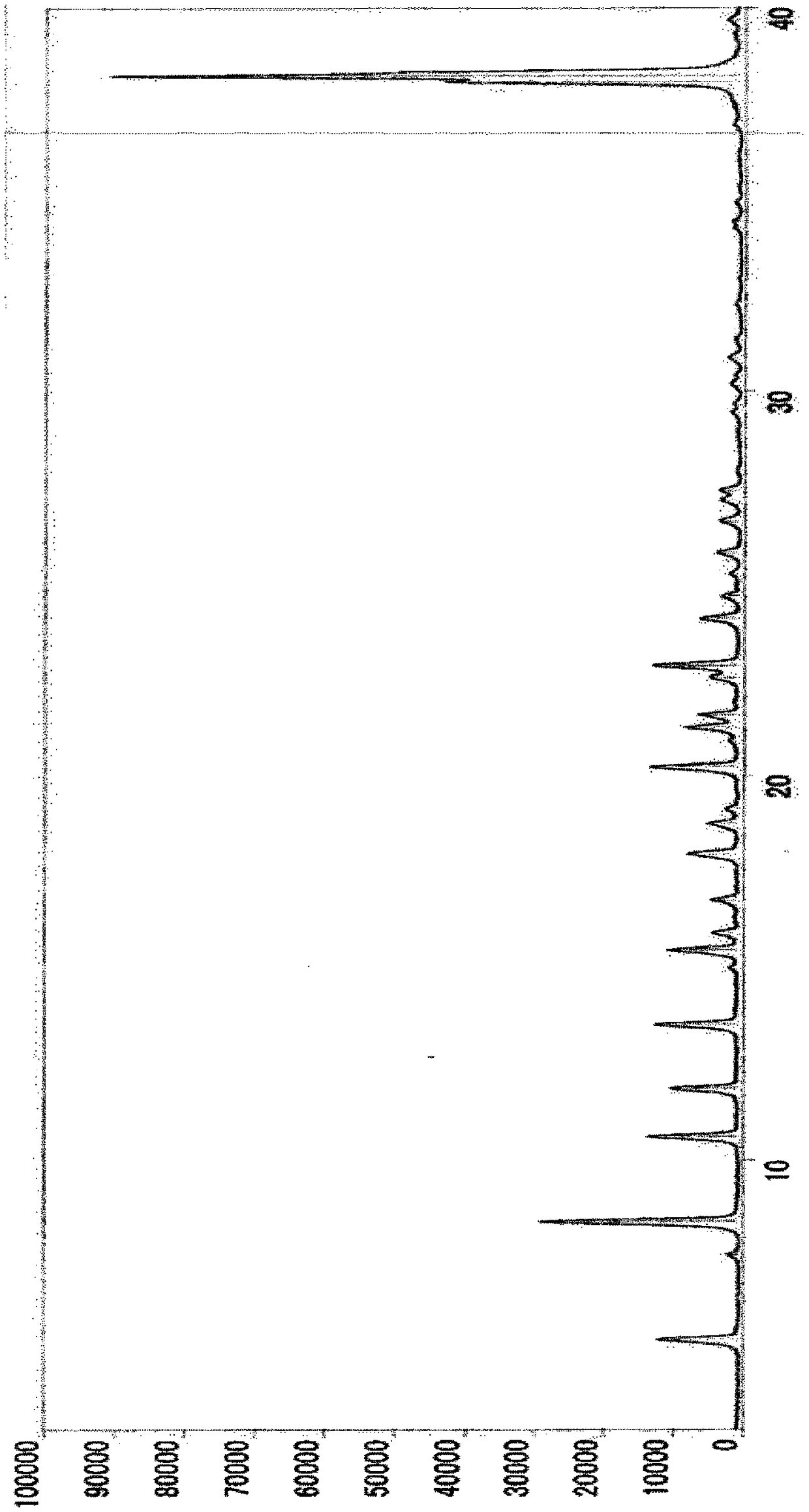
Method for producing substituted polycyclic pyridone derivative and crystal of same
A crystal, unsubstituted technology, applied in the field of preparation of substituted polycyclic pyridone derivatives and their crystals, which can solve the problems of optical purity reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
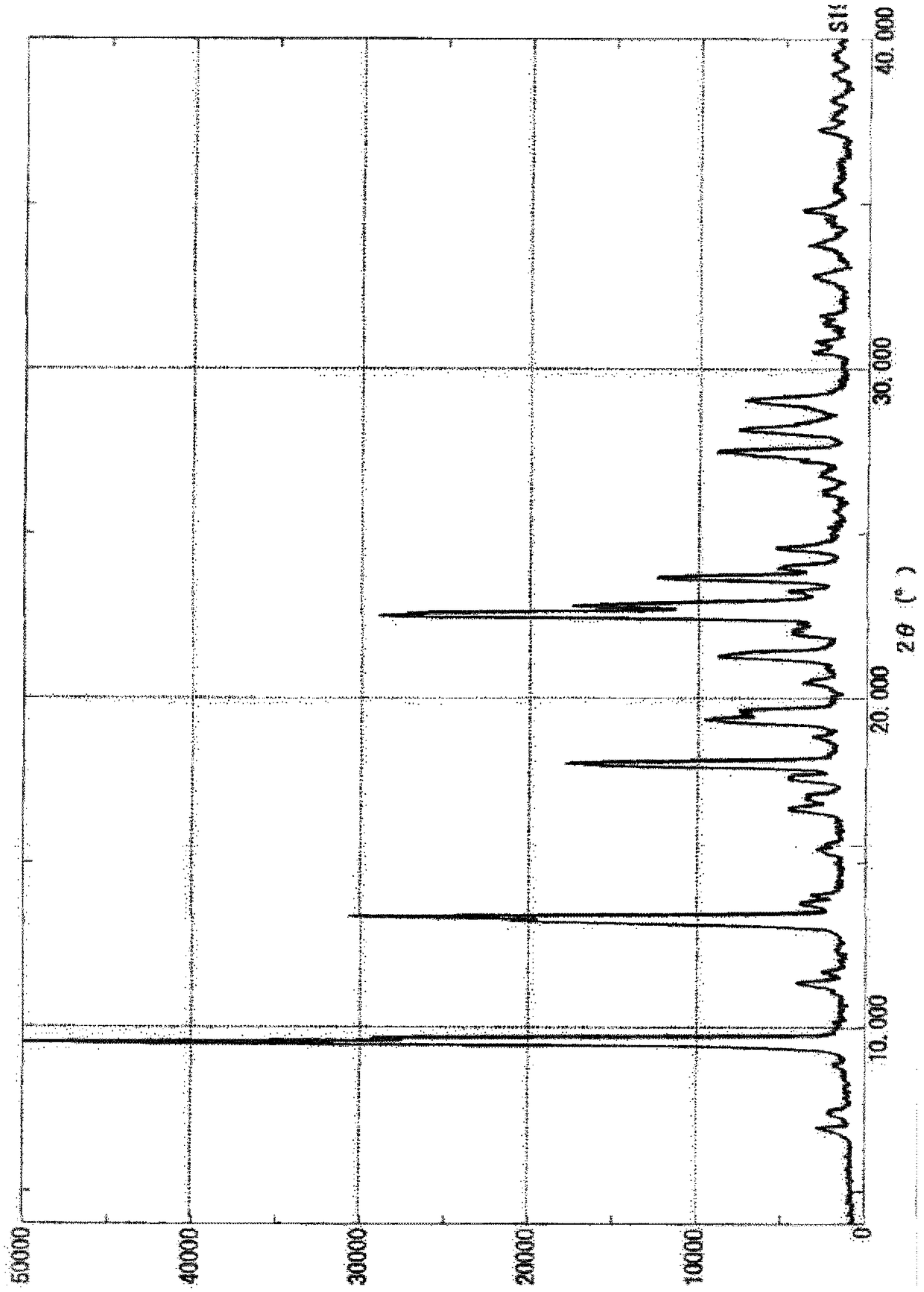
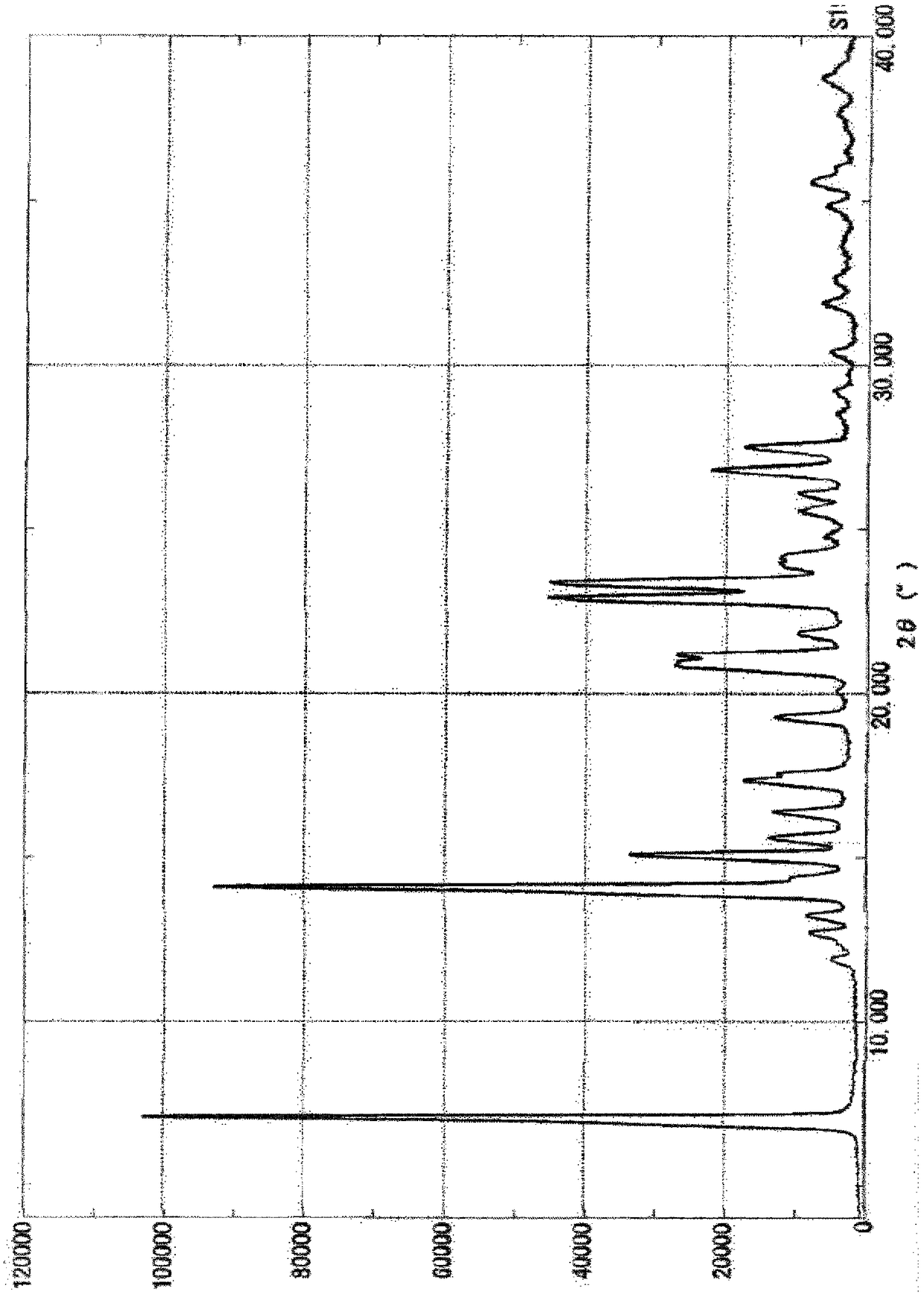
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0149] (Preparation of the compound of the present invention)
[0150] The following exemplifies general methods for preparing compounds of the invention. In addition, extraction, purification, and the like can be performed by conventional methods practiced in organic chemistry experiments.
[0151] The synthesis of the compounds of the present invention can be carried out with reference to methods known in the art.
[0152] As the starting compound, commercially available compounds, compounds described in this specification, compounds described in references cited in this specification, and other known compounds can be utilized.
