RPA (Recombinase polymerase amplification) primer, probe, kit and detection method for detecting ralstonia solanacearum
A technology of tobacco bacterial wilt bacteria and detection method, which can be applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc. High, false positives, low equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039]R. solanacearum was used for the screening of RPA primers and probes. Taking the Rip TALI-9 gene of R. solanacearum as the target gene; according to the requirements of the TwistDX operation manual, the primers that can be used in the RPA kit (TwistAmp nfo) were designed and screened, and the primers with high amplification efficiency, sensitivity and specificity were obtained. right. The sequences of the best primers obtained by screening (ie, the upstream and downstream primers of the RPA primers) are shown in SEQ ID No: 1 and SEQ ID No: 2. Then the above primers were modified, and a biotin (Biotin) labeling site was added to the 5' end of the downstream primer of the RPA primer. In addition, a probe with a size of 45bp-54bp was designed according to the amplified fragment of the RPA primer. The 'end was labeled with FAM, the 3' end was modified with C3-Spacer, and the probe was modified with THF at a distance of 34 bp from the 5' end. Finally, according to the requi...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Establishment of RPA Detection Method for Tobacco R. solanacearum
[0045] The detection method for detecting tobacco bacterial wilt bacteria of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0046] (1) Extract the DNA in the sample;
[0047] (2) using the DNA extracted in step (1) as the DNA template to be detected, using the RPA primers and RPA probes described in Example 1 to carry out RPA amplification reaction in an RPA reaction tube;
[0048] The reaction conditions of the RPA amplification reaction in step (2) are: react at 38° C. for 20 minutes, and then terminate the reaction on ice;
[0049] The reaction system of the RPA amplification reaction in step (2) is calculated as 50 μL:
[0050]
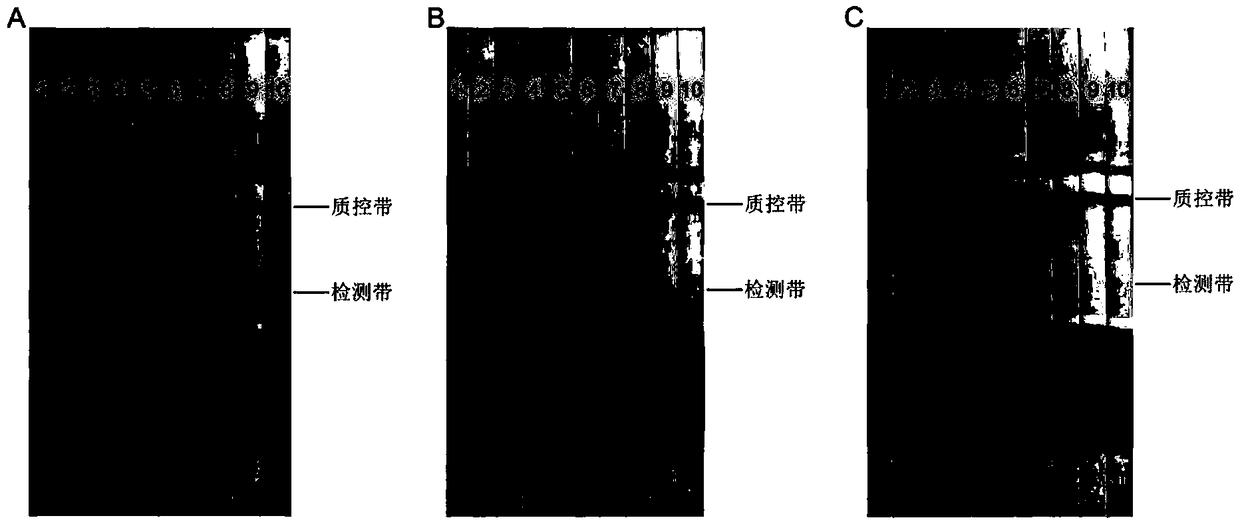
[0051] (3) Analyze the RPA amplification product; take the RPA amplification product and mix it with the buffer to prepare a mixed solution (take the above-mentioned 1 μL of the RPA amplification product and add it to 49 μL of PBST buffer and mix, wherein the ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Specific detection of RPA primers and probes for R. solanacearum
[0056] The detection method for detecting R. solanacearum of the present embodiment is the same as the embodiment 2, and the difference is:
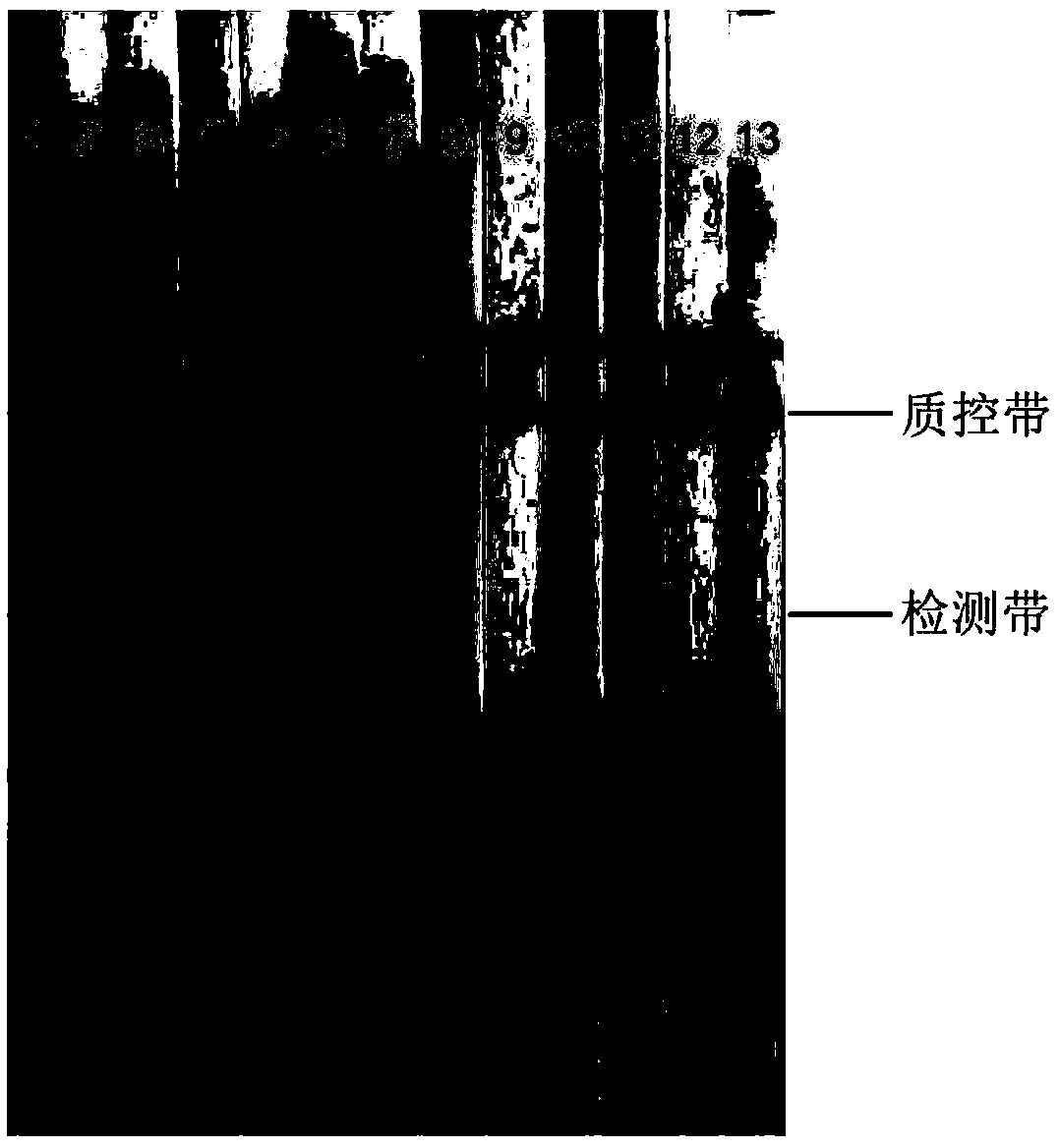
[0057] The samples are respectively R. solanacearum, Flavobacterium, Arthrobacter, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Arthrobacter saprophyte, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Paenibacillus, Bacillus subtilis, Serratia marcescens. fungus, rice bacterial leaf spot, Phytophthora nicotianae and tobacco root black rot.
