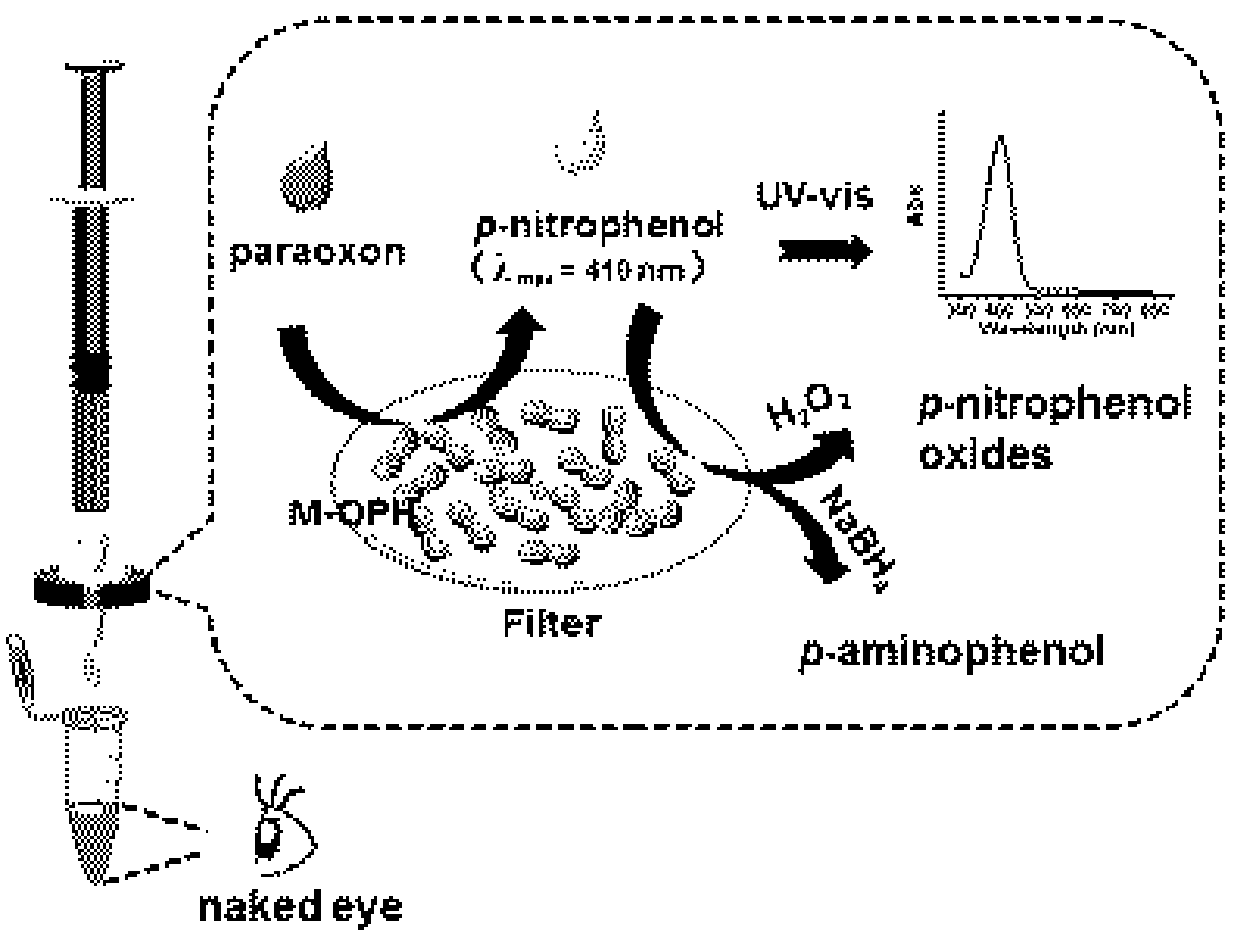
A device and application for rapid detection and degradation of organophosphorus pesticides
A technology of organophosphorus pesticides and organophosphorus, which is applied in the directions of measuring devices, color/spectral characteristic measurement, and analysis through chemical reactions of materials to achieve high sensitivity, selectivity, and low detection limit.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Preparation of microorganisms displaying organophosphate hydrolases on their surface:
[0043] Specifically, genes for ankyrin and organophosphate hydrolase (OPH) were inserted into plasmids and transformed into competent unicellular microorganisms ( E. coli BL21), the engineered bacteria were shaken and cultivated in LB medium containing kanamycin resistance at 37 °C; when the absorbance value of the culture solution at 600 nm (abbreviated as OD 600nm ) was about 0.6, adding isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactoside induced the expression of anchoring protein and OPH and displayed on the surface of cell microorganisms; after 10 hours of shaking culture at 37 °C, centrifuge (6000 rpm, 5 minutes) to collect bacteria. (References for preparation method: X. Tang, B. Liang, T. Yi, G.Manco, I. Palchetti, A. Liu, Cell Surface Display of Organophosphorus Hydrolase for Sensitive Spectrophotometric Detection of p-Nitrophenol Substituted Organophosphates. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Microbial-copper phosphate hybrid catalytic material (Cu 3 (PO 4 ) 2 @M-OPH) Preparation:
[0046] (1) The surface exhibits organophosphate hydrolase E. coli (final OD 600 nm = 6) Add to phosphate buffer and mix well;
[0047] (2) Add copper sulfate aqueous solution (0.5 mmol / L) to the above mixed solution and mix well. After standing at room temperature for one day, the generated copper phosphate salt is uniformly deposited and distributed on the surface of microorganisms, thus forming a microbe with organophosphate hydrolase on the surface. Microbial-copper phosphate hybrid catalytic materials;
[0048] (3) Centrifuge the above reaction solution, remove the supernatant containing unreacted components, collect the precipitate, and store it at 4°C for future use. E. coli OD 600 nm remember.
