Maskless parallel pick-and-place transfer of micro-devices
A micro-device and transfer printing technology, which is applied in the direction of photolithographic exposure device, printed circuit, printed circuit manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of manufacturing, technical and manufacturing obstacles, and the difficulty of micro-LED panels, so as to increase production and save chip space , The effect of reducing manufacturing time and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
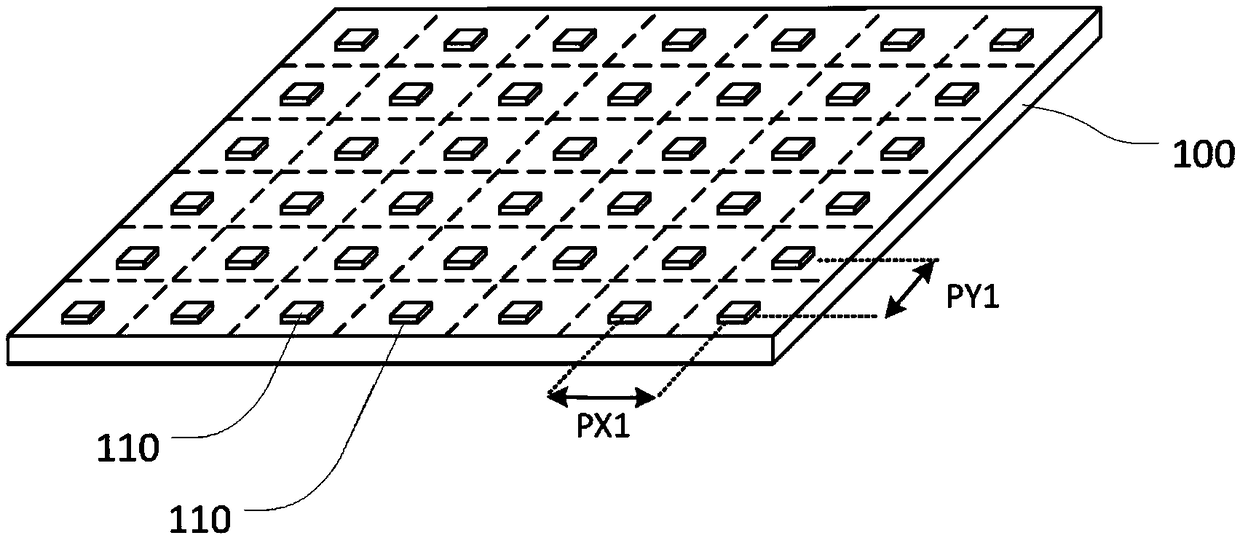
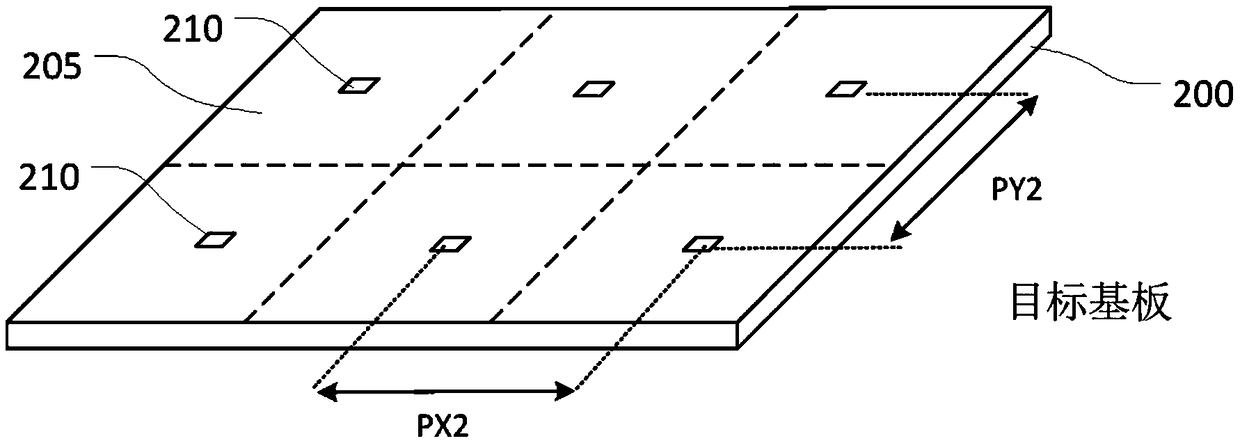
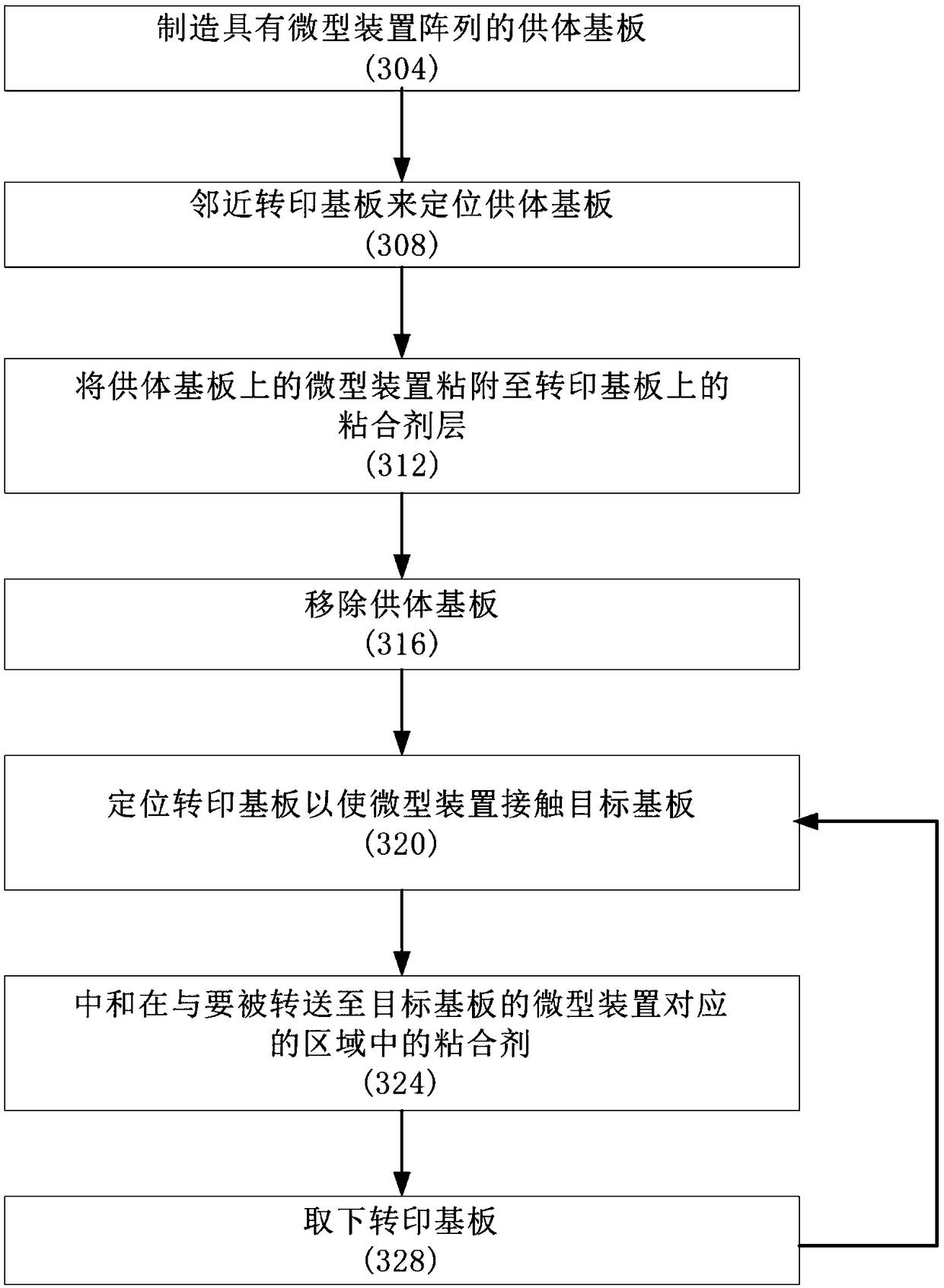
[0045] In order to fabricate some devices, new technologies are needed to accurately and economically provide microdevices on substrates such as large-area substrates or flexible substrates. For example, it is desirable to provide LED panels based on III-V semiconductor technology because micro-LEDs have significant brightness, lifetime and efficiency advantages over organic light emitting diode (OLED) devices.
[0046] A method for fabricating a device comprising an array of individual microdevices is to fabricate the microdevices together on an initial substrate and then transfer the microdevices to a receiving or target substrate that will form part of the product. One reason for building microdevices on an initial substrate is that the target substrate may be a material that is incompatible with the fabrication processes such as etching and deposition required to form the microdevices. In the case of LEDs, for example, deposition of LEDs is an epitaxial growth process in w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com