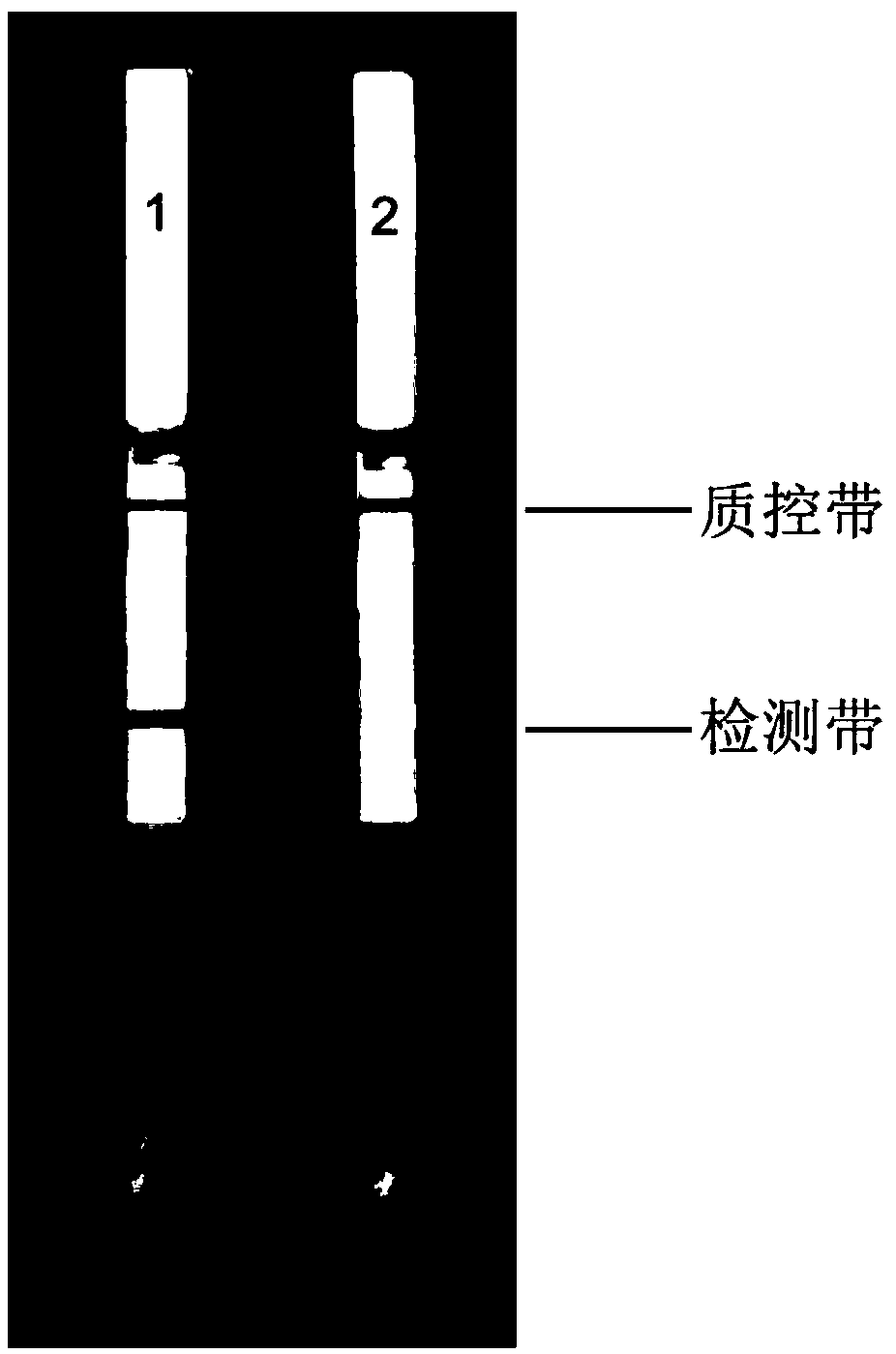
[0058] like figure 2 shown, figure 2 The symbol "1" in the refers to the detection result of tobacco wilt bacteria, figure 2 The symbol "2" in the genus refers to the detection result of Flavobacterium, figure 2 The symbol "3" in the refers to the detection result of Arthrobacter, figure 2 The symbol "4" in the refers to the detection result of Escherichia coli, figure 2 The symbol "5" in the refers to the detection result of Pseudomonas, figure 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com