Tissue engineering scaffold with vascular structure and preparation method thereof
A tissue engineering scaffold and vascular structure technology, applied in the field of biomedicine and tissue engineering materials, can solve the problems of poor material exchange and transport capacity, difficulty in forming a vascular network, difficulty in maintaining cell activity, etc., and achieve high plasticity, mechanical strength and mechanical strength. Excellent performance and the effect of maintaining cell viability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
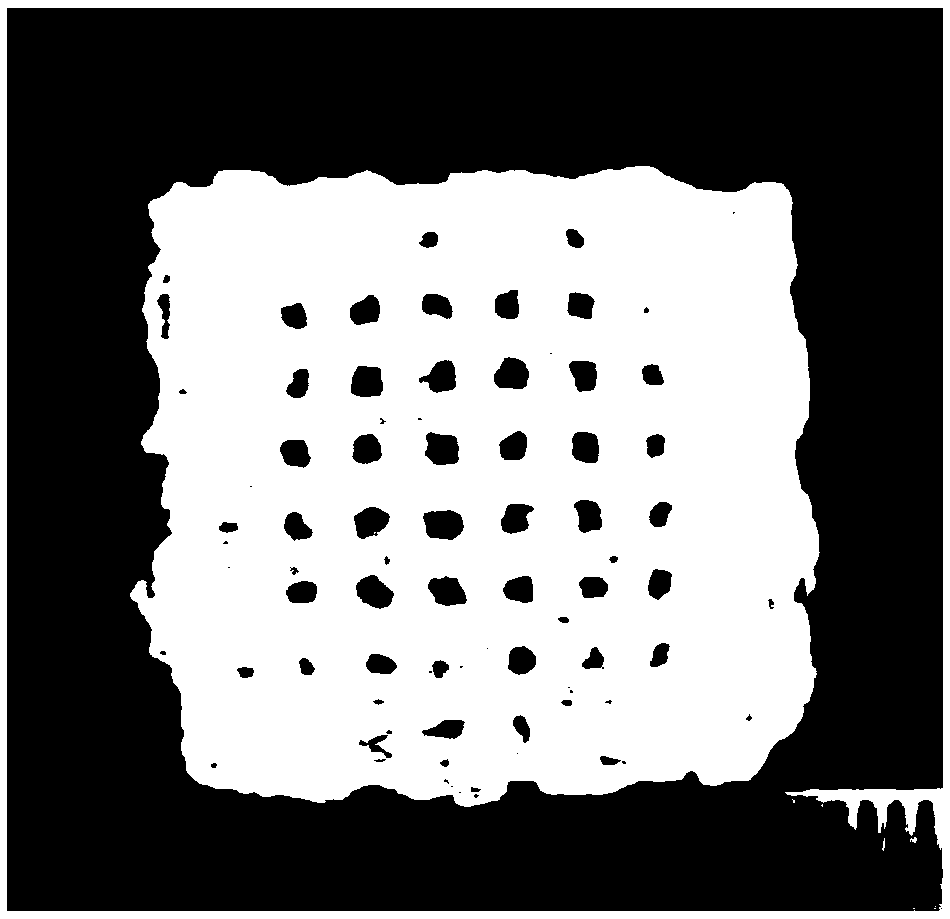
[0014] Provide a kind of preparation method of the tissue engineering scaffold with vascular structure in one embodiment of the present invention, comprise the following steps:
[0015] S1. Construct a three-dimensional network model, and print out the support of the three-dimensional network structure through 3D printing;
[0016] S2. Immerse the scaffold printed by S1 in the ethanol mixed solution of calcium salt, and obtain the scaffold with calcium salt on the surface after the ethanol volatilizes;
[0017] S3. filling the modified photocurable polymer in the sacrificial scaffold in step S2, and forming a cured hydrogel scaffold through photocuring;
[0018] S4. Put the cured hydrogel scaffold in water, PBS or cell culture medium to remove the sacrificial scaffold to obtain the tissue engineering scaffold with bionic vascular network.
[0019] The sacrificial stent material used in the preparation of the tissue engineering stent with vascular structure in the present inve...
Embodiment 1
[0023] A preparation method of a tissue engineering scaffold with a vascular structure, comprising the following steps:
[0024] S1. Construct a three-dimensional network model, and print out the support of the three-dimensional network structure through 3D printing:
[0025] Concretely include: building a three-dimensional network model through MIMICS software, pouring a fructose solution with a concentration of 3g / ml into the barrel of the 3D printer, setting the temperature of the syringe to 120°C, the temperature of the receiving plate to 30°C, and the inner diameter of the needle to 0.13 mm, the distance between the needle head and the bracket receiving device is 0.5mm, the distance between the XY axes is 1.5mm, the moving speed of the XY axis platform is 1.5mm / s, and the extrusion rate is 0.01mm 3 / s, the Z-axis step height is 0.5mm, and the size is 20mm×20mm, and the sacrificial fructose support of the three-dimensional network structure with the gap of 1.5mm is obtaine...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A preparation method of a tissue engineering scaffold with a vascular structure, comprising the following steps:
[0037] S1. Construct a three-dimensional network model, and print out the support of the three-dimensional network structure through 3D printing:
[0038] Concretely include: building a three-dimensional network model through MIMICS software, pouring a glucose solution with a concentration of 2g / ml into the barrel of the 3D printer, setting the temperature of the syringe to 150°C, the temperature of the receiving plate to 30°C, and the inner diameter of the needle to 0.6 mm, the distance between the needle head and the bracket receiving device is 0.5mm, the distance between the XY axes is 1.5mm, the moving speed of the XY axis platform is 1.5mm / s, and the extrusion rate is 0.01mm 3 / s, the Z-axis step height is 0.5mm, and a sacrificial glucose scaffold with a three-dimensional network structure with a size of 20mm×20mm and a gap of 1.5mm is obtained;
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com