[0153] If a salt of the compound of the present invention is desired, in the case of obtaining the compound of the present invention in the form of a salt, it can be purified as it is. In the case where the compound is obtained in a free form, it is dissolved or suspended in a suitable organic solvent, and an acid or base is added by a conventiona...
Embodiment 1
[0241] Embodiment 1: the preparation of compound 3
[0242] [Chemical Scheme 23]
[0243]
[0244] Step 1: Compound 3
[0245] DMA (300 mL) was added to compound 1 (100.00 g, 406 mmol) and the mixture was stirred. Sodium bicarbonate (44.41 g, 529 mmol), dimethyl sulfate (58.91 g, 467 mmol) and DMA (100 mL) were added and stirred at 25°C for 7 hours. Synthetic hydrochloric acid (16.90 g) and water (500 g) were added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted twice with ethyl acetate (1000 mL and 550 mL). The organic layer was washed with 5% brine (300 g) and water (300 g). The combined organic layers were concentrated to about 500 g under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate (350 mL) was added to the concentrate, and the resulting solution was concentrated to about 500 g under reduced pressure. DMA (300 mL) was added to the concentrate, and the resulting solution was concentrated to about 400 g under reduced pressure. Pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate (265.42 g) and...
Embodiment 2
[0250] Embodiment 2: the preparation of compound 9
[0251] [Chemical Scheme 24]
[0252]
[0253] Step 1: Compound 6
[0254] Compound 5 (28.29 g, 167.4 mmol) and DMA (65 mL) were added to compound 4 (20.00 g, 104.6 mmol), and the mixture was stirred. After warming the mixture to 40°C, sodium tert-butoxide (15.09 g, 157.0 mmol) was added slowly. The reaction mixture was stirred at 40°C for 3 hours and then cooled to 20°C. Acetic acid (3.14 g) and 10% aqueous sodium chloride solution (64 g) were added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted twice with ethyl acetate (60 mL). Water (144 mL) was added to the combined organic layers, and the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. The resulting yellowish white precipitate was collected by filtration. The resulting solid was washed with a mixture of methanol (5.4 g) and water (48.6 g), and dried to give compound 6 (20.44 g, yield 78%) as a pale yellow-white solid.
[0255] 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 )δ: 3.34(s, 6H), 3.53(d, J=5....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com