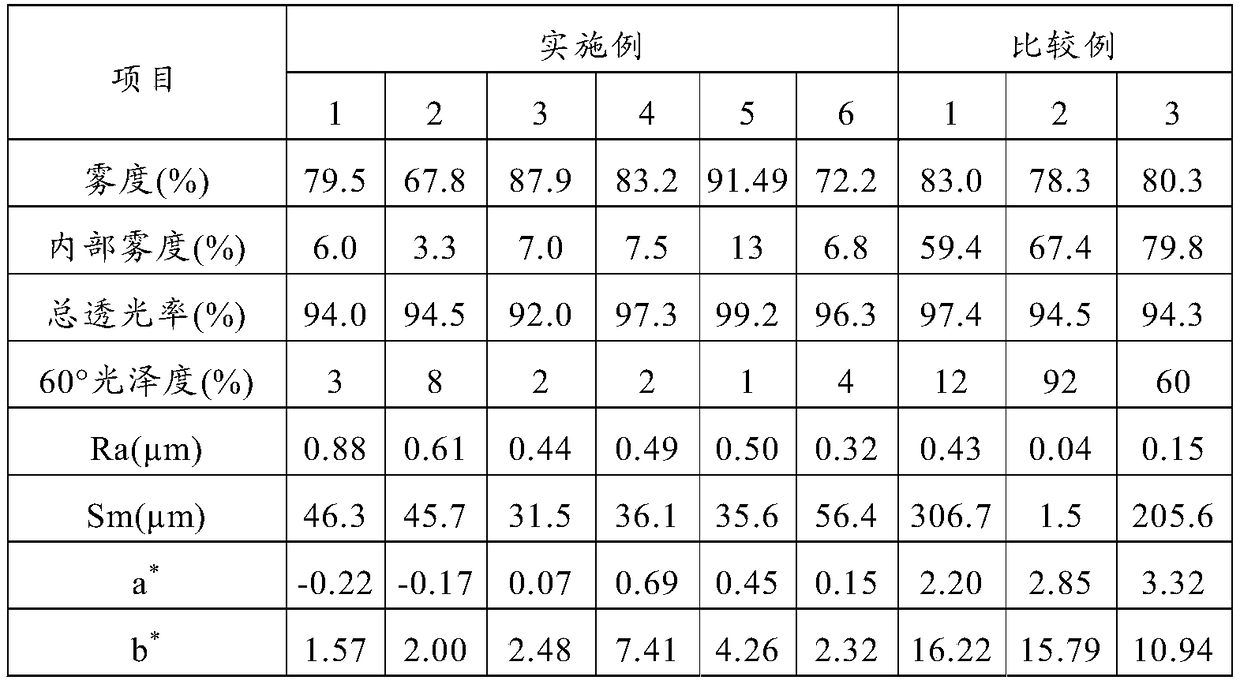
Embodiment 1
[0141] 12.5 parts by weight of an acrylic polymer having a polymerizable group, 4 parts by weight of cellulose acetate propionate, 150 parts by weight of an acrylic UV-curable compound A containing nano-silica, 1 part by weight of silicone acrylate, and 1 part by weight of initiator A and 1 part by weight of photoinitiator B were dissolved in a mixed solvent of 81 parts by weight of methyl ethyl ketone, 24 parts by weight of 1-butanol and 13 parts by weight of 1-methoxy-2-propanol. After casting this solution on a PET film using a wire bar #20, it was left in an oven at 80° C. for 1 minute to evaporate the solvent, thereby forming a coating layer having a thickness of about 9 μm. Then, the coating layer was irradiated with ultraviolet rays from a high-pressure mercury lamp for about 5 seconds to perform UV curing treatment to obtain a light-diffusing film.
Embodiment 2
[0143] 15.0 parts by weight of an acrylic polymer having a polymerizable group, 3 parts by weight of cellulose acetate propionate, 50 parts by weight of an acrylic UV-curable compound A containing nano-silica, 1 part by weight of silicone acrylate, and 1 part by weight of initiator A and 1 part by weight of photoinitiator B were dissolved in a mixed solvent of 101 parts by weight of methyl ethyl ketone and 24 parts by weight of 1-butanol. After casting this solution on a PET film using a wire bar #20, it was left in an oven at 80° C. for 1 minute to evaporate the solvent, thereby forming a coating layer having a thickness of about 9 μm. Then, the coating layer was irradiated with ultraviolet rays from a high-pressure mercury lamp for about 5 seconds to perform UV curing treatment to obtain a light-diffusing film.
Embodiment 3
[0145] 12.5 parts by weight of acrylic polymer having a polymerizable group, 4 parts by weight of cellulose acetate propionate, 209.3 parts by weight of acrylic UV-curable compound B containing nano-silica, 1 part by weight of silicone acrylate, optical 1 part by weight of initiator A and 1 part by weight of photoinitiator B were dissolved in a mixed solvent of 31 parts by weight of methyl ethyl ketone, 25 parts by weight of 1-butanol and 12 parts by weight of 1-methoxy-2-propanol. After casting this solution on a PET film using a wire bar #20, it was left in an oven at 80° C. for 1 minute to evaporate the solvent, thereby forming a coating layer having a thickness of about 9 μm. Then, the coating layer was irradiated with ultraviolet rays from a high-pressure mercury lamp for about 5 seconds to perform UV curing treatment to obtain a light-diffusing film.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com