Full Stokes polarization imaging element and preparation method thereof
A polarization imaging and component technology, applied in the field of full Stokes polarization imaging components and their preparation, can solve the problems of incompatibility, low optical performance, complex process, etc., and achieve the effect of great application value and high technical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
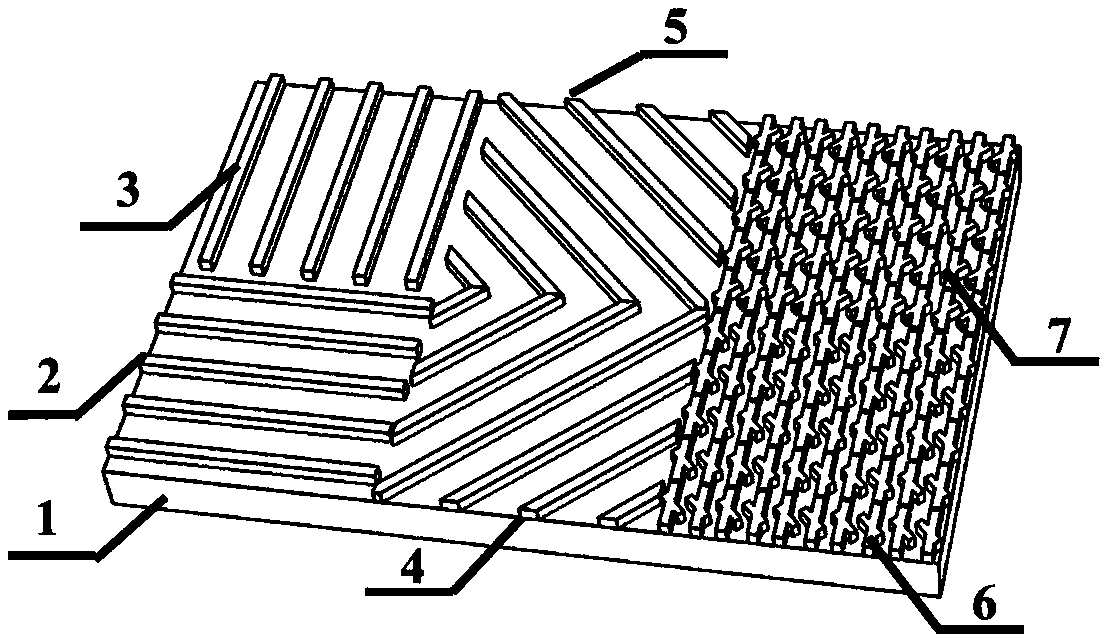
[0037] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of embodiment 1 of the full-Stokes polarization imaging element, including a dielectric wire grid structure with a 0° orientation, a dielectric wire grid structure with a 90° orientation, a dielectric wire grid structure with a 45° orientation, and a dielectric wire grid structure with a 135° orientation structure, left-handed rotation symmetric chiral medium structure and right-handed rotational symmetric chiral medium structure.
[0038] This element is made by following steps:
[0039] (1) A layer of silicon is grown on the surface of silicon dioxide by electron beam evaporation or chemical vapor deposition;
[0040] (2) Use a glue leveler to coat a layer of electron beam photoresist negative glue on the silicon layer;
[0041] (3) Use electron beam exposure and development technology to obtain wire grids with different orientations of 0°, 90°, 45° and 135° according to specific parameters and photoresist structure patt...
