A method for enter transaction data of a block chain without arbitration
A technology of transaction data and blockchain, applied in digital data protection, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of timeliness lag, lack of data non-tamperable attributes, data not completely credible, etc., and achieve the effect of low overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
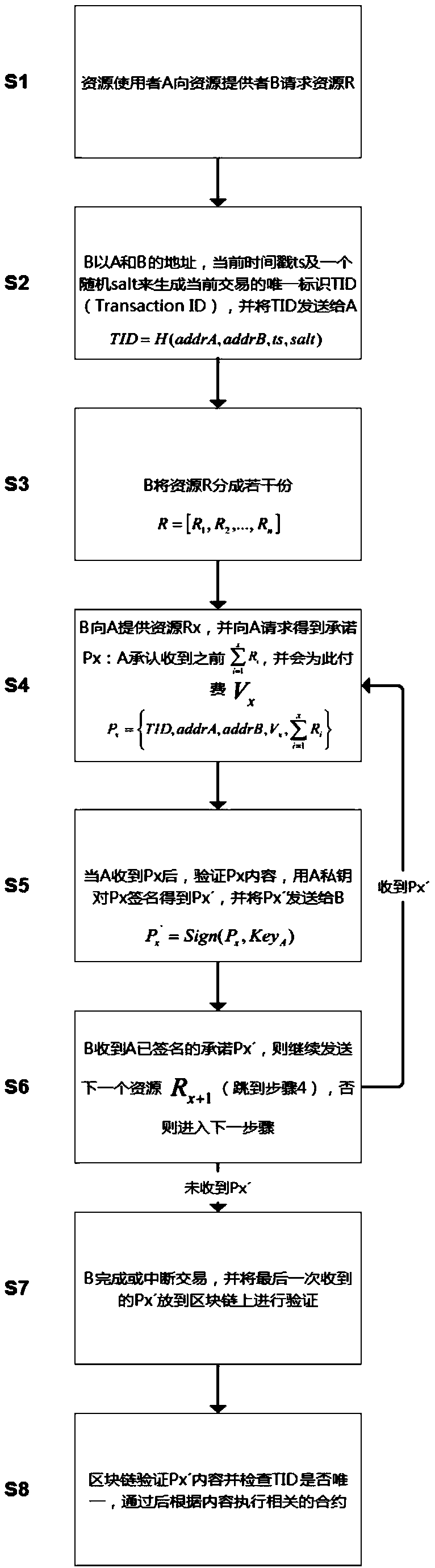
[0023] S1: Resource user A requests resource R from resource provider B;
[0024] S2: B uses the addresses of A and B, the current timestamp ts and a random salt to generate the unique identifier TID (Transaction ID) of the current transaction, and sends the TID to ATID=H (addrA, addrB, ts, salt);
[0025] S3: B divides the resource R into several shares R=[R1, R2,...,RN];
[0026] S4: B provides resource RX to A, and requests A to get the promise PX: before A acknowledges receipt and will pay for it
[0027] S5: After A receives PX, verify the content of PX, sign Px with A's private key to get PX', and send PX' to BPX'=Sign(PX,KeyA);
[0028] S6: B receives A's signed commitment PX', then continue to send the next resource RX+1 (skip to step 4), otherwise enter the next step;
[0029] S7: B completes or interrupts the transaction, and puts the last received PX' on the blockchain for verification;
[0030] S8: The blockchain verifies the content of PX' and checks whethe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com