[0049] Another control experiment: with no display E. coli Alternative surface display of organophosphate hydrolases E. coli, Other experimental conditions and steps...
Embodiment 3
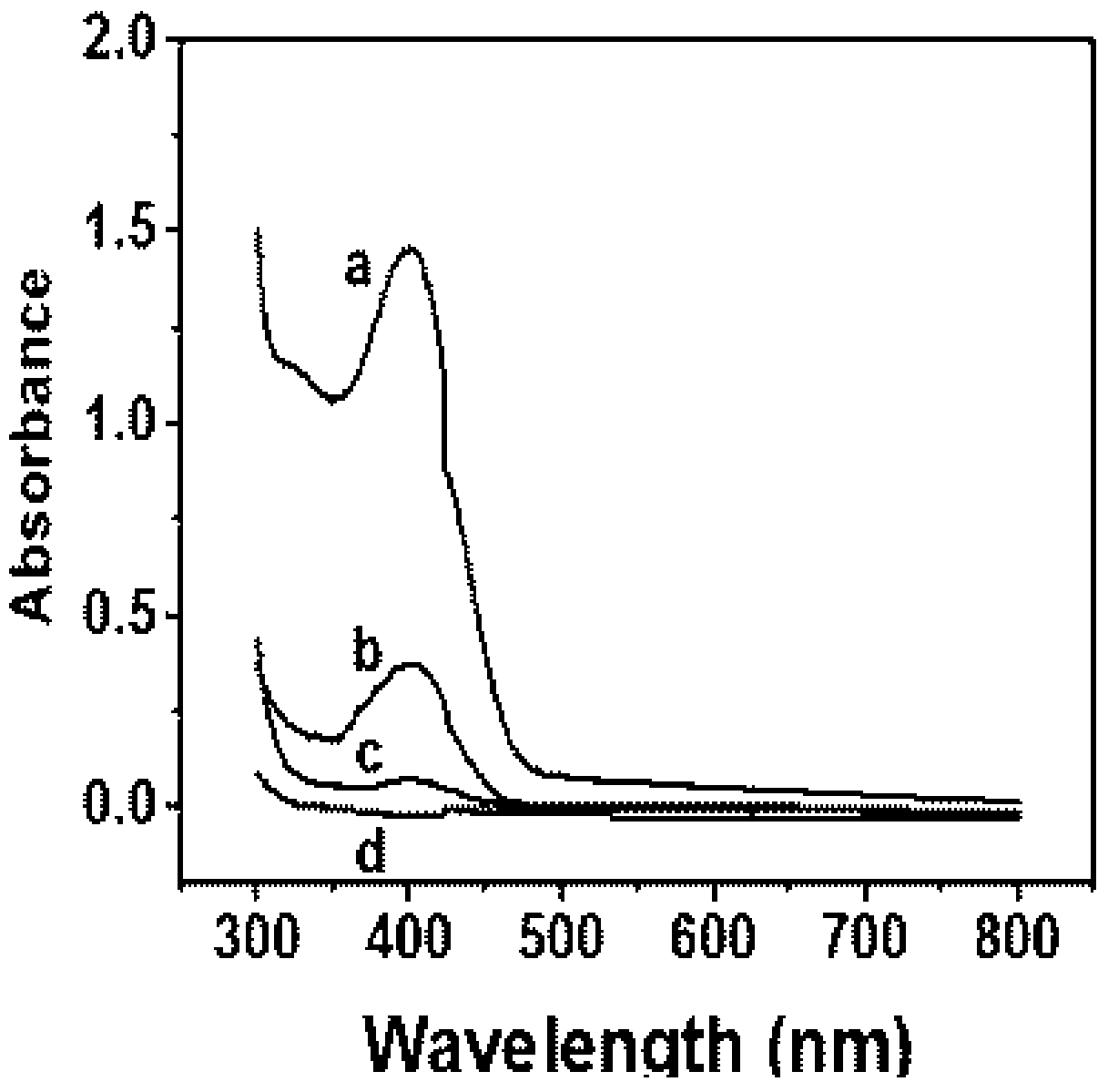
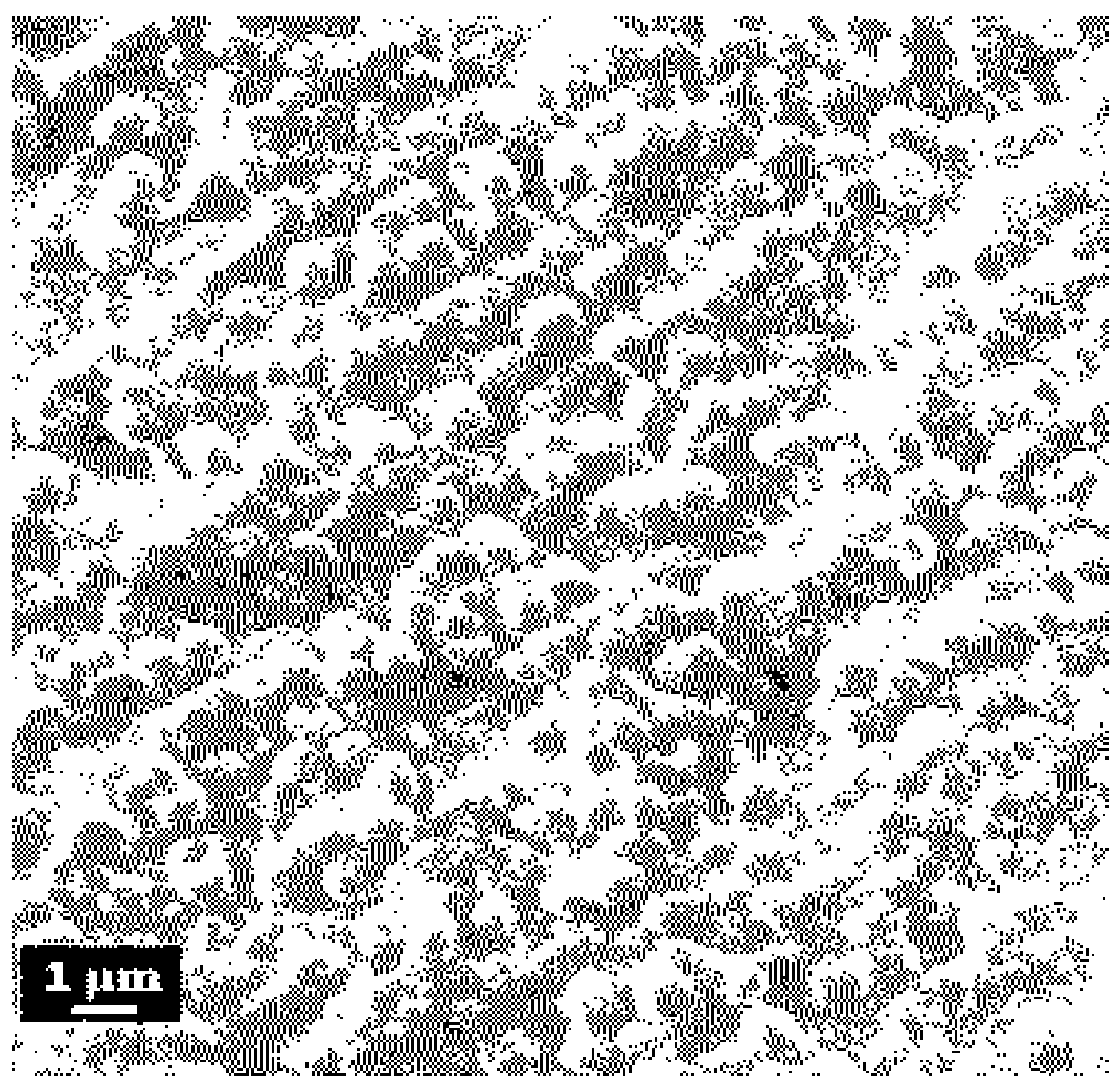
[0051] Hybrid catalytic material Cu 3 (PO 4 ) 2 Morphological analysis of @M-OPH:
[0052] Will Cu 3 (PO 4 ) 2 A certain amount of @M-OPH material suspension was dropped on a cellulose acetate filter membrane, dried at room temperature, sprayed with gold, and its morphology was analyzed by a scanning electron microscope.
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, the prepared Cu 3 (PO 4 ) 2 The @M-OPH hybrid catalytic material has a spindle-shaped structure with uniform morphology and relatively uniform distribution.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com