Radial Displacement Observation Method for Low Speed and Zero Speed Rotor of Bearingless Flux Switching Motor
A magnetic flux switching motor, radial displacement technology, applied in the direction of electronic commutation motor control, generator control, motor control, etc., to avoid adverse effects, reduce weight, and simplify motor design.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
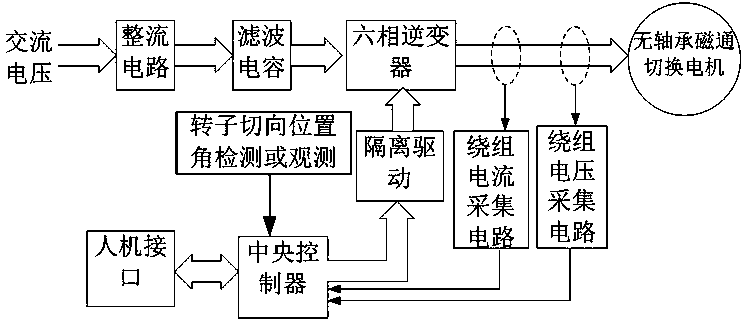
[0057] This embodiment provides a drive system hardware structure such as image 3 As shown, it includes: rectifier circuit, filter capacitor, six-phase inverter, bearingless flux switching motor, winding current acquisition circuit, winding voltage acquisition circuit, isolation drive, central controller, and man-machine interface. If there is a DC power supply, the rectification and filtering links can also be omitted. The power tube in the inverter adopts IGBT or MOFET, and the central controller adopts DSP or single-chip microcomputer. The winding current acquisition circuit is formed by combining a Hall current sensor and an operational amplifier, or by combining a winding string power resistor followed by a differential operational amplifier. The electrical isolation between the control loop and the main loop can be effectively realized by using the Hall solution, and the cost of the drive system can be reduced by using the winding string power resistor solution. The w...
Embodiment 2
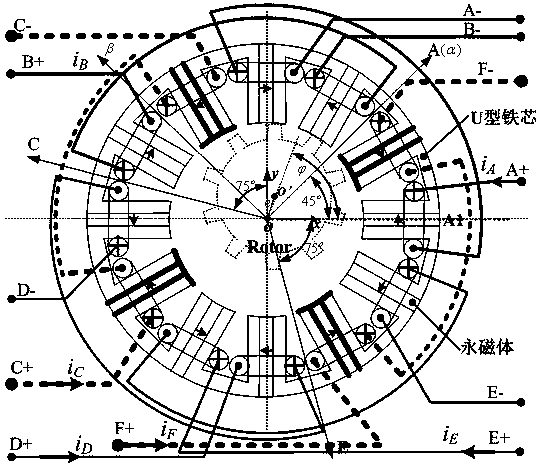
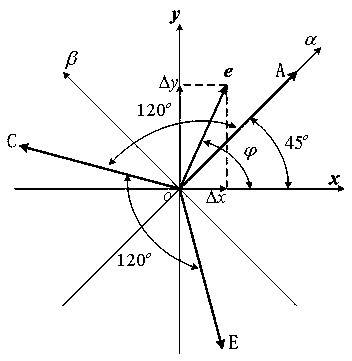
[0061] Define the coordinate system as Figure 4 shown. Among them, e is the rotor offset vector, and its projection on the xy axis is Δx and Δy, respectively. A, C, and E are the axes of the windings A, C, and E respectively, and are αβ static rectangular coordinate systems, where α coincides with the axis of the A-phase winding. The double salient pole structure of BFSM is equivalent to the hidden pole structure. Suppose the air gap length of the hidden pole motor after equivalent is l 0 , and the area of each pole is S, then the air gap reluctance R is as follows:
[0062]
[0063] Among them, μ 0 is the vacuum permeability.
[0064] The corresponding air gap permeability Λ is as follows
[0065]
[0066] Assuming that the air gap length is shortened by Δl due to rotor eccentricity, the corresponding air gap permeance Λ is as follows:
[0067]
[0068] suppose as Figure 4 As shown, the rotor along the Angular direction eccentric e, then mapped to the x...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com