Embodiment 2
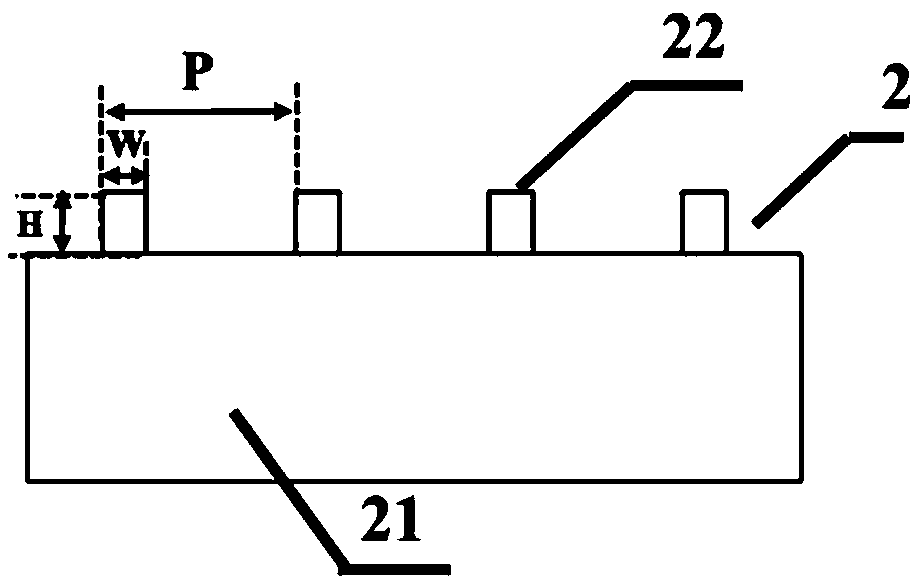
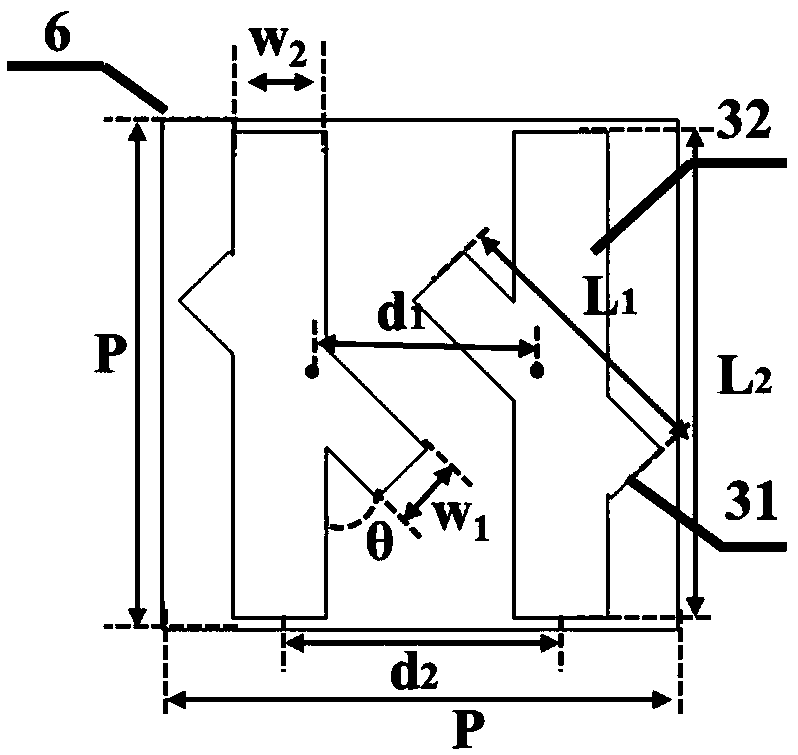
[0049] The parameters of the rotationally symmetrical chiral structure are: the thickness H of the dielectric structure layer is 0.26 μm; the period P of the rotationally symmetrical chiral structure is 1.0 μm, the arm length L1 is 0.5 μm, the arm length L2 is 1.0 μm, and the distance between the two arms L1 The distance d1 is 0.21 μm, the distance d2 between the two arms L2 is 0.24 μm, the arm width W1 is 0.12 μm, the arm width W2 is 0.17 μm, and the angle θ between the two arms is 40°; the period of the dielectric wire grid structure P is 1.0 μm, and the wire grid width W is 0.2 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0051] The parameters of the rotationally symmetrical chiral structure are: the thickness H of the dielectric structure layer is 0.29 μm; the period P of the rotationally symmetrical chiral structure is 1.2 μm, the arm length L1 is 0.8 μm, the arm length L2 is 1.07 μm, and the distance between the two arms L1 The distance d1 is 0.27 μm, the distance d2 between the two arms L2 is 0.33 μm, the arm width W1 is 0.21 μm, the arm width W2 is 0.26 μm, and the angle θ between the two arms is 55°; the period of the dielectric wire grid structure P is 1.2 μm, and the wire grid width W is 0.3 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com